Why Migraines Deserve Serious Attention
Migraines aren’t just “bad headaches.” They’re intense, often debilitating neurological events that can disrupt your ability to work, function, or even speak. For millions of people, migraines interfere with daily life, making simple tasks feel impossible. Understanding what causes migraines, how to recognize the symptoms, and what relief strategies truly work is crucial for anyone living with—or supporting someone with—this condition.
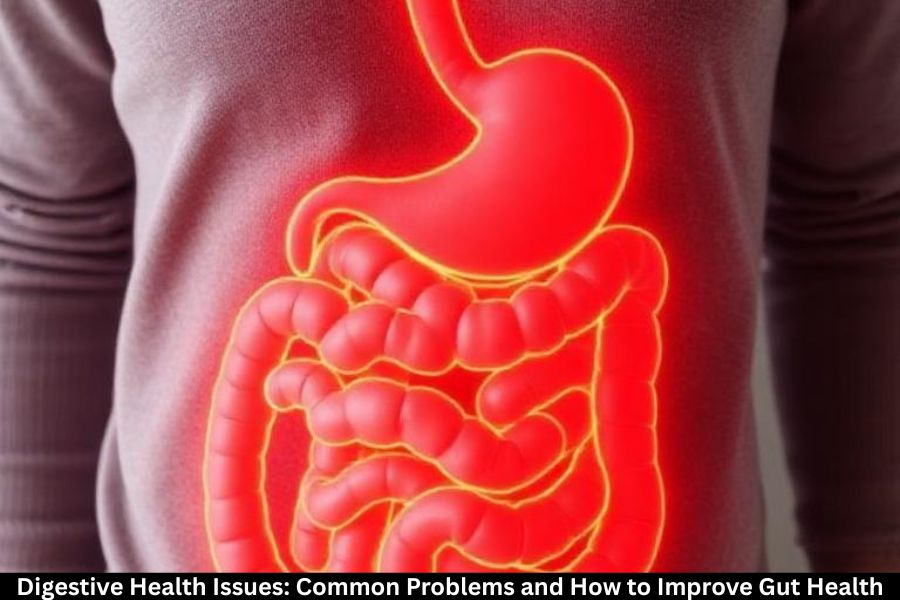
What Are Migraines?
How Migraines Differ From Regular Headaches
Unlike tension headaches, which cause mild to moderate pain, migraines come with severe, throbbing pain usually on one side of the head. They often bring additional symptoms like nausea, vomiting, light sensitivity, and sound sensitivity. Migraines can last anywhere from a few hours to several days.
The Four Stages of a Migraine
Migraines often develop in stages, although not everyone experiences all of them:
- Prodrome – Early signs such as fatigue, mood changes, or food cravings.
- Aura – Visual or sensory disturbances like flashing lights or tingling (in some people).
- Attack – The migraine pain itself, usually accompanied by several symptoms.
- Postdrome – Feelings of exhaustion or confusion after the pain subsides.
Common Causes and Triggers of Migraines
Genetic Factors
Migraines often run in families. If one or both of your parents have migraines, you are more likely to develop them too.
Hormonal Changes
Hormones, especially estrogen, play a big role in migraines. Many women notice migraines during menstrual cycles, pregnancy, or menopause.
Stress and Emotional Triggers
Stress is one of the most common triggers. High levels of emotional stress can tighten muscles and change brain chemicals, increasing migraine likelihood.
Dietary Triggers
Foods that frequently trigger migraines include:
- Aged cheeses
- Chocolate
- Alcohol (especially red wine)
- Caffeine
- Processed meats
Environmental Factors
Bright lights, loud noises, strong smells, and weather changes—especially drops in barometric pressure—can trigger migraines.
Sleep Disturbances
Both too much and too little sleep can set off a migraine. Consistency is key for migraine sufferers.
Symptoms of Migraines
Physical Symptoms
- Intense throbbing pain on one or both sides of the head
- Nausea or vomiting
- Dizziness
- Extreme fatigue
Sensory Symptoms
- Sensitivity to light, sound, and smells
- Visual disturbances (flashes, blind spots, zigzag lines)
- Tingling or numbness in the face or limbs
Emotional and Cognitive Symptoms
- Irritability
- Difficulty concentrating
- Brain fog
Types of Migraines
Migraine With Aura
These migraines involve sensory warnings before the pain hits. Auras may include flashing lights, temporary vision loss, or tingling sensations.
Migraine Without Aura
The most common type, these migraines occur without any warning signs before the pain.
Chronic Migraines
Chronic migraine sufferers experience migraines at least 15 days a month—often severe and life-disrupting.
Vestibular Migraines
These involve dizziness, balance issues, or vertigo, often without severe head pain.
Relief Strategies for Migraines
Lifestyle Adjustments
Sleep Routine
A regular sleep schedule helps regulate your brain chemicals and prevent migraines.
Hydration and Diet
Dehydration is a sneaky migraine trigger. Drinking plenty of water and maintaining a consistent eating schedule can help reduce attacks.
Natural Remedies
Magnesium and Supplements
Magnesium deficiency is linked to migraines. Supplements like magnesium, riboflavin (B2), and CoQ10 may reduce frequency.
Essential Oils
Peppermint and lavender essential oils can help relax muscles and ease migraine discomfort when applied to the temples.
At-Home Pain Management
Cold Compress
Applying a cold pack to your forehead or neck can reduce inflammation and numb pain.
Dark Room Rest
Since migraines often cause sensitivity to light, resting in a cool, dark room can help ease symptoms.
Medical Treatments
Over-the-Counter Medications
Pain relievers like ibuprofen, aspirin, or acetaminophen may help if taken early in the attack.
Prescription Medications
For severe or frequent migraines, doctors may prescribe triptans, anti-nausea meds, or preventive medications like beta-blockers or CGRP inhibitors.
Preventing Future Migraine Attacks
Identifying Triggers
Keeping track of what triggers your migraines helps reduce their frequency.
Creating a Migraine Diary
Record:
- Foods you eat
- Stress levels
- Sleep patterns
- Weather changes
- Symptom intensity
This helps you spot trends and avoid known triggers.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Regular exercise, balanced meals, and stress-relief practices can significantly lower migraine frequency.
When to See a Doctor
You should seek medical help if:
- Your migraines worsen over time
- You’re having more than four attacks per month
- Over-the-counter medication doesn’t help
- You experience sudden severe headaches or neurological symptoms
Conclusion
Migraines can feel overwhelming and unpredictable, but understanding the causes, symptoms, and relief options can empower you to manage them more effectively. By identifying triggers, practicing self-care, and exploring medical treatment when necessary, you can reduce the frequency and intensity of migraine attacks—and reclaim control over your daily life.
FAQs
Are migraines hereditary?
Yes, migraines often run in families due to genetic factors.
Can stress cause migraines?
Absolutely—stress is one of the most common migraine triggers.
Do migraines always involve aura?
No, only about 25% of migraine sufferers experience aura symptoms.
What foods should I avoid to prevent migraines?
Common triggers include alcohol, aged cheeses, chocolate, and processed meats.
Can migraines be cured?
There is no cure, but treatments and lifestyle changes can significantly reduce their frequency and severity.



actionfuelsmomentum.bond – Love the vibe here, everything loads fast and looks super clean.
actionfuelsmomentum.bond – Love the vibe here, everything loads fast and looks super clean.
directionenergizesgrowth.bond – Really helpful info, I’ll be coming back to read more soon.
progressflowhub – Well-structured pages make it easy to find key information.
growthstreamline – Layout supports understanding and keeps focus on essential points.
clarityleadsmovement.bond – Nice layout and simple flow, made it easy to find what I needed.
energizedforwardhub – Layout is simple and easy to navigate, with smooth performance.
Progress Movement – Everything is laid out clearly and the point is made without confusion.
workflowprogresshub – Helpful strategies are structured clearly for fast understanding.
forwardstreamline – Content flows naturally and is easy to scan.
forwardmotionactivatednow.bond – Great work on this site, feels polished and surprisingly easy to navigate.
Momentum Direction Page – Straight to the point, with information that’s easy to absorb.
growthplanner – Great structure, the approach to growth is both practical and easy to follow.
goalfocushub – Practical advice that helps maintain attention on key objectives.
actioncreatesforwardpath.bond – Clear direction shown here, information feels structured and purposeful throughout.
claritysetsdirection.bond – Pretty solid content, I enjoyed reading through the pages today.
Official Action Driven Site – Simple presentation that quickly explains the purpose without confusion.
making ideas clear – Well explained, the site turns confusion into understanding.
velocityprogress – Great advice, strategies here make moving forward easier and faster.
steermomentum – Inspiring advice, clear guidance ensures progress continues smoothly.
motionforwardpath – Guidance is logical and easy to follow for long-term objectives.
conceptmomentumhub – Information is structured logically, making the site easy to navigate.
directionshapesoutcomes.bond – Smooth experience overall, pages are organized and load without any lag.
growth with direction – Easy to follow, purpose keeps growth efforts aligned.
nextstepmomentum – Simple, intuitive structure that keeps the user focused.
ideasforward – Very actionable, concepts push progress in meaningful ways.
focuscompass – Very helpful, understanding focus really guides daily priorities.
focusedgrowth – Inspiring advice, clarity combined with focus drives consistent advancement.
definedstrategyhub – Clear guidance ensures tasks are completed in an organized manner.
advancesignalhub – Content is structured for easy comprehension and smooth navigation.
pathenergy – Inspiring advice, direction here gives energy to move toward set goals.
forwardsignals – Great insights, following signals helps push ideas ahead effectively.
actionpro – Methodical moves make tasks feel simpler.
momentum strategy – Well framed, direction keeps momentum productive.
Clarity Experience – The organization keeps the content clear and engaging.
progressmovespurposefully.bond – Interesting site, the structure makes sense and keeps things straightforward.
actionpower – Great content, taking action consistently generates real forward movement.
clearintentprogress – Very helpful, setting clear goals keeps tasks moving efficiently.
energizefocusstream – Information is presented clearly, with a logical page hierarchy.
strategicflowcenter – Guidance is structured and makes decision-making easier.
progressbeacon – Timely signals help work flow naturally and maintain consistent momentum.
directionlens – Helpful notes, clear focus shapes decisions and sets direction confidently.
activatedmindset – Very helpful, content encourages forward thinking while keeping it simple.
actionengine – Focused effort improves results and keeps projects moving steadily.
ideapropel – Helpful advice, signals make advancing concepts simpler and more structured.
taskbeacon – Clear signals help guide daily work toward intended outcomes.
intentional motion – Good perspective, focus keeps momentum from slipping.
pathwaytogrowth – Smooth navigation and clear messaging make the site easy to explore.
progressenergycenter – Smooth navigation and concise sections improve usability.
alignmentforgrowth – Practical advice, aligning daily actions ensures growth feels achievable.
goalbeacon – Structured guidance makes advancing toward goals easier and more organized.
growthaccelerator – Motivating content, signals make it easier to implement effective growth measures.
progressplannerhub – Tips are clear, helping prioritize steps effectively.
focusdecisions – Very helpful, focused guidance helps prioritize choices effectively.
directionactivatesprogress.bond – Clean design and clear message, it actually feels trustworthy to browse.
actionpathway – Excellent pointers, acting regularly helps projects advance without delay.
goalengine – Focused attention improves results and helps maintain steady productivity.
focusengine – Very helpful, sustained focus acts like an engine pushing projects forward.
strategicalliancenetwork – Very helpful, global partnerships are presented as reliable and well organized.
successcompass – Clear direction drives better results with less effort.
from thought to action – Encouraging insights, ideas are clearly connected to real progress.
strategyengine – Taking action repeatedly generates momentum and drives goals forward.
forwardflowguide – Simple layout enhances readability and keeps the focus on key content.
momentumpathfinder – Well-laid-out sections with messaging that’s straightforward and understandable.
nextstepforward – Encouraging content, the guidance inspires me to take the next steps confidently.
forwardmotionguide – Very motivating, advice here ensures consistent progress in daily tasks.
progressbeacon – Guidance here ensures projects move forward with clarity and precision.
dependablenetwork – Connect with reliable individuals for lasting, productive relationships.
innovationpathstream – Clear guidance helps turn concepts into actionable steps.
signalledgrowth – Very practical, following signals helps growth progress in a clear way.
focusinsightstream – Guidance is easy to understand and improves daily productivity.
collectiveimpact – Foster unity and teamwork for meaningful and sustainable outcomes.
mindactivation – Helpful guidance, encourages forward thinking without feeling overwhelming.
trustedpartners – Well executed, partnerships seem dependable and globally relevant.
actionmovesforwardclean.bond – Good read, I found a couple sections that were genuinely useful.
actionflow – Practical tips, applying signals strategically enhances velocity and keeps tasks on track.
progressstream – Great guidance, following clear steps makes forward movement feel natural and easy.
strategicbusinessbond – Insightful, strategies here are aligned to benefit all participants equally.
driveplanner – Clear logic behind forward movement helps prioritize what matters.
workflowbeacon – Thoughtful growth strategies ensure progress flows naturally and consistently.
clear direction path – Nicely shared, focus simplifies where to go next.
nextstepaction – Clear visual hierarchy guides the user effortlessly.
focusedpathway – Excellent guidance, staying on a focused pathway ensures forward momentum.
confidenceengine – Practical guidance, action fuels self-confidence efficiently.
clarityforwardguide – Steps are straightforward and enhance focus on daily priorities.
clarityinprogress – Excellent guidance, deliberate growth choices make following through easier.
Explore This Platform – Everything loads promptly and the details are simple to understand.
progressigniter – Great strategies, small consistent actions make velocity noticeable quickly.
longlastinglinks – Form bonds that are reliable, valuable, and consistently supportive.
claritydirectionhub – Suggestions keep workflow clear and help focus on meaningful actions.
signalcreatesalignment.bond – Looks great on mobile too, everything feels quick and nicely put together.
collabnetwork – Build networks that encourage trust, cooperation, and long-term success.
taskbeacon – Concentrated effort keeps tasks moving forward consistently and predictably.
dailyactionguide – Practical tips, following these actions daily fuels forward progress naturally.
workflowbeacon – Structured growth methods simplify progress and improve efficiency.
forwardbeacon – Unlocking ideas here supports growth and maintains steady advancement.
trustedgrowthnetwork – Excellent advice, trust-driven strategies create meaningful and consistent development.
actionflowhub – Great advice, deliberate action keeps momentum moving forward efficiently.
focused growth guide – Helpful explanation, growth concepts are laid out in a clean way.
focusedpathway – Nice guidance, focused direction ensures steady progress toward goals.
actionpathway – Excellent tips, signals provide a clear route for moving forward.
guidedenergyhub – Content is easy to understand and actionable without confusion.
momentumpath – Encouraging tips, momentum builds naturally when action is taken regularly.
forwardpathgrowth – Practical advice, keeps growth insights easy to understand and apply.
clarityengine – Organized planning helps projects advance efficiently and without confusion.
ideasurge – Excellent suggestions, consistent follow-through helps ideas gain momentum effortlessly.
jointachievementnetwork – Insightful guidance, cooperative strategies maximize success and ensure everyone benefits.
partnerrelationshub – Insightful, this hub gives guidance for better partner management and collaboration.
impactengine – Using energy with intention produces stronger results.
momentumengine – Proper guidance generates leverage, making project momentum easier to sustain.
tractionpathguide – Content is concise, making it simple to implement strategies effectively.
strategicallies – Collaborate with professionals who enhance your influence and business impact.
workflowflowguide – Excellent reminder, signals make managing steps in projects much easier.
forwardbydesign – Nice insights, structured steps make achieving outcomes simpler and more reliable.
momentumengine – Clear signals keep daily tasks moving forward with purpose.
momentumengine – Steady forward energy helps sustain progress and achieve goals smoothly.
signalinsighthub – Practical tips help understand what action to take next.
enginemotion – Great explanations, understanding motion feels simple and practical.
directioncatalyst – Very helpful, each action contributes to steering progress efficiently.
forwardclarity – Very practical, the clear layout helps me take action confidently.
claritycorner – Very helpful, this site turns clear ideas into practical actions smoothly.
mutualsuccessnetwork – Very useful, strategies focus on ensuring all parties benefit and grow together.
planbeacon – A clear plan gives direction and reduces uncertainty.
taskengine – Clear signals improve workflow and keep projects moving efficiently.
growth clarity insights – Well structured, the growth process feels well thought out.
ideaengine – Strategic insights turn ideas into practical steps that move projects forward.
strategicreserve – Thoughtful planning that drives durable business achievements.
clarityproduces – Helpful content, clear focus makes moving from plan to result easier today.
enterpriseconnect – Connect with enterprises and individuals to create meaningful collaborations.
progressmotionhub – Suggestions are practical and help maintain consistent progress.
focusedpath – Clear guidance, keeping focus on core tasks ensures growth moves forward effectively.
directioncatalyst – Very helpful, each action contributes to steering progress efficiently.
steadyclimb – Excellent perspective, slow progress ensures long-term stability.
clearroute – Inspiring content, having a clear route forward really helps in accomplishing goals.
futurepartnerscircle – Helpful, the circle encourages growth, vision alignment, and meaningful interactions.
clarityhub – Directional clarity ensures work flows efficiently and effectively.
strategictrustedpartners – Helpful insights, strategic trust drives better partnership outcomes.
ideahub – Having clear direction ensures ideas move forward without delay.
actionbeacon – Clear signals anchor growth and ensure momentum continues.
growthsimplified – Nice advice, clear methods help make steady growth feel achievable.
strategyengine – Focused clarity allows teams to advance projects efficiently and with purpose.
growth with intent – Smart guidance, focusing on intention strengthens growth decisions.
actionenergy – Helpful notes, proper focus channels energy and accelerates progress.
powercollabcircle – Practical, working with powerful groups fosters innovation and sustainable outcomes.
forwardthinking – Great advice, concepts about moving forward are explained clearly and practically.
strategicpartners – Build lasting relationships that foster mutual success and alignment.
energyflowhub – Advice is concise, allowing tasks to be prioritized efficiently.
innovationengine – Great tips, forward-thinking approaches really help in applying ideas efficiently.
sharedvisionbond – Excellent, common vision here reinforces purpose and strategic cohesion.
directionbeacon – Signals guide decisions and improve efficiency in everyday work.
directionalguide – Helpful advice, the signals shared here really point the way forward.
forwardengine – Energy produced by focus powers tasks and keeps projects advancing consistently.
claritypilot – A systematic approach ensures tasks progress smoothly and predictably.
ideas2results – Great guidance, actionable steps make moving from idea to result easier.
clarityboost – Practical suggestions, having clarity helps maintain forward motion every day.
synergygrowthcircle – Very practical, collaboration here creates synergy that accelerates growth for everyone involved.
collaborativeleadershipbond – Very useful, collaboration among leaders improves credibility and drives strategic results.
actionmap – Very motivating, taking deliberate steps builds a clear route to progress efficiently.
growthstrategieshub – Practical tips to strengthen partnerships and drive long-term growth.
partnerflow – Thoughtful alliance setup, partnerships appear meaningful and useful.
motionpathguide – Advice is straightforward, guiding understanding of motion and progress.
claritybeacon – Proper direction fuels progress and helps teams achieve results with ease.
guidedirection – Excellent advice, these signals effectively point out the right direction for action.
progressiveleadersbond – Practical advice, leadership messaging encourages innovation and preparing for future challenges.
forwardbeacon – Practical ideas become tangible progress when applied systematically.
growthplanpower – Practical advice, implementing these strategies accelerates growth while reducing uncertainty.
alliancenetwork – Join networks that maximize trust, teamwork, and long-term results.
actionfuelsmomentum.bond – Love the vibe here, everything loads fast and looks super clean.
forwardactioncenter – Motivating tips, enables consistent forward movement in tasks.
strategybeacon – Steady action maintains momentum and supports project goals efficiently.
collaborationleadersbond – Helpful perspective, this hub encourages strategic alliances and productive collaboration.
topprolinks – Access top professionals to expand your influence and collaborative potential.
Collaborative Growth Platform – Suggests real potential for partnership-driven success worldwide.
directionenergizesgrowth.bond – Really helpful info, I’ll be coming back to read more soon.
growthnetwork – Connect with trusted professionals to expand your impact and effectiveness.
goalcompass – Sustained focus drives higher velocity and better results.
GlobalFutureGrowth – Clean layout, conveys professionalism and clarity in every section.
forwardbeacon – Proper guidance provides energy for growth and keeps projects on track.
progressfocuscenter – Steps are easy to implement, improving movement toward goals.
TrustedCircleLink – Useful articles, I often return to read new posts.
clarityleadsmovement.bond – Nice layout and simple flow, made it easy to find what I needed.
TrustConnectInternational – Professional feel, content is logically arranged.
GlobalGrowthAlliance – Professional presentation, information is logically structured.
brainstormzone – Connect with thinkers and turn ideas into actionable projects.
BondedHubLinks – Clear structure, I found the key details in no time.
impacthub – A hub to connect professionals and strengthen teamwork effectively.
AllianceBridge – Simple navigation, content is clear and useful for professionals.
ideasintopractice – Useful guidance, helps convert creative thoughts into actions efficiently.
claritybeacon – Forward motion becomes easier to manage with proper guidance.
BondedLearningHub – Very organized lessons, guides are simple to follow and practical.
GlobalNextGenLink – Smooth interface, content is easy to locate and navigate.
forwardmotionactivatednow.bond – Great work on this site, feels polished and surprisingly easy to navigate.
Learn About Business Bonds – Clear visuals and wording help the idea land smoothly.
AllianceLearningHub – Smooth navigation and clear examples, I grasped the key points fast.
BondedUnityNetwork – Well-laid-out, information feels focused and approachable.
BlueChipBondGuide – Clear tutorials and structured content, made learning easy.
SummitLinkNetwork – Clear navigation, learning materials are organized intuitively.
bizallies – Reliable partners helping you achieve collaborative success and steady growth.
UnityBondLink – Easy-to-follow lessons and clear instructions, bonds are simpler to understand now.
SteadfastCircle – Guides are clear and actionable, I rely on this site often.
CapitalCirclePathway – Very practical tips, content is clear and well-organized.
alliancenetwork – Develop relationships that support growth, cooperation, and professional impact.
BondTrustNetwork – Clear tutorials with actionable advice, I found learning bonds straightforward.
ProfessionalBondHub – Clean and clear, found the guidance I was seeking without effort.
Principles Bond Learning Hub – Stepwise, easy-to-follow content that makes bonds understandable in no time.
AllianceLearningCore – Easy-to-understand tutorials, I learned multiple key points efficiently.
growthpathguide – Advice is structured, helping to plan and execute growth effectively.
claritysetsdirection.bond – Pretty solid content, I enjoyed reading through the pages today.
GlobalTrustedLeaders – Professional tone, ideas are presented in a straightforward way.
strategycompass – Anchoring actions with clarity improves overall progress.
HeritageUnityInfo – Guides are concise and informative, found everything quickly.
UnityPartnersNetwork – Concise layout, platform communicates trustworthiness effectively.
BondedStrengthCircle – Excellent explanations, I absorbed practical advice immediately.
BondBridgeNetwork – Helpful content with clear instructions, navigating and learning is simple.
BTHubPortal – Friendly content with helpful tips, I discovered multiple useful methods.
EverCoreGuide – User-friendly tutorials and helpful tips, grasping bond concepts felt effortless.
SecureLinkNetwork – Very readable content, structure makes finding what you need fast.
GlobalGrowthFocus – Organized layout, helpful insights are easy to return to later.
CapitalTrust Learning – Quick tips and resources that make complicated topics approachable.
trustcircle – Strong emphasis on relationships, trust clearly feels like the foundation here.
VisionInsightPortal – Well-written and structured guides, I picked up useful tips quickly.
directionshapesoutcomes.bond – Smooth experience overall, pages are organized and load without any lag.
ValueBondPortalHub – Clear navigation, lessons are easy to understand and apply.
GrowthPathNetwork – Simple and effective, inspires confidence in future growth.
SharedSuccessLink – Clear design, navigation feels effortless and logical.
AlliedCapitalHub – Very practical content, helped me understand concepts quickly.
HubOfBondedVisions – Smooth interface, the site makes learning or exploring content effortless.
UnityBondHub – Smooth navigation and concise lessons, understanding strategies was simple today.
AllianceVisionLink – Great insights, the content makes investing strategies easy to grasp.
UnityBond Learning – Clear guidance with an intuitive layout for fast comprehension.
UnityResources – Informative content, every section is actionable and easy to digest.
taskengine – Following through on tasks turns long-term goals into reality.
Bonded Stability Knowledge – Organized content that simplifies networking for both beginners and pros.
HarmonyCoreLearning – Clear, concise examples, made grasping concepts fast and simple.
AllianceResourcesHub – Guides are informative and approachable, I learned several new tips.
MutualStrengthPortal – Guides are concise and very helpful, improved my knowledge efficiently.
progressmovespurposefully.bond – Interesting site, the structure makes sense and keeps things straightforward.
UnitySphere – Well-laid-out content, makes browsing smooth and intuitive.
GlobalAllianceHub – Friendly layout, makes exploring resources smooth and enjoyable.
NexusTrustNetwork – Practical tips and examples, everything is clear and simple to follow.
SynergyNetworkHub – Informative layout, guides make advanced concepts simple to follow.
ProsperityBondPortal – Excellent layout and useful resources, I discovered valuable tips efficiently.
BondPrimeNetwork – Very readable content, guides are practical and easy to follow.
strategyhub – Strong positioning, the collaborative focus comes across clearly and confidently.
Collective Trust Hub – Clear, actionable insights that made learning practical strategies simple and quick.
Prime Capital Guide – Well-organized pages and guidance make everything easier to follow.
HarborBondInsights – Well-laid-out tutorials, perfect for beginners and experienced users alike.
PillarLink – Tutorials are clear and actionable, very useful for beginners.
UnityPathInfo – Clear guidance and practical resources, I learned important concepts fast.
EverTrust Hub – Well-structured guides make understanding simple and effective today.
directionactivatesprogress.bond – Clean design and clear message, it actually feels trustworthy to browse.
UnitedGrowthSphere – Clear layout, content communicates purpose effectively without clutter.
Trust Hub Insights – Intuitive layout and concise instructions make information easy to find.
NetworkTrustHub – Organized and approachable, community updates are useful.
BCPartnersInfo – Excellent tutorials and helpful guides, I discovered key insights fast.
UnityBridgeLinkHub – Smooth tutorials, information is presented clearly for quick comprehension.
TrustFlow Center – Reliable and friendly content that’s perfect for both beginners and pros.
bondedalliancehub.bond – Well-laid-out content makes understanding complex topics much easier.
SolidBondLink – Smooth navigation and helpful articles make networking strategies accessible.
Capital Insights Portal – Smooth navigation and informative resources made learning simple.
Integrity Bond Hub Central – Reliable resources and a friendly approach make exploring simple and effective.
CornerstoneLink – Helpful guides, site feels organized and responsive.
capitaltrustline articles – Informative content with step-by-step guidance made topics easy to follow.
BondNetworkHub – Well-organized content, I learned several useful approaches efficiently.
TrueBondResourcesHub – Helpful tutorials, even complicated ideas are broken down simply.
GrandUnity Network – Smooth navigation and practical examples made finding insights quick and easy.
GlobalDrivenGrowth – Easy navigation, content loads quickly and instructions are straightforward.
actionmovesforwardclean.bond – Good read, I found a couple sections that were genuinely useful.
SmartConnectNetwork – Minimalist interface, content makes collaboration intuitive.
EverlastingLinkCenter – Easy-to-understand content, lessons made difficult concepts clear.
BondingCornerstoneNetwork – Clear and practical advice, very helpful for my current projects.
CircleBondPortal – Smooth tutorials and clear guidance, bonds are easier to understand now.
Bonding Group Central – Well-organized pages and concise tips make exploring easy.
AllianceLink – Helpful resources, very organized and simple to use.
partnerbridge – Thoughtful approach, partnerships are positioned for cross-border cooperation.
Lineage Knowledge Base – Clear layout and actionable tips make comprehension fast and effortless.
AllianceCircle – Clean design and clear instructions make navigation effortless.
Collective Value Bond Hub – Step-by-step guides and tutorials make complex concepts easy to understand.
TrustLineCore – Practical tutorials that are easy to follow, I absorbed the key points quickly.
trustforge.bond overview – Clear instructions and practical content make understanding easier today.
BondedCapitalHubLink – Clear content and smooth navigation, very beginner-friendly today.
trustaxis insights – Organized materials and practical tips make concepts easy to grasp.
BusinessBondConnect – Smooth structure, content encourages meaningful professional connections.
trustbridgegroup.bond – Informative resources and clear layout made understanding bonds fast and simple.
BusinessLinkGlobal – Smooth presentation, platform communicates trust and direction.
signalcreatesalignment.bond – Looks great on mobile too, everything feels quick and nicely put together.
CoreTrustPath – Clear lessons with real examples, content is simple to follow.
HeritageBondPortal – Easy-to-read articles, everything loads fast and feels organized.
IroncladPartnerNetwork – Everything is structured nicely, makes following steps very easy.
TrustedBond Center – Smooth user experience combined with practical, reliable information.
KeystonePartners Info Hub – Simple structure and clear points make learning smooth.
Trusted Allied Bond Hub – Fast-loading pages with clear content make navigating effortless today.
Growth Hub Learning Center – Organized content and stepwise explanations help concepts stick.
SynergyKnowledgeHub – Easy-to-follow articles, I was able to understand multiple concepts fast.
HorizonsPortalBond – Practical lessons with easy explanations, I learned multiple strategies.
BondHubAlliance – Clear and concise, I picked up several actionable ideas fast.
integrityaxis.bond – Clear layout and structured content make exploring bond topics easy today.
CoreAlliance – Very clear and practical content, perfect for getting started quickly.
bondedtrustcore knowledge – Friendly explanations and simple layout make understanding fast.
unitydrivenbond.bond – Smooth, fast navigation with reliable content, making it a great experience overall.
ReliableBondWorld – Smooth navigation, messaging feels stable and approachable.
BPResources – Very structured content, I learned multiple techniques without confusion.
BondedPartnershipsHub – Very informative, offers actionable networking advice for professionals.
TrustLegacyCircle – Clear, concise lessons with practical examples, I learned key strategies fast.
Unity Secure Hub – Everything is easy to find and simple to comprehend.
LongView Alliance Resources – Well-laid-out tutorials helped me grasp strategies effectively.
connectionpartners – Professional tone, relationships seem credible and clearly defined.
NobleBridge – Simple interface, instructions are easy to follow and apply.
HorizonPathwayCore – Guides are practical, well-organized, and easy to digest.
BondedEnduranceInsights – Guides are simple and concise, I applied tips immediately.
Growth Circle Central – Well-organized content and practical examples made grasping ideas straightforward.
GlobalGrowthTrust – Professional layout, platform emphasizes long-term planning clearly.
unitydrivenbond.bond – Well-organized and quick to load, navigation is simple and effective.
UnityNetworkBond – Guides are concise and practical, I learned new strategies quickly.
bondedpillars.bond tips – Well-structured articles make learning new techniques simple and fast.
BondedCollective Info Hub – Concepts are presented clearly, saving time while learning.
HubMutualCenter – Clear explanations and examples, understanding strategies was simple.
CapitalBondNetwork – Informative and well-structured, learned multiple key points today.
trustfoundry tutorials – Smooth navigation and concise explanations allowed me to learn quickly.
Evergreen Bond Insights – Organized content that helps users quickly understand key ideas.
AllianceCenter – Easy to navigate, learned several approaches I can implement today.
BondUnityPortal – Content is structured and simple, making it easy to follow along.
Bonded Legacy Guides – Step-by-step explanations and smooth navigation make browsing easy.
CapitalBondNetwork – Tutorials are structured well and very helpful for learning quickly.
Bonded Strength Essentials – Everything is clearly arranged, making the guidance feel reliable.
Growth Insights Hub – Practical examples and structured content support fast comprehension.
Secure Path Tips – Helpful suggestions that make learning and application straightforward.
CollectiveBond Academy – Stepwise lessons and clear tutorials that make learning simple and effective.
unitystronghold.bond insights – Well-organized pages and practical guidance make learning fast.
bondednexus center – Practical tips and structured pages make understanding simple.
Foundation Alliance Tutorials – Practical explanations and a clean look make this site memorable.
Trusted Foundation Hub – Clear explanations and structured layout make learning easy today.
unitydrivenbond.bond – Excellent info and fast, easy-to-navigate site made my experience great today.
unitybondcraft.bond center resources – Practical advice and organized content make following concepts easy.
bondedvaluechain support – Clear explanations and organized lessons make studying easier today.
Covenant Partners Hub – Clear, professional language makes the site feel trustworthy while exploring.
Enduring Knowledge Center – Well-explained tips and structured guides enhance comprehension effectively.
Bond Network Insights – Smooth design and actionable guidance make decision-making easier.
unitykeystone.bond insights – Fast loading lessons and practical tips make content simple to understand.
Trust Circle Guide – Easy-to-read material that supports thinking ahead.
bondedtrustway lessons – Fast-loading content with practical guidance ensures a smooth learning experience.
Core Learning Portal – Clear explanations and simple layouts make the content approachable.
Shared Future Insights – Smooth layout and practical examples promote strategic thinking.
StrategicTrustAlliance – Straightforward presentation, partnership focus is clear.
capitalties.bond guide – Well-explained examples and actionable tips made concepts easier to follow.
capitalbondline learning – Easy navigation and practical examples made understanding topics simple.
Bonded Knowledge Portal – Practical examples and clean interface support confident learning.
Trusted Bond Knowledge – Helpful guides and clean interface make learning efficient.
Synergy Connection Platform – Feels like a useful tool for businesses seeking shared goals.
trustcontinuity.bond walkthroughs – Concise guides and well-laid-out content make navigating the site effortless.
Reliable Alliance – Overall design is neat, and everything loads quickly.
unitycatalyst study – Helpful steps and practical guidance simplify complex topics.
Unity Resource Hub – Stepwise guidance and clear content improve comprehension efficiently.
PartnershipVisionPro – Concise and clear, messaging is modern and well thought out.
trustlineage.bond walkthroughs – Practical tips and clear explanations make studying efficient today.
unitybondworks study – Clear instructions and useful lessons simplified complex ideas.
Ledger Hub – Site layout is clean, and details are straightforward.
GlobalPartnerSphere – Professional structure, content flows logically and purposefully.
GlobalUnityForum – Smooth flow, collaboration goals are presented naturally.
ActionBase – Well-structured pages, everything was easy to locate.
bondedcontinuum link – Design feels modern, information looks solid, and loading is fast.
AnchorEngine – Well-organized layout and intuitive features, guiding direction feels natural.
AnchorWorks – Informative guides and clear structure, navigating was quick and easy.
DigitalSphere – Clear layout and creative ideas make exploring content enjoyable.
Trust Harvest Online – Random visit turned into a productive browsing session.
MotionSphere – Logical layout and quick responsiveness keep me focused during visits.
PathSphere – Practical guidance, making planning and choices easy to handle.
ClarityBase – Simple explanations that made complex ideas manageable.
ChannelWorks – Clear guides with intuitive navigation make exploring information effortless.
GoalFlow – Practical instructions and smooth navigation help understand concepts quickly.
DesignHub – The layout is simple, making it easy to find useful advice.
FocusEdge – Well-structured layout and practical advice, staying on task feels simple.
VisionCore – Friendly layout and helpful instructions, understanding content feels smooth and easy.
TaskDock – Simple interface, enabling fast planning and project organization.
MapStructure – Everything feels organized, browsing was efficient.
steadfastlink main site – The structure supports simple and clear communication.
PathActivator – Simple layout, exploring ideas and steps feels effortless.
FocusHubPro – Well-laid-out guides and readable content make navigating simple.
LogicFlow – Clear design, site helps exploring strategies feel natural today.
FlowController – Well-structured content with helpful tips makes using the site effortless.
Action Blueprint – Well-organized guides make understanding strategies simple.
ActionBase – Simple yet robust, everything works exactly as expected.
CornerStyle – Sleek design, easy navigation, site makes browsing effortless.
ActivationHub – Very clear structure, finding and following steps feels effortless.
VectorLab – Well-structured content, making information accessible and simple.
TrendMap – Well-presented tips with lots of visual inspiration.
PathVision – Well-laid-out content and clear instructions make grasping strategies fast.
ProgressFlow – Helpful resources, learning steps is simple and smooth.
BrightWorks – Clear structure and practical content make exploring simple.
IdeaMotion – Interactive guides, learning new concepts feels natural and smooth.
AnchorFocus – Smooth flow and organized sections, maintaining concentration is fast and simple.
Growth Insights – Well-structured pages help concepts feel easy to grasp.
bondedcoregroup platform – Pages feel legit and the organization makes finding things quick.
ForgeYourGrowth – Smooth design and practical content, learning feels straightforward and fast.
FocusSphere – Clear advice and organized content make strategy planning intuitive.
FlowForge – Clear layout and practical instructions make exploring strategies easy.
VisionHub – Friendly layout and helpful tips, learning strategies feels natural.
TrendOutline – Consistently updated with practical information.
MotionFlow – Practical tips, exploring strategies is simple and intuitive.
FocusLink – Smooth structure with helpful tips, understanding content feels easy.
PlanetLoopPlus – Concise steps and intuitive guides make exploring smooth and enjoyable.
IdeaEngine – Smooth navigation, following ideas feels easy and quick.
BondBridge – Organized structure and practical tips, navigating content is effortless today.
AnchorDirection – Smooth interface and practical resources, shaping paths feels natural.
Idea Architecture – Clean layout makes reviewing strategies straightforward.
SecureUnity – Smooth interface and practical instructions simplify learning.
BondedHub – Smooth interface with clear guidance, learning strategies is straightforward.
IdeaCompass – Clear layout with interactive tools makes planning and learning enjoyable.
LinkBridge – Organized interface, connecting ideas and resources feels effortless.
ActionFlow – Well-structured guides, understanding concepts is smooth and simple.
TaskTracker – Smooth browsing experience and practical advice throughout.
PathHub – Clear layout and helpful tips make navigating strategies effortless.
FirstDirection – Clear layout and helpful tips, navigating the site feels smooth and simple.
ClarityNest – Clean design with helpful instructions, navigating concepts feels natural.
CapitalFlowPath – Friendly interface with practical tips, navigating content is fast and smooth.
FocusMap – Clean presentation makes finding information easy.
strategicbonding web hub – Helpful insights shared in a clean, simple layout.
MomentumEdge – Clear design and practical guidance make following through simple and reliable.
FrameworkVault – Smooth navigation with helpful guides makes understanding easy.
DesignBridge – Friendly interface, learning concepts feels effortless and smooth.
BondFocus – Smooth design with helpful guidance, exploring strategies is simple and quick.
IdeaForge – Helpful content, exploring ideas on the site is smooth and simple.
MoneyBridge – Practical guides make exploring strategies effortless.
VisionNavigator – Practical articles and easy navigation make understanding concepts quick.
FocusLaunch – Smooth interface, exploring articles and tips feels fast and intuitive.
LaunchDock – Simple interface, making brand planning fast and practical.
WealthWayline – Clear layout and practical advice make navigation easy.
TrailMomentum – Practical tips, following instructions is simple and quick.
TrustFlow – Smooth layout with clear advice, learning concepts is fast and easy.
InsightTrend – Easy-to-follow menus and practical advice, exploring ideas is quick.
PathMatrix – Smooth navigation and thoughtfully organized resources.
AnchorSystems – Smooth layout and actionable tips, staying on top of growth tasks is easy.
MoneyPath – Practical steps and organized layout simplify understanding concepts.
ZoneIntellect – Friendly interface, exploring concepts is simple and smooth.
IdeaSphere – Interactive guides and clear layout make exploring ideas enjoyable and efficient.
Vision Organizer – Clean sections help ideas come together quickly.
DirectionSphere – Easy-to-follow guides with organized content simplify learning approaches.
CorePathway – Organized interface and practical tips, understanding ideas is straightforward.
CoreBridge – Structured guidance and concise tips simplify understanding.
capital bond landing – The design looks refined and the copy reads well.
StepNavigator – Organized layout, resources make planning and executing actions simple.
ActionLoop – Simple layout, and resources are practical and straightforward.
ActionSpot – Clear interface, learning and applying strategies feels intuitive and smooth.
InsightBond – Intuitive menus with clear tips, navigating strategies is quick and simple.
GrowthCore – Balanced design and actionable tips, makes planning straightforward.
ExecutionFocus – Clear menus and organized guidance, planning strategies is simple.
ClarityHub – Explanations are simple and effective, easy to follow.
FlowNavigator – Clear structure and friendly design, applying strategies is simple today.
TrajectoryMap – Well-organized content, learning and navigating feels simple and enjoyable.
Growth Lane Hub – Well-organized content helps strategies click quickly.
BridgeGuide – Friendly interface, learning and planning is simple and efficient.
ClarityLoop – Easy navigation and readable content make the site very accessible.
WealthSynergy – Clear steps and organized design make understanding ideas fast.
SecureTrust – Well-organized steps help visitors navigate ideas easily.
StrongholdGate – Friendly design with practical guidance, understanding strategies is straightforward.
PathNavigator – Well-structured content and helpful tips, exploring and applying ideas is fast and simple.
FrameworkEdge – Organized layout with intuitive explanations makes studying motion smooth.
ClarityFlow – Clear interface, learning and applying strategies is fast and effortless.
CapitalPath – Friendly layout with helpful guidance, navigating information feels easy.
ClarityWorks – Well-laid-out information, giving users confidence in the platform.
BoostNavigator – Friendly design with practical tips makes exploring information simple.
InsightHub – Clean layout and practical tips, exploring information is fast and easy.
ProgressHub – Easy experience with updates that stay relevant.
anchorunity link – Information flows logically and is easy to understand at a glance.
Thought Starter – Clean design and smart navigation feel natural.
VictoryChain – Organized content, learning strategies is effortless and enjoyable.
FlowNest – User-friendly design, learning processes is quick and intuitive.
SecureCircle – Helpful walkthroughs make strategy exploration stress-free.
TrustFlowPath – Practical tips and clear steps make learning effortless.
SynergyNetwork – Smooth guidance and structured layout make following strategies fast.
LegacyVision – Friendly interface with helpful tips, learning content feels effortless.
MoodBeat – Smooth layout, reading posts and browsing topics is simple.
RankPath – User-friendly interface and organized resources make learning simple.
SystemTracker – Helpful content, following steps is easy and intuitive for users.
FlowFocus – Well-organized layout and concise guidance, exploring strategies feels effortless.
GrowthVault – Easy interface and helpful guides make exploring efficient.
SafeAlliance – Intuitive navigation and helpful guidance, accessing content is straightforward.
NextGrowth – Friendly interface, following strategies is easy and efficient.
SecureFoundation – Practical instructions help users navigate resources quickly.
LinkPathway – Friendly layout, exploring and connecting concepts feels natural and quick.
MomentumDock – Practical resources and smooth interface make understanding fast.
ElitePath – Intuitive layout, browsing information feels quick and smooth.
BondedPath – Clean pages and practical advice, navigating strategies feels smooth.
bondedgrowthline site – Visuals look polished and everything loads without delays.
FocusedPath – Clear and organized content, site makes learning strategies intuitive.
PathProgress – Clear steps, learning strategies is effortless and fast.
FuturePathway – Friendly interface with clear guidance, understanding strategies is quick and easy.
FlowTracker – Smooth interface, and organizing steps feels natural.
FusionHub – Smooth interface and clear guidance, exploring ideas is quick and simple today.
UnityHub – Smooth layout and practical tips, browsing content feels quick and effortless.
MatrixLab – Helpful resources, learning new concepts feels natural and straightforward.
SecureBridge – Clear, practical instructions make following strategies simple.
ActionHub – Friendly layout, learning and following steps is quick and simple.
GlobalVault – Well-laid-out resources, navigating the site feels natural and fast.
PureDesign – Elegant layout, exploring ideas and inspiration is simple and smooth.
ProgressTracker – User-friendly layout, site makes following steps effortless and intuitive.
HubFocusPoint – Clean design and helpful guidance, navigating content feels effortless.
CapitalConnect – Stepwise advice helps users access information smoothly.
UnityBondHub – Friendly interface, organized layout, navigating resources feels fast and effortless now.
TrustJourney – Friendly menus and practical guides, exploring content feels smooth.
Motion Playbook – Clear steps and seamless navigation make planning simple.
ConvergeNetwork – Structured guidance and easy-to-follow steps make content navigation simple.
PillarNest – Smooth menus with clear guidance, navigating content feels effortless.
IdeaCurrent – Friendly layout and clear structure, exploring ideas is quick and simple.
WorksVault – Smooth layout and helpful tips make understanding content quick.
TrustNest – Clean layout with practical guidance, finding resources is fast.
BondHub – Friendly interface with practical tips, navigating content is simple today.
WealthPath – Intuitive instructions make navigating ideas quick and easy.
SecureValue – Well-organized resources ensure browsing ideas is intuitive and fast.
CapitalPath – Friendly layout and concise advice, finding information is smooth.
AnchorTrack – Smooth structure with concise tips, exploring ideas is straightforward.
CapitalPath – Helpful pointers make learning and following strategies natural.
official growth ledger – The site is organized and presents information reliably.
WaypointTrust – Clear guides and smooth layout, navigating ideas feels simple and effortless.
TrustBridge – Smooth layout and helpful steps make exploring strategies intuitive.
reliable harbor site – Pages are easy to navigate and the content inspires confidence.
ForwardGuide – Smooth layout, following instructions feels effortless today.
simple secure link – Professional and clear, making it easy for new users to navigate.
CapitalHub – Organized menus and clear instructions, exploring content feels natural and easy.
AlliancePath – Friendly guidance and organized steps make navigating topics easy.
start here – Navigation is intuitive and the content is easy to digest.
collective portal – Interesting material, logically structured for easy comprehension.
DesignStream – Well-organized site, discovering new concepts is quick and easy.
learn more here – Content is clear, well-structured, and simple to follow.
explore capital trust – Everything is structured in a way that makes sense.
trustalignment.bond – The site feels reliable, and the messaging is easy to understand.
simple vision link – Everything is presented clearly, making it easy to follow.
ImpactPath – Well-structured content, navigating the site is simple and quick.
check this platform – Informative content presented cleanly without unnecessary distractions.
learn more here – Everything is presented thoughtfully and easy to understand.
FuturePortal – Easy-to-use design, navigating the site is quick and efficient.
simple progress link – The name may be unusual, but the message is communicated confidently.
Harvest Insights – Pages are clean and easy to follow, key points stand out.
TrustLine Overview – Layout is clear, all important info is visible at a glance.
powers movement portal – Content is easy to digest and the structure is clean.
Waypoint Hub – Pages are organized and easy to explore, making research simple.
Bonded Navigator – Well-structured pages make understanding and navigation effortless.
Assurance Portal – User-friendly layout, information is straightforward and well organized.
BusinessNavigator – Well-structured layout, reviewing guides is smooth and effortless.
official forward motion – Content is fast-loading, and everything is presented clearly.
Bridgeworth Connect Pro – Intuitive layout with detailed, readable information.
Matrix Portal Pro – Information is concise yet comprehensive, perfect for quick learning.
Link Insights – Clear headings, easy-to-read sections, and responsive pages.
Capital Info – I could easily understand the steps, very approachable.
Bonded Portal – Navigation is smooth, and pages are clearly organized.
Balanced Guide – Information is arranged clearly, making comprehension effortless.
Harbor Labs – Great for understanding investment basics quickly.
North Resource – Information is presented logically, helping users digest material faster.
Trustline Portal – Content is straightforward, with no unnecessary clutter.
Bonded Guide – Smooth interface, content is approachable and simple to understand.
CK Zone – Browsing feels natural, and the site is easy to explore.
Bond Overview – Simple and professional layout, details are easy to follow.
Prime Connect Pro – Logical layout makes content easy to navigate and comprehend.
CL Insights – Everything is intuitive and easy to understand.
Crest Tracker – Consistent design and organized content make the pages very approachable.
Stronghold Resource – Clean layout and clear instructions make the platform approachable.
CN Insights – Easy to follow content, I grasped everything quickly.
Union Connect – Quick-loading pages with intuitive menus make exploring the site simple.
Axis Insights – Information hierarchy is intuitive, making browsing seamless.
Vertex Hub – Simple and professional, all sections are easy to navigate.
Centurion Bond site – Found this page helpful, layout feels clean and simple.
Vector Overview – Clean interface and clear headings make key information easy to locate.
Bond overview – Smooth, intuitive design that makes content easy to read.
Bonded Portal – Clear headings and concise sections make reading efficient.
Dependable info – Practical and clear content with smooth browsing throughout.
AboutUs – Clear sections, intuitive navigation, and a professional feel.
Capital Space – Easy to browse, content is straightforward and reliable.
FAQ – Straightforward answers, well-arranged sections, and smooth browsing.
Login – Sign-in pages are fast, and forms are easy to complete.
The Honest Hub – Clean first impression, layout is tidy, and information is easy to follow.
ClearPath resource – Nice experience overall, pages work as expected.
Official CoreStead – Well-written information that’s practical and easy to follow.
Features – Well-structured pages, clear content, and smooth navigation.
Compass Overview – Easy-to-follow layout, content is structured and accessible.
The Ironclad Link – Professional layout, headings are clear, and content is simple to follow.
The LB Link – Pages load fast, layout is tidy, and reading content is effortless.
Bonding services – Intuitive structure with content that’s clear and practical.
CB Lighthouse – Clear layout, all information is easy to access.
Login – Quick access, well-structured layout, and intuitive interface.
Contact – Contact info is straightforward, and pages display without delay.
Optimum Corner – Pages load fast, menus are clear, and content is easy to scan.
Honor Corner – Smooth interface, pages respond instantly, and information is organized clearly.
ClearView resource – Content is straightforward and easy to read.
Community – Easy to explore, organized content, and intuitive browsing.
CoreWard website – Smooth experience with content that feels well-written.
Support – Design is tidy, navigation flows smoothly, and content is easy to digest.
ML Hub Online – Pages load quickly, layout is clean, and content is easy to digest.
The KH Link – Fast-loading pages, clean structure, and reading content is easy.
Bonding platform – Pages are clear, and the information is presented logically.
Optimum Gateway – Fast-loading pages, headings are clear, and content is easy to read.
Support – Help pages are clear, and navigating support options is straightforward.
Services – Minimal design, pages load quickly, and text is straightforward.
Horizon Spot – Modern interface with smooth transitions, content is concise and well-organized.
Home – Pages are clear, navigation is fast, and browsing is smooth.
Downloads – Fast navigation, clear sections, and user-friendly experience.
Coalition services – Nicely structured site that’s easy to browse.
CornerPeak resource – Smooth user experience with neatly presented information.
Mainstay Spot – Sleek interface, organized sections, and content is readable.
Summit Navigator – Intuitive layout, user-friendly navigation, and content is clear and helpful.
Features – Neat layout, smooth interface, and content is understandable.
Orbit Portal – Pages render quickly, layout is clear, and content is straightforward.
Blog – Articles are easy to read, and switching between posts is seamless.
Bond reference – Logical layout with concise and readable information for quick understanding.
Horizon Space – Clean interface, responsive design, and content is straightforward.
Shop – Fast-loading pages, clear structure, and intuitive browsing experience.
Community – Neat interface, simple navigation, and content feels approachable.
Vector Central Hub – Quick-loading pages, clean design, and browsing through information is effortless.
Cohesion Bond page – Easy learning experience with clear information.
Cornerstone Axis page – Easy to move around, organized content, and good first impression.
Vertex Bond Portal – Smooth navigation, concise content, and layout looks professional.
AboutUs – Organized sections, simple navigation, and professional look.
Bond Gateway – Smooth scrolling, organized sections, and content is readable.
Summit Gateway – The interface is easy to navigate and pages respond quickly every time.
Bond Online – Clean design, smooth navigation, and information is straightforward.
The Impact Hub – Pages load fast, layout is tidy, and information is easy to digest.
About Us – Text is clear, and the page feels uncluttered.
Terms – Legal pages are clear, and navigating between sections is effortless.
Bonding platform – Simple structure and content that’s easy to digest throughout.
Partners – Professional design, smooth menus, and information is easy to digest.
Collective Anchor portal – Browsing feels effortless and stable.
Covenant hub – Informative pages with a clean structure, easy to browse.
Support – Minimalist pages, navigation is clear, and details are easy to read.
Alloy Link – User-friendly layout, clear headings, and browsing content is effortless.
Trusted Legacy Insight – Pages are organized, content is readable, and navigation feels intuitive.
Victory Bond Center – Clean design, intuitive navigation, and content is readable and well-structured.
Measured Connect – Navigation feels natural, pages load quickly, and content is readable.
Zenith Overview – The site design is simple and user-friendly, making it easy to read.
Home – The pages are easy to navigate, and information is well organized.
PB Hub Online – Clean design, intuitive menus, and content is concise and helpful.
Events – Organized pages, simple to browse, and information is easy to locate.
Visit Summit Trust – Professional design ensures content is easy to locate and understand.
IB Portal – Professional appearance, smooth navigation, and all information is accessible.
Newsletter – Subscribing is simple, and the format is tidy.
Bond support site – Helpful breakdowns that get straight to the point.
Home – Clean design, smooth browsing, and content is easy to follow.
CrestLink page – Well-laid-out information and smooth browsing make a good impression.
Shop – Smooth experience, pages are nicely structured and easy to navigate.
Merit Online – Clean structure, responsive pages, and information is easy to follow.
Visit Vigilant Bond – Pages load quickly, design feels professional, and information is straightforward.
About Us – Layout is clean, and text is clear and readable.
Products – Clean pages, navigation works well, and information is easy to read.
Features – Organized layout, smooth navigation, and text is easy to read.
Visit Unified Anchor – Navigation flows smoothly and content is concise and clear.
Paramount Central – Well-organized layout, smooth browsing, and information is concise.
Bond Link – User-friendly layout, headings are clear, and browsing is effortless.
Surefoot Central – Simple interface and fast pages make it easy to locate information.
HB Online – Modern look with intuitive navigation, everything displays correctly.
Pricing – Simple navigation, fast-loading pages, and organized sections.
Bond overview – Well-laid-out pages with readable text and effortless navigation.
BoldSphere – Current insights and logical layout make exploring trends fast and fun.
Confluence Bond site – Very user-friendly, content loads quickly and is easy to follow.
Testimonials – Well-organized pages and trustworthy content.
Resources – Guides are easy to find, and pages are logically structured.
Merit Spot – Interface is clean, sections are tidy, and content is easy to follow.
web presence – Visual layout is clean, menus are easy to use, and content feels well paced
Vital Bonding Guide – Layout is organized, browsing is smooth, and content is easy to understand.
Bond Info Center – Pages are structured clearly and information is easy to scan.
Pathfinder Online Hub – Clear layout, smooth navigation, and content is easy to digest.
The IB Link – Polished pages, fast loading, and information is well-organized.
Explore SurePath – Navigation feels intuitive and the layout is simple and clean.
Unity Harbor Online – Information is structured well and easy to understand.
page link – A simple approach, executed well, and inspires group learning and interaction
Home – Clean layout, smooth navigation, and pages load quickly with reliable content.
Heritage Gateway – Appears polished, navigation works without issues and content is accessible.
AnchorFlow – Organized guides and simple layout help manage schedules efficiently.
Crossroad network – Simple structure and readable content make it straightforward to browse.
CoreBridge network – Well-organized content that’s fun to explore.
Careers – Job listings are straightforward, and the structure feels approachable.
News – Crisp design, pages load fast, and content is clear and informative.
Testimonials – Pleasant layout, fast browsing, and information is easy to access.
MB Portal – Navigation flows naturally, pages load quickly, and content is easy to read.
Resources – Neat structure, helpful content, and effortless browsing.
landing page – The layout is clear, navigation is smooth, and information is easy to digest
Wardstone Portal Online – Design is polished, navigation works well, and content is readable and organized.
Integrity Connect – Navigation feels natural, fast-loading pages, and information is clear.
Pathway Connect Hub – Simple design, pages load quickly, and content is clear.
Synergy Bonded – Clear layout makes it easy for users to grasp services without any hassle.
Valor Bond – Layout is clean, navigation is smooth, and information is easy to follow.
browse here – Innovative ideas are presented well, navigation feels natural, and it inspires imagination
Bond Central – Pages load quickly, content is clear, and navigation is intuitive.
TrendDock – Very approachable, and learning about trends is fast.
Bond overview – Helpful explanations and fast page performance.
Bond reference – Easy-to-read sections with professional styling and clear explanations.
Blog – Modern layout, smooth flow, and content is easy to follow.
WardTrust Portal Online – Interface feels professional, pages load fast, and content is simple to read.
Bond Hub Online – Navigation works smoothly, sections are well-labeled, and content is readable.
Visit Site – Layout is crisp, browsing is easy, and content feels trustworthy and clear.
web portal – Nicely organized sections, stable navigation, and readable content throughout
Products – Crisp layout, pages load fast, and information is digestible.
Gallery – Attractive and organized pages, finding info is effortless.
Visit Site – Layout is crisp, browsing is easy, and content feels trustworthy and clear.
Iron Hub – Layout is clean, navigation feels intuitive, and content is easy to digest.
Peakline Capital – Easy browsing, concise content, and site structure is very clear.
Services – Intuitive menus, clean design, and details are easy to find.
Talon Connect – Quick-loading pages with navigation that feels simple and user-friendly.
Help Online – Clear navigation, responsive layout, and content is well-organized and easy to understand.
Value Crest Connect – Content is well-organized, navigation is smooth, making the site user-friendly.
web access – Content is clearly organized, exploring the pages feels effortless
Bond Central – Clean layout, pages load instantly, and all information is easy to read.
ActionWorks – Practical guidance and smooth layout simplify following processes.
WestBridge Guide – Smooth browsing, organized layout, and content is trustworthy and readable.
Mutual Axis Hub – Layout is tidy, pages load fast, and information is easy to follow.
start here – Browsing feels effortless, the design is sharp, and content is clear
Portfolio – Neat structure, simple navigation, and content is professional and clear.
About Us – Well-structured pages, menus are intuitive, and content is clear.
AboutUs – Well-organized content, clear sections, and smooth browsing.
PeakTrust Portal Online – Easy navigation, content is well-structured, and browsing experience is pleasant.
Talon Resource Center – Navigation is smooth, and information is laid out clearly for quick reading.
check this platform – Creative ideas are easy to explore, inspiring thoughts while scrolling
Support – Well-arranged content, smooth browsing, and professional feel.
Vantage Bond Guide – Clean and readable content helps users find what they need quickly.
ChoiceEdge – Organized content and responsive design make finding what I need effortless.
Westward Hub Online – Navigation is intuitive, design is clean, and content is easy to follow.
homepage link – Navigation flows well, pages are responsive, and details are easy to follow
Signup – Simple design, easy to follow, and content is understandable.
Blog – Modern layout, fast-loading pages, and text is simple to read.
About Us – Well-structured pages, smooth menus, and information feels professional.
True Harbor Resource Center – Smooth layout and clear messaging make browsing simple and enjoyable.
check this store – Items are easy to browse, pricing is sensible, and information is helpful
Testimonials – Clean presentation, smooth browsing, and content is easy to read.
Veracity Bond Base – Information is structured clearly, and the layout feels neat and professional.
Whitestone Link – Well-laid-out interface, pages load fast, and content is concise and easy to read.
Significant Cinema Hub – Smooth navigation, organized layout, and information is concise and readable.
CoreFocus – Practical tips and intuitive navigation make using the site simple.
need a video? italian production service company offering full-cycle services: concept, scripting, filming, editing and post-production. Commercials, corporate videos, social media content and branded storytelling. Professional crew, modern equipment and a creative approach tailored to your goals.
About Us – Well-organized pages, smooth menus, and information is clear and concise.
main site – The page feels welcoming, design stays simple, and information is easy to absorb
Login – Simple design, pages load quickly, and instructions are easy to follow.
visit site – A variety of innovative concepts, pages flow nicely and encourage creativity
Explore True Path – Intuitive menus guide visitors to information without confusion.
Worthline Access – Pages respond quickly, layout is organized, and information is clear and well-laid-out.
Verifiable Bond Portal – Simple layout, clear headings, and quick-loading pages make it easy to browse.
Portfolio – Neat structure, simple menus, and content is professional and approachable.
DesignPulse – Clear layout and practical tips make organizing projects straightforward.
check this site – Navigation feels natural, pages are organized, and content is easy to read
web access – Cool fashion displayed clearly, browsing is intuitive and enjoyable
Veritas Capital Online – Clear headings, smooth browsing, and content is well-organized and readable.
CoreAction – Logical layout and concise guidance make executing actions simple and fast.
RestoQ Platform – User-friendly design, content is easy to follow, and pages are well-structured.
Community – Neat interface, smooth navigation, and content is approachable.
web hub – Simple layout choices make browsing smooth and information clear
page link – Easy to browse site, layout is intuitive, and content is readily accessible
site entry – The layout feels trustworthy, pages load swiftly, and content is orderly
page link – Trendy selections are easy to view, overall vibe is fashionable and modern
russell cahill – The layout is straightforward, navigation feels intuitive, and content is clear for readers
browse here – Concept is straightforward, implemented effectively, and promotes teamwork
CoreMerge portal – Information is structured clearly, and navigation feels effortless.
A thoughtfully built store – The items and layout work together nicely.
Emberwild Store finds – Browsing here was pleasant, and products are carefully presented.
Deepwater finds – The boutique has a relaxed vibe, and browsing felt effortless with curated selections.
Friendly Golden Maple Finds – Layout is tidy, and items are easy to browse.
Login – Simple design, quick-loading pages, and instructions are easy to follow.
CoreStead resource – Helpful and concise content that’s simple to understand.
Inviting Evening Meadow finds – Shopping feels relaxing, and items stand out naturally.
Clean and simple shop – The layout makes browsing quick and comfortable.
Peaceful product corner – The shop feels inviting, and product details are easy to read.
Golden Rift Market Corner – Products are well-arranged, and pages load quickly.
Evening Orchard Online Treasures – Browsing is simple, and items are displayed clearly.
Bonding site – Easy navigation, fast performance, and trustworthy material.
Hollow Creek Finds Shop – Layout is tidy, products are easy to explore and shopping feels simple.
Clean online marketplace – Pages load quickly and the overall design feels uncluttered.
Ivory Branch Deals – Smooth experience and products are straightforward to find.
Friendly Golden Shore Boutique – Navigation is intuitive, and shopping feels straightforward.
Drift Pine online boutique – Navigation is smooth, and the products feel thoughtfully curated.
MF Collection – Smooth pages, well-organized products, and simple navigation.
Evening Tide Select Finds – Items are easy to view, and descriptions are clear and helpful.
Bond overview – Well-structured pages and a polished, professional design.
Larkspur Collection – Pages load quickly and products feel carefully selected.
Hollow Ridge Emporium – Pleasant browsing experience, items are well curated and pages load quickly.
Moonfall Select – Fast-loading pages and items feel thoughtfully chosen.
Artisan craft finds – Every product feels carefully made, with a noticeable attention to detail.
Golden Tide Boutique – Navigation is easy and shopping feels enjoyable.
Everbloom Boutique Hub – Shopping feels smooth, and every item looks carefully chosen.
Driftstone boutique corner – Products are easy to view, and the collection feels thoughtfully assembled.
Cornerstone Axis portal – Intuitive structure that makes exploring content simple.
Everoak Select Picks – The site is tidy, and product descriptions are helpful.
Moonfall Select – Fast-loading pages and items feel thoughtfully chosen.
Lighthouse Hub Online – Well-organized items and a smooth browsing experience.
Golden Thread Picks – Simple design and products are clearly displayed.
HoneyFern Finds Online – Browsing is enjoyable, products feel natural and well chosen.
Curated fashion store – Products are presented attractively, giving a polished and inviting impression.
Driftwood Lane product hub – Browsing flows naturally, and the shop is easy to navigate.
Covenant network – Easy navigation and naturally written explanations make the site enjoyable.
Fog Harbor Curated Corner – Browsing is straightforward, and products feel well selected.
MF Picks – Fast navigation and enjoyable layout with clearly displayed items.
Lighthouse Online Shop – Clean layout and enjoyable shopping experience.
Vein of Gold – Pleasant experience, pages load fast and shopping is effortless.
Curated Ember Coast shop – The layout is tidy, and exploring items is enjoyable.
Sea-inspired online store – The products are displayed nicely, and navigation is smooth.
Friendly Frostline Boutique – Navigation is intuitive, and items are easy to find.
Bond overview – Simple structure with concise content that’s easy to follow.
Edouard Chambost Link – Fast pages, easy layout, and information is straightforward and professional.
Moonfall Collection – Smooth interface with products that are easy to find and explore.
LinenWild Essentials – Clean design and enjoyable browsing experience.
Harbor Light Outlet – Smooth layout, selections feel curated and checkout is easy.
Inked Meadow Online – Pleasant browsing experience, pages load quickly and items look well curated.
Signup – Organized design, quick navigation, and content is clear and easy to digest.
Emberfield curated hub – Navigation is effortless, and products are well-organized.
Copper Grove online outlet – Items are easy to browse, and checkout is hassle-free.
Gold Branch Curated Goods – Layout is clean, making it easy to explore all items.
Продажа тяговых https://faamru.com аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков, ричтраков, электротележек и штабелеров. Решения для интенсивной складской работы: стабильная мощность, долгий ресурс, надёжная работа в сменном режиме, помощь с подбором АКБ по параметрам техники и оперативная поставка под задачу
CrestPoint learning – Straightforward design and natural content flow make information easy to follow.
MF Deals – Clean design, fast pages, and products are thoughtfully arranged.
LunarBay Essentials – Quick navigation and well-curated selections.
Harvest Lumen – Lovely store layout, browsing feels easy and products are appealing.
reliable grain supplier – Nice mix of options, fair value overall and shipping didn’t take long at all.
Iron Hollow Finds – Nice layout, products appear high-quality and browsing is effortless.
Golden Loam Market Corner – Products are nicely arranged, and pages load quickly.
a href=”https://moonpetalcollective.shop/” />moon petal finds – Smooth browsing and a selection of distinctive items made it fun.
Emberleaf online boutique – Navigation is smooth, and product descriptions are helpful and clear.
Lovely curated finds – The shop feels approachable, with clear images and organized pages.
fashiondailydeals.click – Stylish finds here, browsing is fast and effortless.
BloomCraft Online – Products feel unique, browsing is enjoyable and ordering is smooth.
shop unique value – Pleasant experience, prices seem fair and ordering is quick.
MF Market – Pleasant interface with fast-loading pages and helpful product descriptions.
Crossroad resource – Well-organized pages with readable and useful information.
Opal Grain Hub – Nice overall experience, layout is simple and shopping is straightforward.
Al-Brett Access – Pages respond quickly, structure is simple, and content is easy to read.
LC Deals – Browsing is straightforward with nicely displayed products.
HighCoast Marketplace – Browsing is easy, products feel curated and the site runs smoothly.
Quiet Stone Marketplace – Nice selection, site is intuitive and finding items is hassle-free.
loom goods online – The designs stood out, browsing felt smooth and checkout was straightforward.
Moon Ridge Trading – Smooth layout with quality products and a simple checkout process.
IronLeaf Hub – Shopping is straightforward and enjoyable.
Curated Ember Quarry finds – Items are simple to explore, and the experience feels professional.
MF Picks – Enjoyable shopping flow with clearly organized items.
shop blue fern online – Easy to find items, pages load fast and ordering is simple.
daily advice hub – Enjoy checking here, layout is clear and information is useful.
Crimson Meadow online – Browsing feels easy, and product details are clear and informative.
Luxury Finds Marketplace – Clear descriptions, products seem high-end and browsing is easy.
Продажа тяговых https://ab-resurs.ru аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков и штабелеров. Надёжные решения для стабильной работы складской техники: большой выбор АКБ, профессиональный подбор по параметрам, консультации специалистов, гарантия и оперативная поставка для складов и производств по всей России
Crown Capital site – Professional structure with easy-to-read and organized content.
Opal Grain Outlet – Nice variety of products, navigation feels smooth and checkout is simple.
LunarFern Treasures – Smooth browsing and items are clearly presented.
High Ridge Shop Online – Intuitive design, items are easy to explore and pages load quickly.
Quiet Stone Online Shop – Items look genuine, layout is clean and exploring is effortless.
creative idea hub – Very interactive overall, great for discovering fresh concepts.
Moon Veil marketplace – Pleasant browsing experience, product info is helpful and images appear genuine.
Emberstone Boutique finds – The shop feels well-curated, and browsing is smooth.
IronLeaf Online – Very user-friendly with clear categories.
MF Market – Pleasant interface with fast-loading pages and helpful product descriptions.
bluehearth store – Easy to explore, items are creative and checkout process is straightforward.
online ideas hub – Informative and well-structured, browsing is effortless.
Smooth shopping hub – The store is easy to explore, and product info is concise and clear.
amberfield unique finds – Products feel distinctive, site layout is clean and easy to navigate.
opalrivercollective.shop – Browsing was smooth, products feel curated and photos look realistic.
LunarField Select – Simple interface and products are thoughtfully arranged.
Moonfall Essentials – Fast navigation, simple browsing, and items are well-described.
Blue Peak Lane – Browsing was easy, products look well-curated and pages load quickly.
fresh harvest shop – Fast site response, carefully selected products and a good first impression.
beach finds store – No waiting for pages, clear details and realistic images.
Quiet Tide Hub – Great selection, browsing is simple and product photos look clear.
IronPetal Shop – Simple navigation and products are clearly displayed.
move forward online – Positive and clear, browsing is fast and engaging.
Opal Shore Boutique Online – Shopping feels smooth, product images are realistic and navigation is intuitive.
crafts by Amber Grove – Warm and genuine, handmade style comes through in every product.
LunarHarvest Finds – Easy navigation and items are presented clearly.
BlueStream Selections – Browsing felt relaxed, products are well-presented and pages load quickly.
morning quartz collection – Easy browsing, minimal interface, and clear information makes it pleasant.
curated emporium – The customer journey feels planned out, with an interface that’s easy.
Rift & Root Picks – Enjoyed browsing, everything looks well curated and the site works smoothly.
IronWave Specials – Smooth experience and thoughtfully selected products.
mindful moments online – Uplifting content, calm interface, and encourages reflection while browsing.
Opal Wild Outlet – Great selection, browsing is easy and products look well-presented.
amber hollow market – Clear and fast site, easy to explore all sections.
Events – Simple interface, intuitive navigation, and content feels organized.
brassfield online store – Products feel authentic, layout is simple and browsing is convenient.
moss & maple market – Beautifully curated items with clear, concise descriptions.
wild trade store – I planned a quick visit but stayed to browse.
riftstoneoutlet.shop – Pleasant browsing, navigation is intuitive and site loads quickly without errors.
inspired ideas hub – Pages load quickly, content is insightful and easy to browse.
petal ember market – Enjoyable experience, items look carefully chosen and site feels organized.
ambertrailgoods.shop – Items seem high-quality, descriptions are thorough and easy to understand.
brass lane collection – Items are curated nicely, pages load fast and the site is user-friendly.
Salt Meadow Boutique – The store has a unique feel and a nice range of products.
mosslight online – Well-organized site, attractive aesthetic, and easy to explore products.
adventure goods hub – The variety made it hard to stop scrolling.
Explore Suncrest Forge – Really liked the selection, everything feels intentional and unique.
Wild Harbor Deals – Enjoyable browsing, and the products feel both original and carefully picked.
Sunwoven Hub – Products were easy to explore and browsing felt effortless.
River Bloom Goods – Very easy to browse, products feel curated and pages load fast.
fresh fashion picks – Enjoyable experience, navigating the site is simple and fast.
Petal Quarry Boutique Online – Smooth experience, items look attractive and pages load fast.
Willow Select – Shopping experience is calm and intuitive, site feels polished.
Shop Brass Quartz Outlet – Good browsing experience, descriptions are clear and buying process feels effortless.
Ashen Fern Shop Click – Pleasant browsing experience, site has a soothing feel and loads fast.
Salt Wind Marketplace – A quiet, artistic vibe comes through while exploring.
Wild Harbor Retail – The shop offers a unique collection and a very pleasant browsing experience.
north bay collection – The site seems credible with a tidy, thoughtful layout.
oak mist collection – Everything here seems intentionally selected, giving a cozy feel.
Suncrest Lane Online Store – Clean design and gentle visuals make discovering items simple.
Visit Thistle & Stone – Enjoyed exploring, the layout is friendly and the aesthetic is warm.
River Quartz Shop – Lovely selection, browsing is simple and items are presented clearly.
Pine Echo Treasures – Easy to browse, products are well curated and pages are responsive.
shop click dayaway – Simple browsing, organized pages, checkout feels effortless.
Wind River Emporium – Found interesting products quickly, layout is clean and easy today.
Bright Ridge Picks – Easy to explore, products look appealing and checkout works well.
Wild Hollow Vendor – Simple, clean layout with pleasing colors makes shopping relaxing.
Ashen Willow Curated Hub – Navigation is simple, product browsing is smooth and enjoyable.
Sea Breeze Atelier – The clean layout and soft colors make browsing feel effortless.
northern petal boutique online – Approachable design, intriguing products, and content is clear.
oak mist goods – Cozy environment with a curated selection of appealing items.
Sunfield Online Shop – Browsing was smooth, with helpful and concise product details.
Thunder Willow Goods – Beautiful visuals and clear product information simplify shopping.
Rose Quartz Studio Shop – Store layout is clean, products are attractive and browsing was effortless.
bronzewillow finds – Cozy and user-friendly, browsing feels smooth and relaxed.
pine harbor shop picks – Enjoyed the experience, products are appealing and pages load smoothly.
Windstone Online – Browsing feels effortless, products are curated nicely and pages are clear.
gift ideas hub – Browsing feels fast and intuitive, great for finding unique gifts.
Harbor Online – Well-structured layout, fast pages, and information is easy to digest.
Wild Lantern Official – Clear and organized layout, shopping is effortless and enjoyable.
aurora valley online shop – Photos are natural, layout is clean and easy to navigate.
BondFlow – Step-by-step tips and smooth interface make browsing fast.
Explore Silk Road Finds – Browsing was smooth and the product explanations were straightforward.
northfield craft collection – Browsing was smooth, I’ll return for more of these types of products.
برای کسی که تریدر جدی هست، اکانت رایگان یا کرکشده تریدینگ ویو واقعاً مناسب نیست. شوپی راه حل قانونی و مطمئن ارائه داده با اکانتهای پرمیوم، پلاس و اسنشیال تریدینگ ویو. تمام اکانتها اورجینال، فعال و تحت گارانتی شوپی هستن و بدون دغدغه میشه باهاش تحلیل حرفهای انجام داد.
Timber Echo Retail – Browsing is intuitive, and the checkout process works smoothly.
Sunforge Collection – The site loads promptly and navigation feels natural on mobile.
Wild Lantern Selection – Smooth navigation and trustworthy design make exploring fun.
rustandpetal.shop – Easy to navigate, products are clear and descriptions informative and helpful.
Pine Veil Hub – Great variety here, pages load fast and shopping feels natural.
Action Guide – Informative and approachable, content is easy to read and absorb.
bright beginnings online – Positive atmosphere, easy browsing, and site feels approachable.
Legacy Space – Clear design, intuitive menus, and content is easy to follow.
Silver Reef Collection – Browsing is straightforward and gives a trustworthy vibe.
Visit Wild Plum Goods – Shopping was smooth, items feel well selected and trustworthy.
BondWise – Helpful walkthroughs make exploring strategies quick and natural.
Timber Echo Studio – Clear navigation and a straightforward checkout make shopping convenient.
Sunharbor Retail – Easy-to-follow design and well-arranged items provide a confident shopping experience.
Sable Fern Boutique – Items appear genuine, navigation is smooth and pages load quickly.
Quiet Orchard Finds – Browsing was easy, items feel well curated and the site loads quickly.
Path to Success – Clean interface, information is straightforward and navigation is smooth.
LL Hub Online – Pages load fast, design is clean, and content is simple to understand.
Wild Shore Marketplace – Layout is intuitive and stylish, the browsing experience is enjoyable.
Soft Lantern Online – The soft visuals create an easy and enjoyable way to browse.
Enable Clarity Now – Content is easy to follow, explanations are clear and helpful.
Saffron Trail Essentials – Easy to navigate, items look genuine and browsing was simple.
Sunharbor Hub – The collective is structured well, making navigation simple for buyers.
Velour Valley Collection – Browsing is relaxed thanks to the soft colors and neat design.
WealthPath – Practical pointers and clean layout make learning effortless.
reader-friendly focus hub – Makes planning smoother by keeping attention on key priorities.
Bond Online – Well-structured pages, fast browsing, and information is straightforward.
Visit Wild Stone Atelier – Browsing is smooth, and the product layout is very straightforward.
Рабочие зеркала площадки на кракен зеркало с круглосуточным доступом для входа без блокировок провайдера
Soft Lantern Finds – The calm presentation makes it easy to enjoy looking around.
recommended action link – Demonstrates that ideas, when focused, lead to real-world outcomes.
Momentum Pathways – Very informative, layout is clean and learning from content is easy.
Wild Thistle Selection – Browsing is easy, the website looks professional, and products are appealing.
Wild Aura Collection – The website is easy to navigate, and discovering items is quick.
Sunmist Retail – The gentle design and simple interface create a soothing environment for browsing.
progresswithpurposefulmotion.click – Well-organized content that guides consistent and effective progress.
flowing energy guide – Shows how consistent energy can drive tasks and goals forward efficiently.
The Longterm Link – Pages load fast, layout is tidy, and reading content is effortless.
Soft Wildflower Goods – Great selection, and the checkout is clean and easy to follow.
Willow Forge Official Store – Easy to explore, items are well presented and the site feels polished.
organized workflow hub – Demonstrates that focus is the key driver of smooth and ongoing progress.
Clear Insights – Useful and readable content, browsing feels smooth and effortless.
Wild Branch Finds – Engaging content and creative layout make the experience enjoyable.
intentionalprogresspath.click – Clean and clear design, inspires deliberate progress every day.
Sunrift Picks – Carefully curated products with pricing that makes sense for the quality offered.
momentum journey – Highlights the importance of pacing and direction to maintain steady growth.
Longview Portal – Smooth interface, fast-loading pages, and content is easy to digest.
Starfall Vendor – The brand’s collection is polished, creative, and carefully assembled.
visit this guidance hub – Highlights that focused direction strengthens productive actions.
Energy Boost – Clear presentation, pages are organized and information is straightforward.
Wild Fern Online – Boutique-style design creates a welcoming and personal shopping experience.
intuitive action page – Inspires purposeful progress and helps simplify next steps.
growth through focus – Reminds readers that intentional focus turns ideas into practical achievements.
Sunspire Boutique – Beautifully arranged products give the store a curated, elegant feel.
straightforward guidance site – Practical insights highlight the importance of staying guided for ongoing growth.
Momentum Over Noise – Enjoyed exploring here, information feels actionable and presented clearly online today.
intuitive planning page – Content inspires a smooth flow of ideas and practical next steps.
traction guide – Shows methods for maintaining steady progress through clear focus.
Wild Grain Marketplace – Engaging content and interactive layout make browsing stimulating and fun.
Sunweave Curated – The boutique feels tidy, and products are easy to explore.
idea refinement page – Encourages careful thought before implementing new concepts.
check this resource – Helps prioritize actions and maintain momentum efficiently.
signal based growth – Demonstrates how awareness of signals improves decision making.
action first mindset – Nicely organized and motivating without being too much.
organized path site – Shows that understanding momentum fundamentals keeps projects moving forward.
recommended focus link – Message is practical and reinforces prioritizing clarity first.
growth alignment tips – Encourages structuring efforts around clear goals to enhance outcomes.
mask safety updates – Friendly tone with structured content, encourages participation easily.
buildmomentumwisely.click – Useful advice, emphasizes planning thoughtfully to gain steady momentum.
Whollywood Scare Fest – Exciting theme, navigating ticket and event info is smooth and intuitive.
Pure Value HQ – Clear structure and engaging content, exploring products is simple and inspiring.
growth clarity click – Feels inspiring without being overwhelming.
Let Them Play Organization – Easy-to-read layout, resources are accessible and straightforward.
creative progress hub – Makes moving from ideas to action feel natural and stress-free.
progress focus hub – Reinforces the idea that steady results come from staying focused.
Berserker Zone – Engaging and fast-paced, users can find info quickly and easily.
Vote Regina – Informative layout, ideas are easy to understand and navigate.
Visit Pepplish – Colorful layout, content is clear and keeps readers engaged easily.
organized productivity resource – Emphasizes that focus and attention enhance efficiency and results.
Learn About Judi – Organized and engaging, pages make understanding the campaign easy.
HEC Ideas – Engaging and easy-to-follow content, with a structure that feels logical.
structured planning page – Advice promotes clarity first to make progress more effective.
effective workflow resource – Shows that steady activity drives momentum and builds measurable outcomes.
Death Ray Gallery – Dynamic and creative, navigation feels natural and information is clear.
Exodus Alliance Hub – Well-organized and friendly, resources are easy to read and understand.
T-Walls Chronicles – Captivating content, site design makes historical exploration smooth.
forward thinking click – Great ideas, clearly shared and easy to follow.
efficient action hub – Shows that proper focus improves results without wasted energy.
Sparxcle Works – Organized and visually appealing, reading info is easy and enjoyable.
Festival Hub Online – Fun and structured, site makes checking schedules simple.
insightful progress page – Demonstrates practical methods for keeping projects moving with clarity.
momentum insights page – Encourages using intelligent steps to ensure steady and effective forward movement.
Vote Ros – User-friendly pages, campaign messages are direct and easy to access.
Quint Tatro Portfolio – Professional showcase, work examples are well-organized and easy to explore.
etiquette guidebook – Smooth reading experience, tips are practical and understandable.
polished workflow hub – Motivational reminder: focus shapes strong and predictable results.
Daily Nutrition Tips – Informative and approachable, site encourages healthy habits in a clear way.
idea execution guide – Easy to follow with ideas that push you forward.
Visit Simons Cider – Attractive design, finding cider details is simple and enjoyable.
action clarity guide – Content is approachable and encourages purposeful action.
Discover Gin – Smooth navigation, product details are detailed yet digestible.
action-focused platform – Highlights that decisive choices help unlock new opportunities.
Explore MDC Jealous – Informative and clear, navigation is smooth and intuitive.
Halloween Party Hub – Well-presented content, site navigation is smooth and easy.
Kim 4 Everyone – Smooth navigation and clear content, making it easy to understand the campaign’s ideas.
forward-thinking direction platform – Inspires mindful action and emphasizes intentional movement forward.
DIY Reuse Projects – Engaging content, navigation is straightforward and enjoyable.
Malton Horse Racing – Clear and engaging, navigating the event information is hassle-free.
progress through action – Everything feels logically connected and easy to follow.
Guitar Collectors Corner – Organized and appealing, site makes finding items effortless.
Shop Maggie Online – Clear sections and readable product details, shopping is enjoyable.
TAHWLA Activities – Informative content, pages are organized for quick and easy access.
Support Missing Kids – Straightforward layout, donation options are simple and clear.
Продажа тяговых ab-resurs.ru аккумуляторных батарей для вилочных погрузчиков и штабелеров. Надёжные решения для стабильной работы складской техники: большой выбор АКБ, профессиональный подбор по параметрам, консультации специалистов, гарантия и оперативная поставка для складов и производств по всей России
creative works by alix – Inviting and clear, navigation is simple and material is easy to follow.
Asterix Movie Info Hub – Clear and playful layout, visitors can quickly access all film info.
Janet 2026 – Smooth layout and helpful info, exploring policies is easy and quick.
mindful progress hub – Clean layout and content helps guide decisions smoothly.
Knockout Zone – Energetic and fun presentation, with content that’s easy to follow.
TAHWLA Resources – Helpful site layout, information is presented clearly for users.
Islington Design Network – Clean interface and easy navigation, making business and event info enjoyable to explore.
colossal reflections – Layout feels calm and organized, information is clear and inviting.
helpful motivation site – Creative framing encourages users to act consistently.
Updating Parents Online – Clean and clear, guidance is easy to navigate and digest.
Holiday Ride Experience – Cheerful design, ride info is clear and presented well.
TM Creative Zone – Interactive and fun, resources are simple to access and understand.
Legacy Farm Info – Clear and approachable, content presents farm practices smoothly.
Mark Mackenzie Info Center – Informative and direct, site communicates messages effectively.
hellgate100 event guide – Great coverage and clear layout, makes exploring event info effortless.
Festival Lark – Colorful and engaging, navigation is intuitive and enjoyable.
< Kionna West Online – Personal site is accessible, navigation flows naturally.
Newlyweds Tour Events – Well-organized site, schedules and logistics are easy to find.
FH Resources – Clean design, information is laid out clearly and professionally.
FilAmericans Justice Alliance – Well-laid-out and motivating, site encourages engagement effectively.
tadros campaign portal – Clean design, presenting key initiatives in a way that’s simple to grasp.
formative brewing tips – Well-presented content, helps readers understand coffee quickly and clearly.
Whollywood Spooky Fest – Exciting and festive, ride and attraction info is easy to find.
daybirdsyr info hub – Clear design, with updates presented in an organized and engaging way.
Philadelphia market hub – Friendly interface, shopping here was simple and enjoyable.
PHL 1911 Archive – Well-organized pages, exploring historical events is simple and clear.
bennington area art info hub – Engaging and easy to browse, gives a wonderful overview of local arts.
insightful clarity hub – Encourages stepping back and reviewing ideas carefully before moving ahead.
Lux Noe Store – Attractive site, details about products are displayed cleanly and clearly.
idea progress guide – Easy to read and full of ideas that inspire action.
BLP Event Insights – Clear structure, content is engaging and well organized for visitors.
Shute Racing Coverage – Professional presentation, site makes exploring schedules and results simple.
nsfeg network – Clean design with updated material that helps visitors find what they need.
Pinellas Learning Hub – Easy-to-read content, site presents information in a logical and user-friendly way.
garymasino network – Neat design, pages load well and information is presented clearly.
hicks campaign portal – User-friendly interface, presenting key information without confusion.
Natasha Campaign Hub – Approachable and clean, visitors can navigate effortlessly.
washpost george will – Well-structured content, layout feels clean and professional.
Team Montes – Smooth and professional site, navigation feels effortless and info is easy to digest.
FrontRoomCorner – Stylish pages and easy-to-use layout provide a friendly online feel.
Sleep Cinema Suites – Innovative concept, navigation is intuitive and booking a stay is straightforward.
wexfordliteraryartsfestival.com – Beautiful festival site, content is engaging and easy to explore naturally.
Democracy Roadshow Info – Navigation feels intuitive, content is engaging and clear.
electcateriarmccabe info – Smooth navigation, users can grasp main campaign points without confusion.
FocusWay – Easy-to-read content combined with smooth navigation for a productive experience.
play-brary corner – Lighthearted and inviting, kept me smiling while browsing around.
GrowthBlueprint – Practical guidance with smooth navigation and easily digestible content.
southbyfreenoms updates hub – Bright and engaging, the event looks exciting and enjoyable.
Support Karen – Clear layout and simple navigation make learning about her platform effortless.
electa murphy campaign info – Well-laid-out pages, content feels reliable and transparent.
Tobias Park Highlights – Inviting and clear, website shows off activities effectively.
di bruno liquor selection – Smooth experience, site is clear and online shopping works well.
polished forward hub – Clean visuals and optimistic energy perfectly complement momentum-focused goals.
PhillyDelights – Easy browsing with a user-friendly design for quick discovery.
StepwiseGrowth – Easy-to-read pages with ideas that feel actionable.
krasner concerns site – Direct and simple, giving visitors a clear overview of the position.
Planning Hub – Content flows naturally and navigation is user-friendly.
clarity guided path – Simple structure and tone make this feel approachable.
Idea Matrix – Organized approach makes exploring topics straightforward.
GrowthJourney – Well-arranged content and smooth navigation create a comfortable reading experience.
Growth Compass – Clean structure allows users to grasp concepts efficiently.
Momentum Path – Straightforward layout and actionable content support productive learning.
nyc bhm info hub – Clear and structured, helps visitors find accurate information efficiently.
Remi PHL Updates – Well designed, details are accessible and simple to comprehend.
democracywatch.org – Well structured, content explains challenges to democracy in a clear, concise way.
romain4reform official site – Easy to explore, campaign goals and key info are clearly displayed.
CallSportsHub – Clear navigation and engaging content keep readers informed quickly.
Idea Nexus – Layout and structure make exploring concepts intuitive and straightforward.
StartSmartFuture – Practical content presented in a friendly and accessible format.
kids aid program – A meaningful project, showing real community support for children.
VelocityPath – Concise and clear, the site delivers focused ideas that inspire action.
ProgressPathway – Clear structure and step-by-step guidance make learning accessible.
clarity centered space – The layout helps everything feel balanced and readable.
Idea Hub – Clean layout with easy-to-follow content makes exploring concepts simple and effective.
Forward Hub – Clear structure and intuitive design make implementing ideas straightforward.
team hagins – Professional presentation, information is accessible and well explained.
mcc theater updates – Friendly and clear, the campaign seems impactful and well-organized.
NuPurple Service Prices – Professional look, navigation is smooth and cost info is transparent.
Growth Hub – Structured layout allows readers to quickly grasp and use the ideas.
insightful clarity hub – Well-laid-out points that encourage daily focus and application.
LearnProgress – Clear explanations paired with smooth navigation make ideas easy to grasp.
ct political portal – Engaging and clear, with content that encourages learning and new insights.
PowerUpPrograms – Well-organized site ensures community services are easy to locate.
Action First – Prioritizes doing over planning endlessly.
MomentumPath – Engaging pages with information delivered in a concise way.
Action Hub – Organized design makes it easy to follow instructions and stay productive.
nerd online marketplace – Pleasant design, site loads quickly and products are easy to view.
Guided Vision Hub – Logical pages and practical advice ensure visitors can act on ideas quickly.
motion driven ideas – Enjoyed reading, everything connects and flows nicely.
astoria together news portal – Approachable and organized, offering fast access to local updates.
Ulay Jasa Services – Efficient design, pages are easy to navigate and content is concise.
Insight Flow – Organized layout ensures concepts are simple to follow.
VisionBlueprint – Polished design highlights inspiring concepts clearly.
life transition resources – The site is well-structured and shares valuable insights for those in transition.
Clarity Path – Navigation feels natural and ideas are easy to take in.
InnovationPath – Modern layout and direct content encourage immediate execution.
energynear info portal – Simple navigation, energy solutions are presented clearly for all users.
ProgressFocus – Simple design with actionable ideas that are easy to navigate.
intentional progress – Thoughtful insights shared here, it reads smoothly from start to finish.
Growth Path – Clean design ensures information is accessible and actionable.
Focus Flow – Clear guidance and neat structure encourage users to take real steps.
action fuels flow – Nicely communicates how taking steps leads to momentum.
Saddle Up Philly – Inviting site, content is accessible and program descriptions are straightforward.
Strategic Flow – Content is logically structured for smooth navigation.
Remi Official Site – User-friendly layout, site communicates details without confusion.
wellnesstourbus online – Clean layout and encouraging content, easy to navigate and read.
PrecisionAction – Well-structured pages make understanding information fast and simple.
mayor candidate info – Authentic feel with messaging that is easy to read and follow.
InsightFlow – Clean design and careful organization make navigation intuitive.
FocusInsight – Easy navigation and straightforward advice make the site highly usable.
MomentumDesign – Well-structured pages allow quick understanding of key points.
Focus Hub – Practical content presented in a clean layout ensures smooth user experience.
Progress Hub – Logical structure with actionable steps ensures visitors can implement insights effectively.
latanya collins online – Informative and approachable, users can quickly find what they need.
Growth Compass – Clear structure guides users through ideas efficiently.
power progress with energy – Short and motivating, making forward movement feel achievable.
GAP Project Overview – Well organized, site presents the initiative in a clean and accessible way.
traction for progress – Clear and motivating, highlights how traction creates steady forward movement.
press bros updates – Informative layout, site is easy to navigate and product descriptions are solid.
IdeaPathways – Well-presented content with smooth and intuitive browsing.
tadros updates hub – Easy-to-follow layout, showing focus areas and values in a clear manner.
PowerGuide – Thoughtful organization ensures readers can access insights with ease.
unlocking potential – Encouraging message, tapping into growth unlocks latent potential effectively.
ideas unleashed – Practical point, letting ideas loose generates momentum quickly and smoothly.
FocusNavigator – Simple design that keeps information understandable and motivating.
Execution Path – Direct explanations and organized pages help users apply ideas effectively.
Action Driven Success Tips – Engaging structure, content is useful and the pages load quickly.
growthstream – Interesting idea, growth moves forward naturally when efforts are continuous and coordinated.
solutionclickhub – Nice resource, one click and you’re guided toward effective solutions today.
Action Flow – Structured content and simple navigation make learning straightforward.
Action Hub – Well-laid-out information helps visitors understand and apply concepts.
guided flow – Friendly and practical, guidance here helps actions move forward without hesitation.
Pet Lovers Boutique – Attractive design, content is clear and makes shopping fun.
move with intention – Subtle encouragement for deliberate, meaningful action.
build clarity – Insightful idea, clarity helps create momentum that drives tasks forward.
FocusedGrowth – Smooth navigation supports practical and motivating content.
team alignment – Strong phrasing, direction creates alignment that benefits both individuals and teams.
Clarity Flow – Organized pages make information easy to understand and practical.
smartgrowthhub – Insightful concept, growth is planned and structured with care for steady results.
Idea Flow – Intuitive layout with practical guidance makes navigation effortless for users.
SelectEase – Streamlines your search to find top choices quickly.
PathFinder – Simple and inviting interface makes exploring concepts enjoyable.
Clarity Nexus – Simple, well-organized layout ensures concepts are actionable.
AdvanceLearnHub – Makes learning new skills fast, simple, and actionable.
power flow direction – Friendly and concise, guiding energy ensures each task gets the momentum it needs.
W4 Candidate Portal – Informative pages, website is simple to navigate and content is concise.
guide growth with clarity – Clear and focused, provides an easy path for thoughtful progress.
GrowthJourney – Nicely structured information that’s quick to understand.
ResultsNavigator – Clean interface and focused advice make understanding steps simple.
purpose directs progress – Clear, motivating phrasing showing how meaningful direction creates forward motion.
uncommittednj site – Organized and concise, makes information clear and easy to understand.
clarity boost – Insightful phrasing, a boost in clarity creates leverage that moves projects forward.
PathToSuccess – Clear navigation paired with actionable insights for everyday use.
Vision Hub – Professional look and logical flow make complex ideas easier to follow.
direction powers motion – Clear point, applying direction thoughtfully powers motion and keeps things moving forward.
Momentum Flow – Clear layout and structured content allow readers to take actionable steps quickly.
EasyBuyHub – Navigate and purchase items intuitively without confusion.
growthframework – Strong phrasing, using design as a framework helps growth move forward smoothly.
forward catalyst – Simple but strong, consistent effort keeps momentum building smoothly.
Strategy Compass – Clear layout helps visitors grasp key concepts quickly.
a href=”https://createimpactplanningframework.click/” />PlanFlow – User-friendly layout ensures projects are easy to outline and follow.
action builds momentum – Short, energetic wording emphasizing steady progress.
ConceptFinder – Encouraging layout that helps users generate new ideas easily.
GoalAchiever – Focused content with actionable tips encourages visitors to take the next step.
progress amplified – Practical, concise wording showing how energy aligns with direction to achieve results.
momentum clarity – Insightful point, clear direction guides velocity efficiently across tasks.
Clarity Path – Well-laid-out structure makes understanding seamless.
progress defined – Strong concept, clear focus defines the direction and momentum of progress.
vital energy flow – Friendly and practical, performing tasks channels energy that enhances progress naturally.
Clarity Flow – Well-laid-out pages and straightforward guidance make learning seamless.
Idea Compass – Logical flow supports quick comprehension and practical use.
ShopNow – Access all your daily essentials with minimal effort.
quickflowaction – Helpful concept, minimizing thought allows movement to feel effortless and fast.
DreamRidgeBoutique – Fun and colorful online shop where browsing is a pleasure.
focus drives action – Short and effective, links attention directly to results.
signal driven steps – Took a look and everything made sense right away.
dynamic thinking – Motivating concept, ideas unlocked spark momentum and drive action efficiently.
ActionPlanner – Well-laid-out site with sharp, engaging content and practical tips.
SkillPath – Guides users to learn effectively and make quick improvements.
forward motion unleashed – Clear and dynamic, emphasizing how energy release propels progress.
Idea Hub – Interactive layout encourages visitors to experiment and understand concepts.
organized advancement – Strong concept, structured methods make advancement more orderly and clean.
flowing energy – Smooth phrasing, energy directed purposefully makes tasks feel manageable.
Progress Path – Well-structured site and clear messaging make applying ideas fast and easy.
NextStepShop – Helps plan purchases ahead and stay organized in daily shopping.
>grabadealcenter – Friendly site, deals are straightforward to find and check out efficiently.
structured insight – Short and effective, showing how structure enhances understanding of concepts.
clarity alignment – Helpful message, alignment through clarity ensures progress is steady and predictable.
clarity leads the way – Concise and encouraging, showing that understanding simplifies advancement.
execution navigator – Clear concept, staying focused helps guide tasks smoothly and efficiently.
organized action – Clear phrasing, action organizes thoughts and improves decision-making flow.
SafeSelect – Quickly find what you need and shop confidently every time.
discoverunexpectedpaths – Smart concept, discovering unexpected paths opens up fresh possibilities for products.
strategic ideas – Smart concept, strategic ideas drive forward outcomes and inspire consistent effort.
focus shapes forward motion – Smooth and encouraging, highlighting intentional effort.
decisive clarity – Concise phrasing, clarity empowers quick and intentional choices.
clarity guides way – Simple idea, clarity helps chart a path forward with confidence.
strategic steps forward – Friendly phrasing that makes systematic advancement feel achievable.
modernretailhub – Practical design, shopping feels enjoyable and stress-free every visit.
TrustedCart – Makes online shopping secure and worry-free every time.
clean growth path – Thoughtful concept, progress flows smoothly when strategy is well structured.
intent-focused flow – Concise and clear, deliberate handling of ideas drives meaningful results.
intentional growth path – Calm, practical phrasing that makes steady advancement feel achievable.
clarity momentum boost – Insightful phrasing, clarity boosts energy and keeps forward motion strong.
signal the way – Short, encouraging phrasing, showing how cues provide natural guidance.
action drives speed – Clear and practical phrasing, showing how velocity emerges from intentional steps.
QuickBasket – Fast and easy shopping for your routine essentials.
discoverproductpaths – Helpful note, discover paths that lead to better product choices daily.
forward energy – Motivating insight, each step of progress generates forward energy that sustains momentum.
progress through ideas – Smooth, practical phrasing connecting inspiration with forward movement.
direction organizes motion – Strong concept, organized direction clarifies motion and enhances productivity.
guided creative flow – Friendly, natural language emphasizing how deliberate planning keeps ideas moving.
QuickSelect – Makes choosing and buying items quick, easy, and stress-free.
shopquicklyonline – Efficient idea, allows users to complete purchases smoothly and without delays.
BargainCart – Makes every purchase simple, convenient, and trustworthy.
purposeful motion counts – Highlights deliberate movement while keeping the wording simple.
motion engine – Thoughtful phrasing, focus functions as an engine that energizes continuous movement.
goal driven clarity – Nicely organized, makes you want to dive deeper into the content.
build momentum – Smooth and practical, showing that structured action produces steady results.
dailydealshop – Great selection, flexible choices help shoppers complete their orders quickly.
buildfuturepath – Creative idea, each decision today shapes a clearer path for long-term success.
Quick Buy Online – Straightforward interface makes finding items simple and stress-free
Online Deals Hub – Clean, modern design allows fast access to products
powerful traction – Smooth, natural language emphasizing how energy focused correctly maintains forward movement.
Safe Purchase Hub – Quick, secure, and easy-to-navigate shopping experience
Metro Market Hub – Organized interface, exploring categories feels smooth and easy
Quick Option Finder – User-friendly pages, makes decision-making smooth and fast
Simple Finds Online – Fast browsing with a neat and simple interface
Innovation Click Center – Promotes creative exploration in a straightforward and accessible way
guidance drives energy – Clear, motivating phrasing showing how structured direction improves outcomes.
City Cart – Simple pages, navigating products is efficient and stress-free
EasyShop Central – User-friendly layout ensures browsing is effortless and efficient
visit capital anchor – Everything looks trustworthy and leaves a solid first impression.
Simple Online Store – Easy-to-navigate platform for hassle-free shopping
Deal Finder Online – Smooth navigation, makes comparing discounts straightforward and clear
Complete Buy Hub – Convenient sections help quickly find the right items
Metro Market Hub – Organized interface, exploring categories feels smooth and easy
Modern Shop Hub – Clean design, makes finding products quick and hassle-free for visitors
direction fuels motion – Concise and encouraging, linking guidance to visible forward action.
World Buy Click – Wide assortment of international products, easy to browse
Simple Shop Click – Easy-to-use pages, shopping and exploring items is fast and clear
ClickFactor Online Hub – Professional design, content is easy to read and users stay interested
Clear Buy Hub – Minimalist design ensures fast, focused browsing
Quick Click Website – The content flows nicely and the layout is easy to follow
BondStable Explorer – Navigation flows naturally across the site
Bond Ward Hub – Sleek and professional, content is easy to navigate without confusion
Metro Market Hub – Organized interface, exploring categories feels smooth and easy
bondedhorizon.bond – The details are presented clearly, making the topic simple to follow.
Global Shopping Spot – Smooth navigation allows quick access to international items
Everyday Shop Online – Intuitive pages, makes exploring daily products simple
Click Buy Hub – Straightforward design makes browsing and comparing products fast
TopPick Store – Clear navigation, products are easy to locate and prices are transparent
Reliable AxisBond Hub – Clean pages, navigation is seamless and information feels dependable
BondNoble Hub – Organized pages, making information accessible and reliable for visitors
BondVertex Zone – Professional structure ensures content is easy to read and navigate
Urban Choice Market – Organized pages, shopping online is quick and stress-free for users today
Action Guide Online – Clean design that makes planning goals intuitive
Metropolitan Shopping Hub – Items are clearly presented and the site feels fresh and organized
Value Buying Hub – Well-organized listings help users locate deals quickly and easily
Centra Bond Online – Simple interface, navigating the site feels natural and smooth
ScaleUp Ideas Hub – Motivates action and creative thinking for pursuing new opportunities
Easy Click Mart – Adaptive design helps navigate products quickly without stress
SafeDeals Online – Professional interface, makes browsing items and buying simple and reliable
Simple Buy Hub – Clean design makes it easy to locate products fast and efficiently
growth clarity tips – Short site, well-structured, easy to absorb.
Skill Growth Portal – Clean layout, tutorials and tips are easy to follow for all learners
Fresh Discount Central – Clear interface helps users find daily savings effortlessly
Outlet FastBuy – Smooth navigation and rapid loading improve the overall experience
Urban Marketplace – User-friendly interface, searching for items is fast and convenient
Capital BondTrustix – Smooth navigation, users can access key content quickly and confidently
learn about unity bonded – The information reads clearly and feels authentic.
Growth Hub – Inspires exploring new ideas and personal development in a simple way
BondAllied Guide – Clean presentation keeps browsing smooth and reliable
Discover & Grow – Professional design, encourages exploring personal growth paths and options efficiently
ValueBuy Online – Clear layout and useful listings improve shopping efficiency
Growth with Purpose – Offers gentle direction without overwhelming visitors
Fast Shopping Market – Smooth browsing, ideal for quick product finds
BondFirm Experts – Organized pages and reliable content provide a smooth experience
Corporate Alliance Center – Easy-to-follow interface, helps visitors understand strategic relationships clearly
Prime Bond Hub – Sleek layout ensures content is accessible and easy to digest
Global Marketplace Online – Informative layout, helps users explore international deals efficiently
Effortless Shopping – Products are easy to locate thanks to the simple layout
Urban Choice Market – Organized pages, shopping online is quick and stress-free for users today
Modern Buying Hub – Clean pages, exploring items and deals online is simple and hassle-free
Daily Digital Deals – Easy to use interface, finding daily products is fast and hassle-free
Wise Buy Online – Product suggestions make shopping efficient and user-friendly
Collaboration Pro Network – Clean design, makes professional connections and teamwork simple and effective
Capital Vision Online – User-friendly layout, financial products and strategies are easy to understand and explore
Quick Shop Central – Easy navigation and clear product info support informed decisions
BondStrength Access – Easy-to-read pages paired with smooth movement between sections
ClickSource Explorer Hub – Inspires creativity and hands-on learning through interactive pages
Direction Finder Hub – Clear guidance helps users discover new paths and opportunities online
Digital Shop Solutions – Organized pages, helps visitors discover solutions and products effortlessly
ValueBuy Online – Clear layout and useful listings improve shopping efficiency
learn about unity – The browsing experience is comfortable with fast loading and simple visuals.
ProgressFinder – Guides toward directions that foster continuous improvement and success.
City Bargain Spot – Well-laid-out site, makes checking products fast and effortless
Simple Shopping Spot – Navigation feels effortless and items are easy to find
Smart Selection Hub – Intuitive layout makes finding products quick and easy
Fast Compare Website – Designed to help compare options without wasting time
TrendSpot Shop – Sleek pages help visitors browse products with ease
Bond Info Center – Well-laid-out site, exploring content is straightforward and smooth
Strategic Partnership Portal – Modern interface, provides insights on nurturing professional relationships over time
Secure Purchase Hub – Well-structured site, buying items online is quick and worry-free
Motivation Today – Well-organized pages make learning about progress simple and enjoyable
Quick Purchase Portal – Clean structure makes finding items quick and shopping effortless
BondCoreX Info – Trusted information with a clean design makes browsing effortless
BondKeystone Network – Clear structure, helps users find relevant information without confusion
Creative Thinking Portal – User-friendly layout, makes discovering better solutions simple and engaging
BondTrusty Capital Online – Organized design, users can review investment information smoothly
Skill Center – Informative layout supports discovering and mastering new concepts
City Bargain Spot – Well-laid-out site, makes checking products fast and effortless
DealFinder Online – Organized deals and clean interface support fast, efficient shopping
Forward Thinking Portal – Smooth navigation, site makes understanding future possibilities simple and clear
Easy Shopping Spot – Minimalist layout allows quick browsing without confusion
Reliable Shop Online – Simple layout ensures users feel confident completing purchases
Answer Click Hub – Simple site design and easy-to-digest solutions
Urban Style Hub – Sleek design makes exploring fashion items effortless and fun
Smart Tactics Online – Concise tips, guides users toward more effective decisions
capitalbondhub.bond – It feels like a well-built platform with a layout that works.
Exclusive Buy Hub – Minimalist design with a smooth shopping experience
Business Bonding Center – Informative pages, browsing information about partnerships feels effortless
Shop Everything Online – Clean interface, shopping feels seamless and convenient for daily needs
Zenith Bargain Spot – Smooth browsing and straightforward product listings
City Shopping Spot – Clean structure, makes online browsing simple and enjoyable
BondTrue Info Online – Clean and organized, finding what you need is effortless
Growth Strategy Portal – Intuitive layout, explains business collaboration ideas clearly and professionally
Growth Mindset Space – Encouraging design that highlights small steps forward
BondLegacy Resource – Logical page flow helps users find details without effort
Simple Picks Online – Clean and organized pages make browsing smooth and quick
Trusted Nex Portal – User-friendly layout, makes learning about topics straightforward
ValuePick Store – Helpful listings guide users to the best deals efficiently
Sustainable Business Hub – Engaging pages, content encourages exploring eco-conscious strategies easily
Growth Insight Online – Engaging content makes discovering new concepts straightforward
Trust Strategy Hub – Clear interface, content is credible and browsing resources is effortless overall
HappyFinds Hub – Playful interface makes discovering products a smooth experience
Choice Advisor – Informative guidance, supports visitors in making confident and effective decisions
Reliable Global Connections – Clean interface supports browsing and understanding collaborations efficiently
EasyShopZone – Makes browsing and buying online simple, fast, and convenient.
Smart Purchase Center – Intuitive pages provide tips and solutions for routine shopping decisions
Business Networking Hub – Informative layout, makes understanding collaborations and building connections simple
International Shopping Guide – A helpful range of products shown in one place
Everyday Market Hub – Clear structure, supports hassle-free browsing of everyday items
ClickIgnite Hub Online – Easy to explore content that keeps the experience lively and engaging
Goal Tracker Hub – Encourages visitors to organize priorities and take focused actions quickly
useful pathway resource – The first visit shows it’s well-structured and reliable.
BondCrest Focus – Clear design, visitors can explore content without difficulty or delay
ClickField Link – Organized design keeps content approachable and intuitive for all visitors
Compare & Choose Portal – Simple structure makes evaluating products straightforward and quick
Reliable Market Click – Easy navigation, users can quickly browse items and find what they need
Knowledge Finder Online – Clear presentation makes learning quick and enjoyable
Pathway to Growth – Easy-to-use pages, site inspires actionable progress and development
QuickDeals Hub – Clean layout allows visitors to shop quickly and efficiently
Online Tech Hub – Easy layout, navigation feels natural and browsing is smooth
Top Picks Online – User-friendly interface with clear product options
Smart Shopping Network – Intuitive interface, browsing products and checking features is fast and easy
Strategic Business Center – Organized pages, provides clear guidance on effective business decisions
Premium Buy Hub – Modern design with a high-end touch, shopping feels refined
Creative Marketplace Online – Fun, approachable style makes exploring items smooth
Trusted Marketplace Online – Navigation is simple and finding deals feels reliable and easy
Deal Finder Hub – Well-organized listings, users can quickly access promotions and offers
Explore Better Paths – Engaging site, provides strategies and insight for growth opportunities
ClickPoint Space – Clear organization that makes online navigation simple
Smart Value Store – Easy-to-navigate interface makes online shopping efficient
TrendEase Shop – Simple layout ensures browsing items is stress-free and fun
Digital Planning Hub – Professional and organized, site helps users understand digital strategies naturally
ValueCart Store – Smooth interface ensures visitors can browse deals quickly
ForwardFocus – Practical layout, content inspires action and measurable progress online
clear growth outline – Compact delivery that still makes sense.
Next Horizon – Fun and informative site promotes exploring potential opportunities
Bondline Knowledge – User-friendly design, browsing topics is easy and enjoyable
Business Growth Alliance Hub – Smooth interface, makes exploring partnerships and corporate opportunities simple for users
ClickSwitch Zone – Browsing feels smooth and distraction-free across pages
FutureSteps – Guides you in making deliberate progress toward your goals.
Global Offers Hub – Browsing international products is simple, and comparisons are clear
Trusted Buys Online – Organized design, browsing products is straightforward and pleasant
Smart Strategy Guide – The content is reflective and gives actionable points to consider
Bond Learning Portal – Smooth interface allows users to review commercial bonds effectively
Value Buying Hub – Well-organized listings help users locate deals quickly and easily
Corporate Growth Portal – User-friendly layout, exploring business alliances feels effortless and clear
ClickSource WorldWide – Clear structure inspires innovative thinking and practical learning
Fashion Trend Hub – Stylish selections and smooth navigation make browsing effortless and fun
Smart Shopper Portal – Clean layout, browsing items feels intuitive and discovering promotions is simple
Innovate Online – Clean design helps users browse and find new concepts easily
Advance Your Learning – Practical design, supports skill enhancement and learning progress smoothly
AlignSmart Click – Well-structured pages, accessing key ideas and information is easy
BondPrimex Focus – Easy-to-read layout supports quick understanding
Professional Growth Collaboration – Clear and structured pages, visitors can easily understand teamwork opportunities
Focused Learning Hub – Organized content guides visitors to grasp important information and act efficiently
Crafty Online Store – Bright design with a clear, easy way to discover products
DealSmart Store – Well-structured pages make navigating offers smooth and intuitive
SaveMore Shop – Clear structure allows shoppers to browse and compare deals smoothly
TrendFresh Portal – Fresh design and organized categories make shopping a breeze
Business Directions Hub – Insightful resources guide users to explore business ideas efficiently
Secure Offers Portal – Smooth navigation and confidence-inspiring design
International Collaboration Hub – Clean design, exploring global business relationships is simple and clear
Strategic Thinking Hub – Inspiring content, guides users to plan ahead and make smart decisions easily
ClickSparkle Pro – Fun layout, content is simple to explore and enjoyable overall
Professional Edge Hub – Engaging interface, helps visitors focus on learning new skills and achieving career goals
Professional Insights Network – Clear structure, exploring topics and ideas is stress-free and fast
ValueBuy Online – Clear layout and useful listings improve shopping efficiency
Swift Buy Hub – Streamlined pages make online shopping straightforward and simple
TrendFinder Online – Smooth navigation and stylish design make finding trends easy
Planning Smarter Today – Clear presentation, content guides users through effective strategies and choices
Innovative Paths Online – Organized sections and inspiring content guide users through new opportunities
Concept Navigator – Fun and interactive, helps visitors learn and explore innovative thoughts
Curiosity Expansion Hub – Clear layout, makes learning new topics fun and easy for visitors
Growth Solutions Hub – Professional design, users can learn about partnerships and growth strategies without confusion
Dependable Online Store – Well-organized design, exploring items is simple and safe for users
BondedNetwork – Smooth pages and useful advice, understanding resources is easy and efficient.
Business Alliance Center – Clean and structured, managing partnerships and professional relationships is easy
Progress Path Portal – Inspiring layout, encourages visitors to move forward and make actionable plans
Networking Resource Center – Sleek interface, discovering professional relationships and ideas is straightforward and fast
thought click hub – Motivates examining ideas in new ways, website is simple to navigate.
Worldwide Market Network – Well-organized pages, finding products and global offers is straightforward for users
click for actionable tips – Provides straightforward guidance that’s ready to apply.
strategic connections platform – Clear, professional layout helps users understand corporate alliance approaches effectively.
insightful action center – Ideas are easy to implement and relevant to everyday decisions.
verified business network – The layout is straightforward and finding information feels effortless.
reliable business hub – Feels credible, easy to find important links and helpful resources.
click for market knowledge – Platform offers easy-to-digest insights for navigating current business trends.
business growth insights – Posts are informative, helping track industry developments clearly.
explore new horizons – Content is structured well, inspires curiosity and positive forward thinking.
smart insights hub – Great advice, helps me make sense of complicated strategies.
understanding business ideas – Clear and practical, simplifies difficult concepts.
growth opportunity guide – Well-structured content, visitors can plan ahead without confusion.
ReliableTradeZone – Online dealings feel safe and trustworthy here.
Learn Digital Skills – Easy navigation, online lessons are accessible and effective for users
practical insights network – Content is straightforward, easy to apply, and immediately useful.
insightful action center – Ideas are easy to implement and relevant to everyday decisions.
industry knowledge click – Insights are clear, keeping readers informed and ready to act on new opportunities.
market intel click – Engaging content, provides practical guidance for staying updated on trends.
business link portal – Focus on building professional relationships is evident and well presented.
stepwise natural growth – Encouraging steps, each action toward goals feels achievable and smooth.
natural advancement tips – Easy-to-follow advice, helps maintain consistent progress without stress.
GrowthGuidePro – Offers clear guidance, making strategies simple to implement.
business alliance insights – Easy-to-follow advice, examples feel very relevant to real markets.
strategic ideas hub – Comes across as thoughtful, the concepts sparked new directions naturally.
trusted business alliances – Practical examples, makes market alliances easy to follow.
smart planning space – Naturally supports brainstorming and forward thinking.
activate your energy – Short, encouraging phrasing linking energy release to practical action.
energy unleashed – Smooth, natural language emphasizing the effect of freed energy on forward movement.
The Daily Market – Simple navigation helps users locate deals effortlessly and efficiently
DigitalFlexStore – Well-organized platform ensures shopping is simple and efficient.
step by step learning – Clear guidance, site inspires consistent progress in a friendly way.
FlexibleShopOnline – Smooth navigation, finding and buying items is quick and hassle-free.
BuyWithConfidence – The process feels secure from start to finish.
OpportunityExplorer – Insightful content, helps identify future opportunities quickly and efficiently.
LongTermOpportunitiesHub – Highly informative, the site makes spotting long-term prospects clear and simple.
securecartcenter – A dependable platform where ordering products online feels safe.
trustedsaleshub – Enjoy a seamless and secure online purchasing process.
Effortless Market – Well-organized pages allow visitors to browse and buy with ease
strategic unity hub – Unity strategies are clear, reading through is smooth and informative.
Value Buying Hub – Well-organized listings help users locate deals quickly and easily
ShopEaseDigital – Browsing is simple, and the design keeps everything easy to access.
build alliances wisely – Advice feels reliable, explanations are easy to follow.
build valuable connections – Great explanations here, guidance feels practical and useful.
fastdigitalsales – Practical and simple, finding and purchasing items online is effortless.
quickshophub – Easy to navigate, online shopping feels fast and stress-free.
strategic growth flows – Clear direction, helps turn ideas into achievable tasks.
networknavigator – Informative and actionable, makes professional networking approachable and reliable.
flowing goal strategies – Very actionable advice, helps maintain focus and reach outcomes successfully.
allianceinsider – Practical and informative, shows structured methods for networking with professionals.
trusted market partnerships – Insightful content, makes alliance concepts relatable and practical.
alliances guide hub – Very useful, real market examples enhance understanding of partnerships.
BusinessGrowthHub – Provides actionable guidance for building effective collaborations.
professional network portal – Well-organized content, network information is easy to digest and practical.
ValueDeals Hub – Well-laid-out pages help users quickly identify the best offers
Alliance Development Center – Well-laid-out pages, guides users through strategic growth insights effectively
clarity moves you ahead – Friendly and natural, highlighting how understanding accelerates results.
clear thinking, steady progress – Practical and approachable phrasing emphasizing ease and consistency in advancement.
CorporateConnectionsHub – Provides dependable info and professional layout makes it simple to use.
ProfessionalTrustNetwork – Reliable corporate content presented with clarity and ease.
alliancenetworkhub – Insightful and actionable, enterprise partnership strategies are structured in a user-friendly way.
growthalliancepath – Insightful and practical, strategies for enterprise alliances are well-organized and easy to follow.
ProfessionalUnityHub – Well-structured content, enterprise frameworks feel simple and practical to follow.
FutureNavigator – Helps you understand upcoming trends in a clear and exciting way.
UnityPathwaysGuide – Clear and professional, enterprise frameworks are easy to explore and apply.
securepurchasehub – Online shopping made simple, trustworthy, and efficient.
thinking clarity portal – Makes evaluating options easy and straightforward.
onlineshopnavigator – Offers a safe, smooth, and reliable way to shop online.
Smart Value Store – Easy-to-navigate interface makes online shopping efficient
SmartIdeasExplorer – Engaging platform, new innovations are explained in a simple way.
Path to Success – Clear guidance and actionable steps make planning future moves easy
continuous learning tips – Feels motivating, with content that’s easy to absorb at your own pace.
CreativeIdeasHub – Easy-to-follow explanations, learning about innovations feels enjoyable.
grow your knowledge – The content encourages curiosity and steady personal development.
trusted professional network – Useful guidance, networking is clear and approachable.
click for professional guidance – Lessons are practical, building professional trust feels doable.
growthplanningguide – Provides step-by-step tips for implementing growth strategies effectively.
growthtipsguide – Makes growth strategies simple to understand and implement successfully.
BusinessConnectPlus – Makes professional networking feel smooth and trustworthy.
bizinsights – Very practical, ideas for market improvement are explained in a straightforward way.
marketpath – Insightful and user-friendly, guides readers through applying market strategies.
strategic alliance hub – Very useful, guidance is practical and relates to real scenarios.
strategic growth hub – Collaboration emphasized, ideas are structured and digestible.
business alliance insights – Easy-to-follow advice, examples feel very relevant to real markets.
ValueShop Central – Informative pages and smooth layout help users discover bargains easily
progress clarity hub – Simple and effective, makes complicated topics understandable.
progress clarity guide – Insightful tips, makes understanding difficult ideas much easier.
Deal Spot Online – Easy navigation, discovering discounts is quick and user-friendly
DecisionEaseOnline – Reliable guidance, simplifying the process of choosing wisely.
ChoiceMasteryHub – Helpful strategies, simplifies evaluating options effectively.
step into progress – Short and motivating, showing that small actions compound into results.
ValueDealsCenter – Shopping is smooth and the deals feel rewarding.
plan, act, advance – Concise and motivating, showing that consistent effort drives movement.
grow your knowledge click – Friendly design, makes exploring topics simple and stress-free.
businessalliances – Offers practical steps to strengthen partnerships and create enterprise value.
partnershipnavigator – Practical strategies for evaluating and sustaining strategic alliances.
QuickPick Deals – Listings are clearly displayed, making it simple to find bargains
Deal Finder Worldwide – Intuitive navigation helps users explore deals from all over quickly
SmartBuyHub – Clear product details help me choose items with confidence.
trusted networking portal – Very clear instructions, building professional connections feels natural.
click for enterprise links – Platform works well, connecting professionally feels straightforward.
futurefocusedskillshub – Excellent platform, skill-building content is clear, practical, and easy to apply.
developfutureskills – Practical insights, skill-building content is well-structured and actionable.
QuickDigitalCart – Smooth platform, buying products online is practical and simple.
shoppingnavigator – Practical and clear, finding and ordering products online is simple.
DigitalShopGuide – Well-organized layout, shopping online feels natural and easy.
easybuyportal – User-focused and straightforward, online purchases are fast and simple.
reliable business connections – Useful explanations, site gives practical advice on sustaining partnerships.
alliances insight platform – Useful tips, simplifies how alliances operate in different markets.
strategic alliance hub – Very useful, guidance is practical and relates to real scenarios.
Solution Picks Online – Organized categories simplify evaluation and selection of products
MinimalBuyHub – Clean presentation makes the shopping experience enjoyable.
modern finds hub – Clean design with a selection that feels current and thoughtful.
trendy shopping hub – Products feel relevant and the experience is smooth and engaging.
Smart Choice Hub – User-friendly design ensures visitors find what they need and choose wisely
BusinessGrowthNavigator – Roadmap insights are easy to follow and apply in real scenarios.
StrategicGrowthHub – Roadmaps are well-organized, making growth planning practical.
efficiency insights – Helpful advice, helps sharpen focus and improve task completion.
attention accelerator – Great resource, learning how to focus improves efficiency significantly.
focused signals – Clear, motivating phrasing, illustrating that attention guided by signals improves outcomes.
progress click center – Layout supports motivation, helping users plan actions smoothly.
signal-led path – Practical and approachable, showing how well-directed indicators maintain progress.
SecureOnlineDeals – Well-organized store with reliable support and payments.
strategicpathway – Provides clear steps to develop and implement strong strategic plans.
strategycompass – Helps navigate strategic decisions with clarity and confidence.
QuickValue Portal – Structured pages help users quickly locate great bargains
Network of Professionals – Smooth interface, finding resources and insights is simple for all users
alliances learning hub – Content is practical, forming partnerships feels clear and achievable.
professional alliance guide – Content is actionable, site makes alliances easier to navigate.
retailcenter – Practical and efficient, the site makes online buying seamless.
strategic pathfinder – Easy to follow, business ideas are laid out logically and simply.
buyingnavigator – Clear and smooth, shopping online is fast and intuitive.
bargainfinderonline – Convenient shopping, deals are easy to find and buy.
dealshoppingcenter – Practical platform, browsing and purchasing deals feels seamless.
StrategySimplified – Makes learning new approaches easy and actionable.
StrategicGrowthPro – Practical insights, building a sustainable business vision feels organized.
StrategicGrowthPro – Practical insights, building a sustainable business vision feels organized.
DealFinder Hub – Easy-to-use interface helps shoppers find offers quickly
strategic alliance hub – Very useful, guidance is practical and relates to real scenarios.
trusted market network – Practical content, makes alliances easy to apply in actual markets.
SecurePurchasePro – Fast and intuitive, shopping online is clear and hassle-free.
TrustedCartOnline – Fast and dependable, buying items online is straightforward and easy.
ValueLearningCenter – Interactive and inspiring, makes discovering new concepts enjoyable.
Bright Thought Lab – Guides users to explore creative ideas in an enjoyable and simple way
InspirationValueHub – Well-organized site that motivates creativity and learning.
trusted business growth – Clear and dependable, growth-focused ideas are well presented throughout.
BetterWayInsights – Advice is practical and easy to put into action.
action direction – Informative tips, helps create structured plans without feeling overwhelming.
ValueFinder Online – Easy browsing experience with helpful listings for users
goal activator – Practical resources, understanding direction makes goal-setting feel natural.
networkingcentral – Helps you find and maintain contacts with confidence.
linkstrategies – Offers insight into making meaningful connections with minimal effort.
enterprise bond help – Comes across as dependable with clear, calm explanations.
enterprise bond insights – Explanations are clear and reinforce a trustworthy image.
GlobalMarketGuide – Makes international business concepts easy to grasp.
innovative insights portal – Browsing here inspires fresh ways to approach challenges thoughtfully.
learn knowledge wisely – Clear and structured lessons, makes understanding simple.
shopnavigator – Practical and easy to use, buying items is straightforward and smooth.
learn and grow – Content is very clear, makes learning new things enjoyable.
shopnavigator – Practical and easy to use, buying items is straightforward and smooth.
QuickValue Portal – Structured pages help users quickly locate great bargains
networkinsights – Helpful and concise, partnership concepts are explained clearly.
alliancesimplified – Very clear, strategies for successful collaboration are easy to grasp.
alliances knowledge base – Structured insights, helps make sense of market partnership dynamics.
market alliance insights – Helpful tips, shows how alliances work in realistic settings.
CustomerHubOnline – Well-structured site that keeps the shopper in mind.
partnership growth network – Engaging and professional, suitable for long-term business partnerships.
corporate collaboration site – Interesting platform, ideal for creating sustainable business partnerships.
path to career success – Informative and intuitive, helps users explore professional options clearly.
CartJoy – Fast and convenient, modern layout enhances user experience.
TrendyDeals – Navigation is seamless, giving a fresh and current experience.
growth strategy hub – Helps users understand sustainable growth with clear explanations.
corporate partnership platform – Great resource for companies seeking strategic alliances.
long-term growth hub – Offers clear strategies and insights for steady growth over time.
smartsolutionshub – Guides you to apply solutions effectively without unnecessary complexity.
solutionpath – Guides you through implementing solutions with minimal effort.
SmartLearningHub – Educational and clear, understanding new concepts is simple and organized.
GrowthPartnerStrategies – Well-structured guidance focused on real-world use.
KnowledgeBoostPro – Clear structure, understanding new topics feels effortless.
ResultDrivenTips – Simple strategies that generate results without wasted effort.
ProActiveTips – Encourages decisive moves that bring real benefits.
explore success avenues – Content is practical, site explains opportunities without overwhelming users.
retailforward – Helpful and concise, platform makes future-oriented retail easy to understand.
futuristcommerce – Clear and actionable, understanding modern retail strategies is straightforward.
strategiccorporatealliances.click – Clear focus on corporate alliances, seems professional and reliable overall.
learn digital strategies – Engaging content, digital lessons feel practical and clear.
businessalliancesnetwork – Strong emphasis on corporate networking, feels credible and organized.
click for digital tutorials – Step-by-step learning, guides are very clear and useful.
enduring business partnerships – Suggests reliability and trustworthiness in joint ventures.
convenientbuyhub – Seamless experience, online shopping is clear and easy to navigate.
digitalpurchasecenter – Very smooth experience, navigating and buying products online is simple.
alliances insight platform – Useful tips, simplifies how alliances operate in different markets.
market alliance insights – Helpful tips, shows how alliances work in realistic settings.
easy shopping spot – Has a calm, organized feel that supports stress-free shopping.
discover practical solutions – Organized layout, users can review options without feeling rushed.
customer care shopping – Comes across as well organized, with a smooth flow built around users.
strategic learning portal – Helps users develop intelligent approaches to learning and scaling.
learning mastery site – Encourages smarter habits and strategies for continuous growth.
DecisionClarityHub – Helps make smart strategic choices without confusion.
StrategicThinkingHub – Explains intricate approaches in a clear, approachable way.
SmartDealsHub – Offers a platform for shoppers seeking the best value purchases.
ValueFinderNetwork – Helps shoppers discover cost-conscious options efficiently.
SimpleDealHub – Makes purchasing straightforward and pleasant.
growth planning hub – Provides explanations that are practical and supportive of future success.
trustycommercialbonds – Step-by-step advice that makes commercial bonding reliable and straightforward.
growth strategy hub – Helps users understand sustainable growth with clear explanations.
commercialtrusthub – Clear instructions for maintaining safe and reliable bond transactions.
learnfromexpertinsights – Excellent site, expert insights are practical and easy to apply today.
new possibilities click – Interactive site makes exploring options easy and inspiring.
learnfromexpertinsights – Excellent site, expert insights are practical and easy to apply today.
industryinsights – Informative and concise, readers can easily understand how top professionals succeed.
industryinsights – Informative and concise, readers can easily understand how top professionals succeed.
strategic business alliances – Professional feel reinforces corporate collaboration goals across the platform.
SmartDecisionHub – Simple and practical tips, content makes navigating decisions easier.
SmartChoiceHub – Practical advice, content helps you make decisions with confidence.
StrategicConnections – Clear advice that supports smarter business collaboration.
LearnSmartHub – Clear structure makes acquiring knowledge engaging and user-friendly.
PracticalSkillsOnline – Resource is user-friendly and delivers meaningful learning experiences.
business alliance hub – Very informative, understanding trust in business is easier.
growth path – Clear tips, content makes prioritizing actions straightforward and effective.
strategic commerce portal – Branding positions the site as a tool for planning intelligent commercial moves.
business alliance hub – Very informative, understanding trust in business is easier.
growth accelerator – Practical insights, clear direction makes moving forward easier and more productive.
future trade network – Branding conveys connectivity and planning for evolving commercial landscapes.
market alliance insights – Helpful tips, shows how alliances work in realistic settings.
decisionmakersguide – Very helpful, guidance for business choices is clear and immediately actionable.
market partnership guide – Clear guidance, real examples make strategies understandable.
efficientbusinesssolutions – Very informative, solutions for business challenges are easy to implement.
ReliableAlliances – Insights are grounded and useful for maintaining strong partnerships.
world e-commerce platform – Strong framework, ideal for managing global online sales efficiently.
EasyShopCenter – Streamlined navigation makes online shopping smooth and fun.
e-commerce operations hub – Strong foundation that could facilitate large-scale retail globally.
DigitalRetailSimplified – Shopping is straightforward with intuitive navigation and layout.
StrategicPartnerNetwork – Appears focused on developing strong enterprise collaboration models.
ProfessionalPartnershipHub – Conveys credibility for enterprise relationship planning.
next-level innovation site – Inspires curiosity and the pursuit of cutting-edge ideas.
valuealliances – Provides actionable insights for creating trustworthy and effective collaborations.
collaborationlens – Provides clear guidance to strengthen alliances and maximize business impact.
flexible buying space – Browsing feels smooth thanks to the range available.
varied shopping outlet – The flexibility in choices makes it fun to explore.
onlineshoppingcenter – Informative and efficient, purchasing items online feels effortless.
buyinghub – Very user-friendly, online orders are quick and hassle-free.
fair pricing hub – Navigation is simple, and buying feels safe and effortless.
online value shop – Offers a reliable shopping experience with reasonably priced items.
StrategicFutureHub – Inspires planning ahead, offering guidance for long-term business strategies.
OnlineSecureShopping – Clear and practical, finding and buying items is convenient.
SteadyBond Resources – Intuitive pages, makes learning and navigating content straightforward
TrustedMarketHub – Reliable and easy to use, online shopping is hassle-free and safe.
trusted partnerships click – Clear and approachable, global partnership ideas are easy to digest.
alliances knowledge click – Easy to browse, insights on global trust partnerships are clear.
strategicplanningclick – Strong focus on planning, ideal for businesses seeking clarity in growth direction.
strategicplanningclick – Strong focus on planning, ideal for businesses seeking clarity in growth direction.
clarity learning hub – Very useful, helps process and apply new information quickly.
guides for clarity – Excellent explanations, makes learning concepts simpler.
dealtrustconnect – Projects professionalism, ideal for secure marketplace activities.
market alliance insights – Helpful tips, shows how alliances work in realistic settings.
trustedtraderhub – Strong sense of trust, ideal for buyers seeking secure transactions online.
future-oriented hub – Encourages looking ahead and considering new directions for growth.
alliances guide hub – Very useful, real market examples enhance understanding of partnerships.
ClickForFreshIdeas – Very practical advice that gave me new ways to approach tasks.
WorldMarketOnline – Intuitive interface, browsing and buying international products is effortless.
corporateframeworkscenter – Clear, actionable advice for enterprise framework implementation.
UniversalShoppingHub – Reliable global store with smooth checkout and simple product discovery.
enterprisedevelopmenthub – Very professional site, providing practical enterprise framework strategies.
BondUnity Online – Well-arranged pages, navigation is simple and users can access content confidently
dailybuyguide – Simplifies everyday purchases by highlighting value options clearly.
Digital Retail Hub – Offers practical tips for smooth and efficient online buying.
valuebuynow – Makes finding quality deals quick and hassle-free for everyday purchases.
Digital Deals Hub – Very helpful, helps quickly compare products and make decisions.
businessmarketguide – Reliable and practical, platform provides clear advice on market relationships.
Workplace Learning Hub – Very useful, with actionable advice that supports professional growth efficiently.
marketrelationspro – Easy to understand, guidance for market relationships is structured and professional.
Skill Building Hub – Straightforward guidance that helps enhance professional knowledge.
ClickForSecureBonds – Clear and practical explanations make understanding easy.
securecommercialalliances – Feels safe and reliable, guidance on alliances is clear and actionable.
sustainable partnerships hub – Emphasizes eco-conscious collaboration, highlighting long-term business responsibility.
OnlineShoppingPortal – Clear and simple platform, helps me shop without confusion.
NextStepOpportunities – Platform highlights actionable insights for exploring professional growth.
SmartCustomerShopping – Easy browsing and clear product presentation make shopping simple.
securecommercialalliances – Feels safe and reliable, guidance on alliances is clear and actionable.
EntrepreneurInsight – Encourages careful evaluation of emerging business opportunities.
BondValue Insights Center – Clean design, key information is easy to identify and digest
growth mindset hub – Practical advice, long-term improvement is easier to visualize here.
growth mindset hub – Practical advice, long-term improvement is easier to visualize here.
secure shopping network – Navigation is straightforward and the design inspires confidence.
everyday items portal – User-friendly layout ensures browsing and buying is quick.
trusted purchase network – Well-organized design gives peace of mind and smooth browsing.
reliable daily shop – Pages load quickly, making regular purchases easy and straightforward.
StrategicThinkerClick – Easy instructions that helped me apply strategic thinking confidently.
market alliance insights – Helpful tips, shows how alliances work in realistic settings.
NextStepPlanner – Guidance is detailed and actionable, making strategic planning straightforward.
strategic market alliances – Easy to apply examples, shows how alliances work in real-world business situations.
PlanSmartNow – Guidance is detailed and practical, strategies are simple to execute.
safeshophub – Gives a sense of security, perfect for buyers looking for reliability.
trustedsalesportal – Professional look and feel, ensures peace of mind while shopping online.
clarity engine – Very clear guidance, helps transform ideas into consistent momentum.
clarity strategies – Great lessons, applying clarity leads to measurable progress.
SmartGrowthLearning – Practical insights, makes planning growth strategies much easier and actionable.
BudgetSaverNetwork – Offers practical options for price-conscious online shoppers.
ClickPathway Learning – Sleek design, helps visitors explore options and take meaningful steps forward
IntelligentScalingTips – Step-by-step guidance, helps execute strategies with confidence.
dailyvaluebuys – Very user-friendly, locating great deals is quick and hassle-free.
SmartSavingsCart – Highlights smart and value-focused shopping experiences.
smartpurchasehub – Convenient and easy, spotting value items online is straightforward.
shopping experience hub – Clean interface suggests easy navigation and enjoyable shopping.
Path to Digital Success – Offers easy-to-follow strategies for improving growth outcomes.
Growth Strategy Lab – Loved the clear explanations, ideas are practical and easy to implement.
FutureGrowthHub – Well-structured content providing actionable long-term strategies.
cityshoppinghub – Easy-to-use and modern, making online shopping efficient and enjoyable.
bizinsights – Concise and helpful, growth strategies are easy to understand and apply.
retailhubonline – Smooth navigation and modern design make shopping online stress-free.
bizboosters – Informative and actionable, strategies for growth are easy to understand and implement.
Smarter Growth Plans – Enjoyed how actionable the advice felt from start to finish.
Business Growth Guide – The explanations felt natural and helped me map things out with confidence.
BusinessInsightsHub – Clear explanations and guides that are simple to use.
TrustedBizAlliances – Branding conveys reliability, suitable for serious enterprise partnerships.
ClickPath Adventures – Playful interface, visitors enjoy exploring content without getting lost
ClickBusinessResources – Very clear and actionable advice for professional learning.
TrustedBizAlliances – Branding conveys reliability, suitable for serious enterprise partnerships.
ClickEnterpriseInsights – Easy-to-follow advice that feels structured and trustworthy.
digital planning guide – Information is concise, each step makes building digital skills achievable.
digital strategy builder – Organized content, planning online goals feels logical and achievable.
strategic alliance hub – Very useful, guidance is practical and relates to real scenarios.
market collaboration hub – Informative advice, alliances explained clearly for market applications.
informed action portal – Focused on guiding careful steps without overwhelming users.
explore new viewpoints – Quick access to ideas that refresh your perspective and thinking.
corporatebondhub – Strong focus on professional connections, projects reliability and clarity.
businessalliancebonds – Clear structure, suggests reliability for professional corporate partnerships.
discover insights portal – Offers content that challenges assumptions and inspires new ideas.
safe purchase hub – A secure environment that inspires trust and peace of mind.
strategiclink – Clear guidance, users can easily follow the steps to strengthen business collaborations.
growth steps – Motivating insights, content breaks growth into manageable pieces.
collabhub – Useful and actionable, explains practical steps for improving partnerships.
secure payment portal – Makes the checkout process feel monitored and protected.
growth framework hub – Useful insights, helps approach complex growth plans with clarity.
bondadvisor – Useful and clear, commercial bond strategies are structured for real-world application.
bondstrategies – Highly actionable, platform presents commercial bond advice professionally.
expansioninsights – Clear, actionable frameworks to support sustainable growth.
growthmap – Makes applying growth frameworks practical and easy to follow.
SmartBuyNetwork – Focuses on cost-conscious purchasing with reliable options.
DiscoverBizGrowth – Easy-to-understand explanations and actionable recommendations.
ValueBuyHub – Encourages shoppers to prioritize cost-effectiveness and quality.
Unified Professionals – The experience feels streamlined and supportive for networking.
Connect for Business – A practical space where connecting with others feels intuitive.
PlanSmartFuture – Encourages forward-looking thinking and methodical strategy creation with ease.
LearnToScaleClick – Clear and actionable guidance for understanding and applying growth methods.
business foresight hub – Encourages planning with the future in mind, perfect for strategic leaders.
FuturePlanningPortal – Focuses on helping users map out strategic goals efficiently.
LearnAndGrowClick – Practical guidance that helps understand business expansion strategies efficiently.
knowledge insights portal – Clear explanations, exploring new ideas is effortless.
knowledge growth portal – Educational material is engaging, exploring concepts feels natural.
business alliance insights – Easy-to-follow advice, examples feel very relevant to real markets.
trusted market network – Practical content, makes alliances easy to apply in actual markets.
ReliableShoppingClick – Easy-to-use platform with accurate information for shoppers.
Market Discovery Lab – Practical advice presented clearly, simplifies understanding complex topics.
Smart Market Paths – Well-structured guidance makes understanding trends simple.
reliable corporate connections – Messaging reinforces stability, encouraging businesses to explore partnerships.
globalenterprisealliances – Informative platform, global alliance strategies are explained clearly and practically.
trusted business network – Messaging communicates reliability, which is attractive for professional collaborations.
ClarityForEntrepreneurs – Makes complex business ideas easy to follow and actionable.
globalenterprisealliances – Informative platform, global alliance strategies are explained clearly and practically.
ClearBizInsights – Simplifies complex business concepts for quick understanding.
bizinsights – Helpful and practical, the advice is concise and easy to apply.
growthmanual – Practical and helpful, strategies are presented clearly for real-world application.
value buy portal – Clear navigation makes it easy to identify the best options.
value shopping network – Deals are clear, and comparing products is seamless.
buildonlinegrowth – Stepwise advice makes digital growth planning easy to follow and implement.
BuySmartOnline – Practical guidance that helps shoppers make informed decisions.
growthpathplanner – Excellent step-by-step approach to enhancing online growth efforts.
alternative methods site – Offers fresh perspectives for solving problems more effectively.
clarity pathways – Great insights, simplifies tracking progress toward goals.
TopBuyOnline – Well-designed platform, shopping experience feels intuitive and premium.
channel your efforts – Great guidance, makes planning and executing tasks more effective.
ElitePurchaseHub – Smooth shopping experience, products are clearly displayed and easy to buy.
Next-Level Ecommerce – The ideas are inspiring without being difficult to follow.
Future-Ready Ecommerce – Enjoyed how the strategies are explained in a clear, usable way.
DigitalFlexMall – Seamless and versatile approach makes shopping convenient and adaptive.
open new doors – I like the vibe, it feels welcoming and exploratory.
NextGenShoppingClick – Very clear and structured, makes understanding modern retail trends straightforward.
FlexiCartOnline – Smooth navigation and adaptive tools enhance the shopping journey.
OnlineShoppingInsights – Easy to navigate, provides useful insights into modern shopping trends.
start exploring – Fun execution, it nudges users to poke around without pressure.
ClickIdeasNow – Clear, actionable tips that made applying ideas simple and efficient.
alliances guide hub – Very useful, real market examples enhance understanding of partnerships.
business alliance insights – Easy-to-follow advice, examples feel very relevant to real markets.
AllianceBuilder – Designed to help businesses form reliable and lasting connections.
strategic guidance click – Easy-to-understand content, strategy concepts are clear and concise.
discover strategy pathways – Practical guidance, complex ideas become easy to follow.
CorporateAlliancePro – Designed to foster dependable enterprise partnerships.
GlobalOnlineBuyingHub – Found this resource valuable, explanations are concise and easy enough.
GlobalOnlineBuyingHub – Found this resource valuable, explanations are concise and easy enough.
strategy evolution portal – Focused on adapting traditional methods to modern business needs.
StrategicPlannerPro – Clear guidance that made mapping out plans straightforward.
NetworkingPro – Easy to engage with others, site provides trustworthy professional resources.
trustbuyclick – Clear trust signal, inspires user confidence in online shopping decisions.
sustainablepartners – Helpful and informative, strategies for building eco-friendly collaborations are simple to implement.
PartnerProConnect – Easy to use, trustworthy content makes networking feel efficient.
ecopartners – Very clear, platform presents sustainable partnership guidance in an understandable way.
shopassureportal – Projected professionalism, encourages users to shop without worry.
fastbuyhub – Very accessible, shopping online is simple and easy to navigate.
Fresh Opportunity Hub – Clear layout helps users explore new options creatively and efficiently
onlinepurchaseportal – Very intuitive, making purchases online feels quick and stress-free.
trusted link hub – Layout feels professional and information is accessible without confusion.
enterprise connections hub – Professional networking feels well-organized, with clear and trustworthy information.
SmartBusinessLearning – Very useful tips that I can apply immediately in my work.
growth planning hub – Insightful content, following these steps brings clarity and purpose to actions.
online shopping hub – Modern and interactive, encouraging extended exploration of products.
intentional growth – Motivating guidance, makes planning growth feel structured and realistic.
digital commerce hub – Modern feel enhances the browsing experience for shoppers.
NextLevelStrategy – Focused on bridging vision with practical steps for achieving business objectives.
TrustedBusinessPortal – Very informative, helps make business decisions with confidence.
GoalStrategyLab – Encourages methodical thinking to achieve strategic clarity and effectiveness.
EnterpriseKnowledgeClick – Structured and clear, helps understand business frameworks effectively.
Business Alliance Insights – Helps identify key factors for long-term collaboration success.
Collaborative Partnership Hub – Provides actionable steps to strengthen and maintain alliances.
ExploreSmartMarkets – Clear and actionable content, market ideas are easy to implement.
enterprise alliances portal – Focuses on fostering cooperative growth strategies for businesses.
StrategicBusinessAlliances – Solid website with practical tips I can apply immediately today.
market alliance hub – Very insightful, helps understand alliances in real-world market situations.
StrategicBusinessAlliances – Solid website with practical tips I can apply immediately today.
ExploreMarketIdeas – Practical guidance, market concepts are presented clearly and understandably.
trusted partnership insights – Well-structured examples, makes alliance strategies easier to follow.
alliances strategy hub – Well-presented concepts, partnership guidance is easy to digest.
alliances success ideas – Clear guidance, alliance strategies are presented in a practical way.
RetailFutureGuide – Informative content that helps anticipate trends effectively.
Focused Strategy Portal – Clean layout makes understanding opportunities and planning ahead straightforward
shopcentral – Very convenient, navigating the platform for purchases is fast and easy.
fastbuycenter – Clear and helpful, shopping online feels seamless.
SmartSavingsCart – Highlights smart and value-focused shopping experiences.
BuySmartOnline – Smooth and straightforward shopping, everything is easy to find.
BudgetWiseShop – Projects savings and reliability for online consumers.
RapidShop – Shopping is straightforward, interface is intuitive and modern.
secureshoppingcenter – Promotes safety and reliability, ideal for long-term shoppers.
secureshopclick – Clear focus on safety, makes shopping feel risk-free and convenient.
ClickForCorpNetworking – Easy-to-follow guidance with trustworthy insights and tips.
retailworldinsights – Helpful platform, global retail analysis is practical and easy to implement.
commerceworldguide – Useful resource, international retail trends are clearly explained and actionable.
modern marketplace – Emphasizes efficiency and usability for contemporary shoppers.
click for insights – Promotes curiosity without pressure or information overload.
knowledge journey – Learning here feels smooth and well-paced.
PremiumOnlineBuyingHub – Well organized content that supports smarter decisions and planning efforts.
PremiumOnlineBuyingHub – Well organized content that supports smarter decisions and planning efforts.
SafeStrategicBonds – Trustworthy platform, learning about strategic bonds is smooth and dependable.
WorkplaceCollabHub – Focused on cooperation, making professional networking feel approachable and valuable.
value buying portal – Easy to navigate, with organized categories and smooth purchasing.
WorkplaceInsightClick – Very clear explanations that provided practical strategies for professional growth.
StrategicPartnerLinks – Designed for professional alliances, prioritizing practical collaboration online.
international value store – Easy navigation and organized options make shopping simple and fast.
ReliableBondGuide – Informative and secure, strategic bond content is easy to understand.
ClickForDecisionTools – Practical advice presented simply, makes evaluation easy.
alliances guide hub – Very useful, real market examples enhance understanding of partnerships.
ClickForChoiceClarity – Useful platform, helps me compare options quickly and with confidence.
partnership insights platform – Very actionable, real-world examples illustrate alliance strategies well.
ResultPath – Strategies here make taking effective action straightforward and easy.
MomentumTips – Provides insights that inspire immediate action and real progress.
Commerce Trend Explorer – Timely updates on global retail help me stay informed and ready.
Retail Commerce Network – The platform delivers actionable information and market analysis.
trusted business bonding – Offers practical guidance, forming partnerships feels straightforward.
check yavlo – Well-structured site, intuitive navigation, very user-friendly
business connection hub – Very clear advice, building strong alliances is simple.
landing hub – Minimal clutter, intuitive layout, content is simple and clear
ProfessionalTrustGuide – Insightful site, helps navigate professional relationships with confidence.
ProfessionalPartnerInsights – Helpful and clear, builds confidence in professional relationship strategies.
bizlink – Very reliable, guides users effectively on forming professional relationships.
networknavigator – Informative and actionable, makes professional networking approachable and reliable.
SmartMarketIdeas – Easy navigation with useful explanations that I can apply immediately.
DigitalGrowthGuide – Provides clear advice for planning online growth in a structured way.
commercial trust network – Promotes confidence in connecting with legitimate business partners.
PathToDigitalGrowth – Provides actionable guidance that feels organized and trustworthy.
cross-border business center – Suggests easy access to partners in multiple regions and international collaborations.
worldwide partnership hub – Useful for connecting with international stakeholders and potential clients.
careerpathresources – Very intuitive, professional growth advice is clear and easy to implement.
growthandlearninghub – Informative and accessible, development tips are easy to understand and use.
ClickRetailVision – Engaging content that makes retail strategy clear and actionable.
safe buying hub – Gives a reliable impression, encouraging repeat use for future shopping.
Growth Strategy Center – Excellent resource, helped me prioritize and understand my options.
Digital Growth Lab – Offers clear guidance, making growth planning easier than expected.
secure purchase platform – Looks professional and dependable, a marketplace I’d use again.
start exploring – Fast pages, smooth interface, content is easy to digest
SafeBuyHub – Shopping experience feels safe and intuitive with simple navigation cues.
alliances knowledge base – Structured insights, helps make sense of market partnership dynamics.
SafeBuyZone – Platform offers a straightforward shopping experience with a trustworthy vibe.
market partnership guide – Clear guidance, real examples make strategies understandable.
resource page – Simple headings, readable content, pages are easy to move through
PremiumShopClick – Easy to navigate, content is professional and helpful.
ClickForOnlineDeals – Easy-to-use platform, content is reliable and navigation flows well.
Opportunity Research Space – Gave me a better sense of what business paths are worth exploring.
AffordableShopLink – Designed for users who want the best deals online.
professional learning portal – Encourages continuous knowledge building in a manageable way.
Business Discovery Hub – The articles highlighted opportunities I hadn’t previously considered.
strategic partnership insights – Advice is actionable, forming business connections feels natural.
SavvyBuyHub – Encourages smart spending with high-value shopping choices.
RelationshipGrowthHub – Well-organized and easy-to-use network guidance.
click for collaboration tips – Very helpful content, site makes alliance planning feel straightforward.
bond education hub – Simplified explanations support quick understanding of bond investment.
official site – Minimalist design, fast performance, content is helpful and accessible
browse yavlo – Pages respond quickly, intuitive layout, very user-friendly experience
enterprise bond resource – Clear and practical advice helps newcomers learn effectively about bonds.
nextgen store – Easy to use, checkout process is quick and efficient.
online retail hub – Clear and intuitive, the site makes purchasing hassle-free.
valuepurchasehub – Clear and simple, navigating deals is fast and intuitive.
smartshoppinghub – Practical and clear, the shopping experience feels smooth and efficient.
TopDealFinder – Easy-to-use site, discovering deals feels smooth and straightforward.
TopSavingsHub – Easy and organized, finding deals is quick and enjoyable.
SafeBizConnect – Platform feels secure and dependable, ideal for online business dealings.
CommercialSafeConnect – Smooth and confident platform, transactions feel secure and professional.
FocusedBusinessClick – Clear and practical advice that improved my decision-making.
reliableshoppingzone – Appears trustworthy, reassuring for cautious online shoppers.
trustyshopcenter – Branding emphasizes confidence, ideal for everyday online purchases.
Discover Growth Paths – Fast-loading content with clear guidance for exploring new options.
Business Insights Hub – Intuitive layout, very straightforward to navigate and explore ideas.
proguidancecenter – Very readable, expert advice is structured for easy understanding and use.
insightfulpros – Practical and actionable, expert content is easy to implement quickly.
global retail portal – Feels oriented to international buying trends and preferences.
strategic global alliances portal – Helps firms explore cooperative strategies on an international scale.
international purchase platform – Broad selection encourages engagement from buyers worldwide.
alliances insight platform – Useful tips, simplifies how alliances operate in different markets.
alliances knowledge base – Structured insights, helps make sense of market partnership dynamics.
EnterpriseCollabCenter – Promotes professional partnerships and efficient inter-company collaboration.
SmartBusinessClarity – Insightful guidance that clarified confusing strategies quickly.
CorporateCollabHub – Professional networking focus is evident, platform promotes team collaboration effectively.
BusinessConnectionHub – Easy-to-follow insights, makes international business concepts straightforward.
GlobalConnectionHub – Clear platform, content helps me understand cross-border business efficiently.
explorebusinessopportunities – Insightful resources, finding business opportunities feels easy and practical here.
explorebusinessopportunities – Insightful resources, finding business opportunities feels easy and practical here.
Networking Trust Center – Content is clear and helps establish meaningful professional relationships.
Alliance Network Insights – Very helpful content for forming strong and reliable business connections.
click through – Quick response times and a neat layout made browsing pleasant
useful resource – Fast pages and a clean structure kept me engaged
alliancesacademy – Practical guidance, corporate partnerships are presented clearly and effectively.
alliancesexpert – Useful and actionable, readers can implement corporate alliances with confidence.
digital shopping hub – Pleasant experience, browsing and choosing products feels natural.
trusted market hub – Name emphasizes trust, creating a sense of safety for online shoppers.
online purchase platform – Smooth navigation, products are easy to compare and select.
BusinessAllianceInsights – Actionable content, helps plan and sustain effective partnerships.
PartnershipStrategyOnline – Easy-to-follow tips, guides on building alliances with lasting impact.
TrustedBuyPro – Simple and secure, checkout process is effortless and smooth.
SafeShopHub – Very reliable platform, online shopping feels secure and hassle-free.
ValueShopHub – Highlights savings, ideal for shoppers looking for the best deals online.
GlobalDigitalShoppingMarket – Really useful site, content feels practical and easy to navigate.
GlobalDigitalShoppingMarket – Really useful site, content feels practical and easy to navigate.
SmartSavingsCart – Highlights smart and value-focused shopping experiences.
discover new ventures – Invites curiosity and exploration into modern business landscapes.
business exploration network – Messaging feels like a guide for finding interesting ventures online.
business professional network – Professional tone and branding suggest a platform for serious corporate partnerships.
strategicbondresources – Helps professionals navigate strategic bonds efficiently and confidently.
corporate connections hub – Strong business-focused impression conveys reliability and trust.
trustedbondguide – Clear, well-explained advice for managing strategic bond investments.
learnfromexecutiveleaders – Insightful platform, strategies from industry leaders are easy to understand and apply.
learnfromexecutiveleaders – Insightful platform, strategies from industry leaders are easy to understand and apply.
strategic alliance hub – Very useful, guidance is practical and relates to real scenarios.
alliances insight platform – Useful tips, simplifies how alliances operate in different markets.
BusinessRelationshipPortal – Encourages steady, meaningful connections for professional growth.
UrbanShopZone – Very enjoyable to explore, provides product info and choices clearly.
CityShopperClick – Smooth experience, makes comparing items quick and simple.
long-term investment alliances – Encourages building partnerships that align with strategic investment goals.
engine of motion – Smooth and practical, showing how energy and focus drive progress.
traction powered progress – Short, encouraging phrasing linking focused force to meaningful results.
business operations hub – Structured presentation makes understanding frameworks intuitive and accessible.
business knowledge portal – Easy-to-follow structure allows for smooth learning of core concepts.
handy page – Clear pages, quick navigation, content is informative and easy to read
Digital Buyer Guide – Clear and practical tips for smarter, faster online shopping.
explore here – Pages load fast, layout is clean, very user-friendly experience
E-Commerce Tips Hub – Makes selecting products easier with actionable advice.
collabstrategies – Very actionable, platform shows how to collaborate effectively in professional settings.
teamworkhub – Clear and efficient, collaboration concepts are easy to understand and apply.
Discover Practical Ideas – Provides actionable tips with clear explanations for daily use.
SwiftCartOnline – Easy-to-use interface, shopping feels efficient and fast.
Actionable Knowledge Hub – Clear, practical guidance that makes implementing ideas straightforward.
BuyQuickHub – Fast and organized platform, items are easy to locate and purchase.
professional insights – Very useful content, makes understanding key concepts easy and practical.
learning navigator – Excellent resource, breaks down professional knowledge into actionable steps.
trusted site – Fast-loading pages, content is concise and readable
trusted site – Fast-loading pages, content is concise and readable
opportunity exploration hub – Promotes thinking beyond the short term to maximize potential.
collaboration opportunities hub – Focused on cooperative ventures and strong partner connections.
ecommercestarterkit – Seems practical, gives small businesses tools to begin selling online immediately.
forward-thinking platform – Encourages decisions that prioritize sustainability and ongoing success.
SecureDealsOnline – Practical and intuitive, shopping feels easy and reliable.
ecommerceeasytools – Clear and uncomplicated, perfect for small teams handling online stores.
shoptrustguide – Ensures a safe, smooth, and enjoyable online purchasing process.
TrustedCartHub – Reliable and well-structured, checkout is fast and worry-free.
purchasehubonline – Checkout is simple and secure, making shopping convenient.
strategic market alliances – Easy to apply examples, shows how alliances work in real-world business situations.
businessnavigator – Clear and informative, offers step-by-step advice for enhancing market partnerships.
strategic market alliances – Easy to apply examples, shows how alliances work in real-world business situations.
marketinsights – Very clear and helpful, offers practical guidance for navigating market relationships.
CareerWisdomPortal – Appears helpful for professionals seeking guidance in their careers.
CareerInsightLab – Useful resource for professionals seeking clarity and actionable advice.
ClickExpertInsights – Clear and practical, shows how to apply professional strategies effectively.
ProInsightsClick – Helpful platform, makes expert strategies much easier to follow.
constructive momentum – Concise and encouraging, linking intentional effort to measurable forward action.
motion mapped out – Practical, concise wording illustrating that intentional construction ensures steady results.
]alliancenavigatorpro – Very helpful, enterprise alliance strategies are presented in a digestible format.
]partnerpath – Concise and user-friendly, strategies for alliances are easy to implement.
BudgetFriendlyCart – Designed to attract shoppers who prioritize value and savings.
main hub – Fast-loading pages and clean layout made it simple to browse
check plavo – Smooth experience, all sections were easy to find and use
BudgetDealsCenter – Designed to appeal to shoppers seeking value and affordability online.
Everyday Buy Zone – Smooth navigation makes checking out products feel easy.
ModernRetailBuyingHub – Enjoyed browsing here, ideas are fresh and well explained clearly.
Smart Daily Purchases – The platform keeps browsing fast and uncomplicated.
ModernRetailBuyingHub – Enjoyed browsing here, ideas are fresh and well explained clearly.
creative problem solving hub – Inspires exploring different techniques and approaches.
smart retail portal – Finding products is simple thanks to the clear layout.
globaldigitalshoppingmarket – Smooth interface, site offers a good overview of digital marketplaces worldwide.
next step shopping – Layout supports fast discovery of products.
globaldigitalshoppingmarket – Smooth interface, site offers a good overview of digital marketplaces worldwide.
BusinessSkillsOnline – Useful insights, learning feels hands-on and practical for real business scenarios.
SkillWiseBusiness – Easy guidance, helps understand and implement core business strategies efficiently.
online management skills – Highlights the flexibility and reach of digital business learning.
online professional skills – Shows how digital learning makes business education more approachable.
secure purchase network – Helpful site, checkout is easy to follow and reassuring.
growthhub – A helpful resource with actionable strategies for business growth.
secure shopping hub – Helpful platform, checkout is fast and gives peace of mind.
growthlens – Helpful tips to make business growth planning both simple and effective.
education expansion platform – Helps users stay curious while advancing knowledge systematically.
smart learning hub – Encourages efficient knowledge building and long-term intellectual growth.
decisionhelperguide – Structured and actionable advice for making smarter choices.
decisioncoachonline – Helps simplify choices with actionable and reliable advice.
StreamlinedRetailOnline – Focused on reducing friction and making digital shopping easy.
QuickRetailSolutions – Platform is user-friendly and designed for efficient online buying.
TrustedCorporateHub – Well-laid-out platform, networking feels professional and effective.
CorporateLinkPro – Organized and practical, building professional connections is effortless.
alliancesmaster – Very clear, long-term strategic partnerships are explained in an easy-to-understand way.
strategicallianceguide – Clear and concise, long-term alliances are explained in a practical manner.
GlobalTrustRelationshipNetwork – Clean layout and thoughtful content make this site enjoyable today.
GlobalTrustRelationshipNetwork – Clean layout and thoughtful content make this site enjoyable today.
Explore This Site – Ran into this by chance and enjoyed the straightforward layout
Nice Simple Layout – Discovered this by chance and liked how clear everything looks
trusted resource – Responsive pages, readable layout, overall experience is enjoyable
NextGen Online Market – Modern platform that enhances online shopping efficiency.
Online Retail Innovation – Great for discovering and buying products with ease.
nexra.click – Simple layout, smooth navigation, very easy to browse today
momentum mindset site – Makes getting started feel natural and achievable.
progress motivation portal – Helps turn ideas into action with encouraging content.
business cooperation portal – Useful for firms searching for growth through collaboration.
joint venture resource – Looks relevant for enterprises planning collaborative initiatives.
businessunity – Clear insights for aligning teams and processes toward sustainable growth.
growthlens – Structured insights for driving enterprise growth effectively.
greenselectionhub – Guides users to buy products that align with environmental responsibility.
sustainablechoicezone – Clear, user-friendly guidance encourages environmentally aware decisions.
SmartValueShop – Great deals, the product details make comparing items really easy.
ClearChoiceShop – Shopping here is efficient, and product details are easy to digest.
strategicalliancesguide – Practical insights, alliances are explained clearly and feel reliable.
partnershipscenter – Very professional, alliance strategies are clear and simple to follow.
UrbanMallOnline – Platform highlights urban retail trends, creating an appealing shopping environment.
CityRetailHubOnline – Urban-centric interface seems functional yet stylish for metropolitan buyers.
BudgetSaverNetwork – Offers practical options for price-conscious online shoppers.
ClarityBoostHub – Offered easy-to-follow advice for immediate application in business.
BizInsightClick – Step-by-step advice that made understanding strategies straightforward.
ShopSmartOnline – Clear tips that made browsing and purchasing much easier.
OnlineDealsHub – Simplified the shopping process and saved me time.
EnterpriseMasteryHub – Insightful content, enterprise frameworks are easy to apply in practice.
connect and grow professionally – Very informative, advice can be applied immediately in work relationships.
TrustedEnterpriseGuide – Informative and clear, frameworks are explained step by step.
online portal – Fast navigation, minimal clutter, content feels structured
trusted resource – Everything works smoothly, content is short and informative
SecureBizConnect – Easy to use, corporate networking advice seems trustworthy and relevant.
TrustedCorporateNetwork – Clear and professional guidance, platform inspires confidence in corporate bonding.
Strategic Alliance Hub – Offers actionable strategies to enhance collaboration across businesses.
Business Relationship Center – Helpful tips for creating dependable and effective business networks.
strategic partnership portal – Appears designed for organizations seeking effective partnership strategies.
corporate alliance hub – Focused on enabling productive business partnerships efficiently.
creative problem solving hub – Inspires exploring different techniques and approaches.
smart workflows hub – Focuses on finding efficient alternatives to traditional methods.
biznetworkcentral – A clear resource for understanding how business networks operate smoothly.
ventureweb – Guides you through the essentials of professional network building.
modern ecom hub – Smooth navigation makes the experience enjoyable.
smart shopping portal – Everything feels streamlined, from browsing to finding items.
reliableonlinecommerce – Safe and reliable, buying products online feels simple and secure today.
entrepreneurial insight portal – Messaging supports smart exploration of new or overlooked markets.
fresh business perspectives – Encourages exploring market ideas from different angles for growth potential.
reliableonlinecommerce – Safe and reliable, buying products online feels simple and secure today.
vyrxo network – Informative pages, simple layout, and overall site feels welcoming
EcoFriendlyPurchasing – Focus on smarter, conscious buying experiences within a structured platform.
vyrxo web – Easy to read, navigation is simple, and design feels modern and uncluttered
IntelligentShoppingHub – Encourages strategic purchasing with an organized ecosystem approach.
bizconnectionstrategies – Very actionable, long-term business relationships are easy to understand and maintain.
bizconnectionstrategies – Very actionable, long-term business relationships are easy to understand and maintain.
progress frameworks – Useful tips, shows how to structure efforts for better growth results.
signal turns action link – Text is easy to read and overall design feels professional
framework builder – Very clear explanations, helps apply strategies effectively.
FindSmarterBusinessMoves – Found this resource valuable, explanations are concise and easy enough.
signalturnsaction – Interesting concept, I like how the content flows naturally here
FindSmarterBusinessMoves – Found this resource valuable, explanations are concise and easy enough.
visit tavro – Pleasant browsing, well-organized content, and seamless page transitions
tavro platform – Easy-to-follow layout and clear content with fast performance
main hub – Smooth browsing experience, minimal clutter, site feels user-friendly
global alliance insights – Clear international partnership ideas, content is easy to follow.
resource page – Pages load quickly, simple structure, browsing feels natural
global alliance insights – Clear international partnership ideas, content is easy to follow.
trusted resource – Concise layout, smooth performance, content is simple to digest
quick link – Clean design, fast response, all information is accessible without confusion
budget shopping portal – Focus on value seems strong, helping shoppers stretch their money further.
smart buy shopping hub – Emphasizes affordability, perfect for those looking for good deals.
Fresh Growth Ideas – Reading this makes me want to experiment more in my work routine.
TrustNetworkInsights – Organized and clear, global networking is accessible and practical.
Ideas for Growth – The suggestions here motivate me to test new ideas regularly.
TrustInsightsGlobal – Insightful and structured, networking worldwide feels organized and reliable.
AffordableShopLink – Designed for users who want the best deals online.
SavvyBuyHub – Encourages smart spending with high-value shopping choices.
trustgreenalliances – Clear tips for forming partnerships that are both sustainable and trustworthy.
greenenterprisealliance – Provides actionable steps to develop sustainable and long-lasting partnerships.
trusted shopping solution – Buying process feels smooth from start to finish.
LearnFutureFocusedSkills – Solid website with practical tips I can apply immediately today.
secure deal portal – Payment process feels controlled and user-friendly.
LearnFutureFocusedSkills – Solid website with practical tips I can apply immediately today.
ClearBusinessInsights – Helps users evaluate challenges and simplify complicated business choices effectively.
streamlined purchase hub – Focused on making the checkout process simpler and faster.
InsightClarityNetwork – Emphasizes clear analysis and strategic thinking for effective business outcomes.
online shopping center – Straightforward branding communicates ease for a broad user base.
zylor network – Fast site performance, minimal distractions, and navigation is intuitive
zylor spot – Clean presentation, content is easy to understand, and pages load quickly
focusamplifiesgrowth online – Minimalistic design, intuitive navigation, and reading is effortless
strategic ideas portal – Helpful explanations, learning strategic concepts feels approachable and clear.
focusamplifiesgrowth page – Logical layout, concise content, and pages respond quickly
BuySmart – Very user-friendly, payment process is quick and secure.
TrustedCart – Very straightforward, transactions are smooth and secure.
useful link – Fast pages, organized sections, content is concise and helpful
handy page – Lightweight interface, quick access to all content, very readable
small business shop portal – Simple and effective, ideal for first-time ecommerce entrepreneurs.
small shop platform – Simple and practical, makes starting ecommerce stress-free.
korixo page – Pages feel organized and simple to move through
korixo page – Pages feel organized and simple to move through
Long-Term Unity Hub – Provides actionable advice to maintain partnerships effectively over time.
Partnership Strategy Center – Very helpful examples for establishing reliable and successful alliances.
LearnAndPlan – Well-structured content, strategies are simple to grasp and implement.
SmartStrategyTools – Practical advice, strategy planning feels natural and well-guided.
SafeBondOptions – Explained the details in a way that was simple to grasp.
SafeBondOptions – Explained the details in a way that was simple to grasp.
ProtectedEcommerceZone – Buyers feel confident navigating and completing transactions here.
ReliableEcommerceLinks – Buyers can feel safe navigating and completing purchases here.
future-focused business guide – Suggests practical ways to structure business plans for lasting impact.
enterprise planning platform – Encourages companies to adopt long-term strategic perspectives for stability.
globalpartnershipinfrastructure – Very detailed, global partnership infrastructure is explained clearly and practically here.
growthflowswithclarity info – Crisp pages, intuitive navigation, and content is helpful and clear
axivo homepage – Easy-to-read information with a tidy and user-friendly layout
globalpartnershipinfrastructure – Very detailed, global partnership infrastructure is explained clearly and practically here.
growthflowswithclarity link – Smooth interface, intuitive navigation, and content is concise and useful
axivo – Clear and simple content, overall experience is pleasant
landing hub – Pages open quickly, navigation is effortless, content is straightforward
trusted resource – Pages are clear and concise, information is presented logically
smart shopping site – Clear value orientation, great for shoppers looking for savings.
budget-friendly shopping portal – Focused on value, likely helpful for finding cost-effective deals.
official store – The process was seamless and shipping alerts arrived on time.
marketplace – Pleasant and smooth shopping, plus reliable delivery tracking.
Business Relationship Hub – Provides actionable tips for building and sustaining corporate bonds.
Business Alliance Hub – Offers clear insights into developing effective corporate partnerships.
QuickShopper – Really clarified things I was struggling with in no time.
OnlineChoiceMaster – Made it simple to understand without any hassle.
shopping site – Smooth browsing, and product presentation is trustworthy.
online shop hub – Well-structured navigation, and products appear authentic.
FuturePathFinder – Inspires users to plan ahead and consider long-term goals thoughtfully.
TomorrowPlanningHub – Highlights planning techniques that help users anticipate the next steps effectively.
securebuyzone – Marketplace feels professional, inspires confidence for first-time shoppers.
safeshophub – Gives a sense of security, perfect for buyers looking for reliability.
mavix marketplace hub – Information presented neatly, loading fast and navigation simple.
mexto info – Well-laid-out pages where information is accessible quickly
progressmovesforwardnow portal link – Clean interface, organized content, and enjoyable to explore
shop mavix – Smooth browsing, clear sections and site performed well on mobile.
explore progressmovesforwardnow – Clean design and well-organized content, easy to browse throughout
official mexto – Well-organized pages, information is simple and intuitive
xavro hub – Clean visuals, headings are clear, and navigation feels effortless
xavro platform – Clean structure, concise content, and pages are easy to follow
explore here – Clear sections, minimal clutter, browsing feels effortless
useful link – Fast pages, neat layout, information comes across clearly
economical marketplace – Emphasizes affordability, helping users maximize savings on purchases.
affordable shopping hub – Appears practical, perfect for finding deals without overspending.
item store – Listings were clear, and the filter options made shopping faster.
Pelixo Market – Pages loaded fast, content structured well and browsing was simple.
Pelixo Center – Site loads fast, layout clean and finding what I needed was simple.
retail website – I liked how organized the products were, filters made selection fast.
Kavix Market – Layout minimal, browsing smooth and finding products effortless.
NextGenOnlineBuying – Nice experience overall, navigation works smoothly and loads quickly everywhere.
NextGenOnlineBuying – Nice experience overall, navigation works smoothly and loads quickly everywhere.
Strategic Choices Hub – Offers actionable insights that simplify complex decisions.
Decision-Making Insights – Simplifies complex choices and boosts confidence in the process.
Voryx Spot – Interface simple, content easy to digest, and site browsing smooth.
Voryx Linker – Clean interface, fast-loading pages, and finding information simple.
TrustPortal – Pages load fast, interface well-structured, and navigation intuitive.
Ulvaro Market – Fast loading, content clear and overall shopping experience reliable.
EasyBrixel – Pages respond fast, interface simple, and browsing feels natural.
Ulvaro Point – Layout neat, browsing smooth and buying process effortless.
official store – Came across this store, fair pricing and a quick, easy checkout.
sales site – Discovered it today, the checkout was simple and the prices fair.
Kavion Path Central Shop – Navigation intuitive, content organized and pages load without delay.
Kavion Path Shop – Browsing effortless, layout clean and product details straightforward.
MasterStrategicSkills – Helps users focus on skill mastery with a strategic, intentional mindset.
StrategicLearningHub – Offers tools and insights for intentional and focused skill development in business.
BondAccess – Clear paths to content, easy to use for all users.
QelaroGo – Accessible design that anyone can understand.
commercialbondconnect – Seems credible, ideal for connecting buyers and sellers of commercial bonds.
commercialbondcenter – Well organized, highlights security for businesses managing bonds digitally.
progressmoveswithfocus point – Layout is intuitive and the information is concise and easy to follow
progressmoveswithfocus web – Easy to navigate, clean style, and messaging is clear and concise
Mavero Network – Fast loading, browsing smooth and site feels reliable.
quick link – Pages load quickly, layout is clear, impression is favorable
start browsing – Minimal clutter, organized structure, site feels reliable and professional
clyra web – Thoughtful layout, readable content, and overall smooth browsing experience
clyra network – Neatly structured pages, content is clear, and design choices are consistent
professional trust portal – Appeals to organizations prioritizing dependable business relations.
Yaveron Market – Pages load quickly, navigation intuitive and buying experience simple.
explorefuturedirections – Inspiring content, learning about future directions feels engaging and useful today.
trusted corporate space – A reassuring presentation for organizations valuing trust.
Visit Yaveron – Layout clean, content loads quickly and browsing felt effortless.
explorefuturedirections – Inspiring content, learning about future directions feels engaging and useful today.
shopping platform – Feels dependable, product pages load fast, and buying is hassle-free.
purchase page – Reliable and fast, product pages load quickly, and ordering is smooth.
ProfessionalBondSolutions – Great platform overall, information is clear and genuinely helpful today.
ProfessionalBondSolutions – Great platform overall, information is clear and genuinely helpful today.
brivox.click – Smooth visit overall, pages open quickly and everything feels easy to read
brivox page – Everything loads smoothly and the content feels well-spaced
Korivo Central – Pages open quickly, interface simple and overall site feels professional.
Online Shopping Tips Hub – Makes choosing the right products online simpler and faster.
Korivo Network – Click redirects quickly, site organized and content helpful and clear.
store page – Fast site, well-organized sections, easy to move around.
Value-Focused Online Shop – Very practical advice for maximizing efficiency and making smart purchases.
Xelivou Lane Shop – Interface minimalistic, pages load quickly and checkout worked perfectly.
online store – Fast loading, well-organized sections, and overall navigation is smooth.
Vixor Link – Clean interface, content well-structured, and navigation was intuitive.
Vixor Online – Fast-loading pages, intuitive layout, and product details easy to understand.
Plivox Lane Hub – Fast loading, interface minimal and shopping process easy.
Plivox Hub – Fast loading pages, layout straightforward and product details easy to understand.
navix web portal – Pages opened quickly, ordering process effortless and overall smooth.
navix hub – No delays, ordering process smooth and pages displayed properly.
AppliedSolutionsCenter – Focuses on delivering immediately usable approaches for practical problem solving.
PracticalThinkersNetwork – Emphasizes real-life strategies over theoretical concepts.
Mivaro Store – Pages open smoothly, layout minimal and overall experience reliable.
Visit Mivaro Space – Navigation smooth, content clear and the site feels very reliable.
trustedalliancenetwork – Projects professionalism, designed to attract consistent and reliable business partners.
trustedbusinesshub – Gives an impression of reliability, ideal for building consistent business connections.
PortalRixar – Layout clear, links worked correctly, and pages loaded without delays.
RixarDirect – Fast-loading pages, clean design, and links all functional.
directionanchorsprogress platform – Smooth experience, minimal clutter, and the information is straightforward
visit nixra – Clean layout and intuitive navigation, really enjoyed exploring
directionanchorsprogress corner – Content is easy to scan, layout is tidy, and pages respond quickly
official site – Smooth experience, minimal design, everything works flawlessly
enterprise synergy hub – Name communicates cross-border collaboration possibilities.
corporate cooperation hub – Implies strong collaborative potential for enterprises worldwide.
official plexin – Well-organized pages, easy-to-read text, and browsing is effortless
plexin web – Clear and concise, navigation works well, and pages load smoothly
store page – My order arrived safely and everything looked great.
NaviroTrack Hub – Pages load quickly, navigation is smooth and content easy to follow.
product site – Packaging was done carefully and the order was hassle-free.
Zorivo Hub Online – Site opens quickly, interface simple and navigation effortless.
zylavo online – Layout simple, product pages clear and browsing straightforward.
Zorivo Hub Next – Pages responsive, interface clean and browsing was hassle-free.
zylavostore online – Layout uncluttered, product details useful and visuals clean.
Explore Smart Options – Well-structured guidance that highlights opportunities I previously overlooked.
Velro Base – Navigation simple, site fast and buying steps easy to follow.
Business Options Guide – The insights helped broaden my thinking around sustainable growth.
BondPortal – Easy-to-read listings, pages load quickly, and products simple to review.
Visit Velro – Clean layout, pages load fast and finding information is effortless.
ZexonSpot – Detailed product pages, smooth browsing, and shopping experience very pleasant.
Qulavo Online – Browsing effortless, pages responsive and content easy to access.
Qulavo Direct – Layout neat, links work properly and finding products is quick.
Zylavo Express – Fast site performance, clear layout, and searching for items was simple.
Visit RavionCore – Pages open fast, layout clean and browsing feels smooth and organized.
Zylavo Express – Fast site performance, clear layout, and searching for items was simple.
top resource – Well-organized interface, quick page loads, information is straightforward
online shopping portal – Sleek and functional, matches modern retail expectations.
zentrik.click – Clear layout, content is easy to follow and navigate
check directionpowersmovement – Clear structure, readable text, and browsing is effortless
retail insights hub – Design and structure align with contemporary shopping behaviors.
directionpowersmovement source – Layout is tidy, content is practical, and navigation feels effortless
xavix link – Clear and professional layout with smooth browsing throughout
xavix web – Attractive layout, smooth browsing, and easy-to-use site structure
xaliro buy – Mobile browsing was smooth, and the categories were easy to follow.
brand store – Layout is logical, mobile navigation was simple and smooth.
tekvo access – Clear layout, concise text, and browsing feels comfortable and natural
official tekvo – Organized sections, readable headings, and browsing feels intuitive
Trixo Central – Pages open quickly, content organized clearly and shopping steps simple.
PlavexNavigator – Pages load quickly, layout clean, and browsing is simple.
PlavexPortal – Clear navigation, organized sections, and moving between pages is easy.
Kryvox Edge – Fast loading site, navigation easy and product details accurate.
Kryvox Hub Online – Site fast, pages structured and browsing felt natural.
ShopEaseOnline – Practical and fast, finding and purchasing items is effortless.
Xelarionix Hub – Smooth interface, layout clear and purchase process intuitive.
main hub – Found it by accident, layout is friendly and information clear.
nolra web hub – Fast-loading pages, simple navigation and clear product listings.
Xelarionix Express – Interface neat, browsing effortless and checkout worked without problems.
xelarion link – Discovered today, appears legit and browsing is comfortable.
nolra online hub – Clean site structure, pages responsive and filtering works well.
Learn From Experts – The material is insightful and gives me ideas I hadn’t considered.
Leadership Insights Lab – Lessons shared here helped me rethink my approach to business challenges.
Xelra Market Hub – Pages load smoothly, navigation intuitive and product info clear.
Xelra Web – Layout minimal, pages load quickly and navigation intuitive for all users.
Zaviro Online – Layout neat, content clear, and purchasing workflow is straightforward.
Zaviro Point – Clear design, pages organized logically, and checkout process intuitive.
Nevironexus Market Hub – Click redirects fine, layout clear and navigation easy to follow.
online marketplace hub – Modern interface emphasizes speed and convenience for today’s users.
main hub – Clear sections, smooth browsing, and information is well structured
digital purchase hub – Reflects current online shopping preferences with clarity and simplicity.
online portal – Everything loads smoothly and explanations are concise and clear
shopping platform – I was happy with how politely they responded.
actionpowersmovement destination – Well-structured layout, clear information, and overall browsing is simple
shopping platform – I was happy with how politely they responded.
actionpowersmovement web – Information is well-presented, navigation is simple, and pages feel responsive
Morix Store – Clean interface, pages open quickly and checkout process works without issues.
Morix Base – Smooth navigation, content loads quickly and shopping feels reliable.
axory page – Simple, clean design with organized information and smooth navigation
axory link – Tidy structure, information is easy to read, and navigation is intuitive
PortalQela – Loaded rapidly, and the pages contained useful details.
ClickHub – Pages loaded instantly, and the content was relevant and helpful.
NolaroView Central – Fast redirect, interface clean and overall browsing experience feels effortless.
zorivoshop link – Fast, clean, and easy to browse without distractions.
Rixaro Direct Shop – Site responsive, content straightforward and buying process simple.
zorivo hub online – Fast-loading pages, navigation smooth and design user-friendly.
Rixaro Direct Shop – Site responsive, content straightforward and buying process simple.
olvra online – Smooth experience, structured content, and dependable information
olvra.click – Fast browsing, content is reliable and pages are neatly organized
International Business Community – Encourages worldwide networking in a simple, organized way.
Worldwide Collaboration Hub – Clear organization that supports international cooperation.
MorixoPortal – User-friendly design, sections easy to navigate, and finding items is quick.
MorixoEase – Responsive design, content well-placed, and browsing feels effortless.
Kryvox Hub – Interface simple, products easy to find and checkout steps straightforward.
Kryvox Market Hub – Browsing easy, interface responsive and product descriptions clear and concise.
brand store – Fresh feel, products are reasonable, and payment went smoothly.
Kelvo Main – Pages loaded quickly, navigation intuitive and overall shopping felt effortless.
official site – Simple structure, responsive pages, everything works as expected
Kelvo Spot – Navigation smooth, product details visible, and checkout simple.
marketplace – Layout is clean, products are reasonable, and ordering was effortless.
explore here – Pages are well-structured, navigation is simple and natural
EasyClickNeviron – Navigation smooth, content structured well, and checkout or actions straightforward.
NevironHome – Pages loaded fast, content informative, and browsing felt smooth and reliable.
ideasbecomeforward link – Pleasant browsing, clear headings, and a well-thought-out structure
ideasbecomeforward link – Pleasant browsing, clear headings, and a well-thought-out structure
Zylavo Hub Online – Interface minimal, pages responsive and product info easy to read today.
olvix portal – Logical layout, readable content, and site feels welcoming for users
olvix portal – Logical layout, readable content, and site feels welcoming for users
nexlo portal – Fast navigation, checkout straightforward and content organized well.
nexlo center – Quick pages, simple checkout, and everything worked as expected.
brand store – Products are organized well, filtering made browsing much easier.
Pelix Central – Fast loading, product info clear and overall shopping experience straightforward.
product site – Items are displayed neatly, filtering options made searching simple.
Pelix Select – Interface clean, content straightforward and checkout process seamless.
Vexaro Lane – Pages open quickly, layout clean and product info easy to read.
Qulavo Hub Shop – Clean design, responsive pages and checkout was easy to follow.
Qulavo Hub Shop – Clean design, responsive pages and checkout was easy to follow.
TrustedDealsOnline – Easy-to-use site, deals are clearly listed and purchasing feels safe.
TrustedDealsOnline – Easy-to-use site, deals are clearly listed and purchasing feels safe.
Korla Store – Navigation easy, pages load fast and the checkout process was clear.
Korla Online Shop – Pages load quickly, layout simple and checkout felt effortless.
marketplace – Found this while browsing and added it to my list.
marketplace – Found this while browsing and added it to my list.
Korva Platform – Found this randomly, everything feels clean and well spaced
Explore Korva – Stumbled onto it and the clean, modern layout stood out
actioncreatesforwardpath link – Minimalistic design, clear headings, and overall user experience is pleasant
actioncreatesforwardpath page – Well-arranged sections, content is digestible, and interface is smooth
Torix Point – Navigation simple, site intuitive, and shopping experience stress-free.
nolix.click – Smooth browsing, interface is tidy and content is immediately clear
Torix Portal – Interface clean, content structured well, and checkout quick and easy.
PrixoSpot – Interface tidy, pages responsive, and buying items easy to complete.
nolix homepage – Easy-to-use layout with content that’s simple to read and understand
PrixoCenter – Pages responsive, navigation intuitive, and purchasing items simple.
QuickBond – Smooth transitions, all pages loaded correctly, and site seemed safe.
XalorNavigator – Very responsive, links worked perfectly, and browsing was simple.
klyvo spot – Clear and minimal layout, content is approachable and trustworthy
click portal – Fast checkout experience, confirmation arrived quickly afterwards.
Cavaro Hub Online – Browsing intuitive, content well structured, and everything worked as expected.
click shop – Payment went through without issues, confirmation showed up fast.
Visit Cavaro – Link opened without issues, layout clear, and information seemed trustworthy.
Zexaro Forge World Shop – Fast pages, intuitive interface and browsing feels effortless.
Visit Zexaro Forge – Pages responsive, layout clear and browsing felt effortless.
retail website – The store layout is clean, info is easy to follow, and images correspond to the items.
shopping site – The site is tidy, product details make sense, and pictures reflect the items well.
Zarix World – Pages load fast, content clear and overall shopping experience reliable.
Zarix Lane Shop – Layout intuitive, product info easy to read and checkout process straightforward.
landing hub – Easy-to-follow design, fast-loading pages, very straightforward browsing
online portal – Fast navigation, intuitive layout, explanations are concise
GlobalBusinessExplorer – Practical and clear, supports learning about international business relationships efficiently.
visit focusdrivesmovement – Straightforward layout, pages load quickly, and content is clear
GlobalBusinessInsights – Structured and helpful, supports learning about worldwide business networks.
focusdrivesmovement source – Structured layout, fast-loading pages, and intuitive navigation throughout
QuickUlvaro – Layout is intuitive, product info is clear, pages open without delays.
EasyUlvaro – Pages open smoothly, product info well laid out, site feels professional.
EasyRixva – Navigation intuitive, site loads fast, and overall experience feels reliable.
RixvaCenter – Layout simple yet professional, pages responsive, and shopping experience pleasant.
Mivaro Network – Layout organized, browsing smooth and checkout steps simple.
Mivaro Center – Layout professional, pages load quickly and finding information was simple.
Brixel Trustee main homepage – The site presents information clearly, with navigation that feels natural.
Check out Brixel Trustee – Navigation is seamless, and the site presents information cleanly.
Explore Maverounity online – A strong presentation that feels both professional and trustworthy.
zaviroplex site – Link functioned as expected, content relevant and easy to read.
Maverounity landing page – The structure and visuals make the project feel trustworthy.
ClickEase – Pages responsive, layout clear, and content accessible without issues.
zaviroplex main – Worked fine, page loaded well and content aligned with expectations.
ClickXpress – Pages open quickly, layout professional, and navigation intuitive.
Quvexa Holdings Official Hub – Professional feel, organized content, and navigation is intuitive throughout.
Zavirobase Express – Pages load promptly, browsing effortless and content clearly displayed.
Zavirobase Click – Site responsive, navigation intuitive and browsing feels natural.
Kryvox Bonding web portal – Simple navigation, tidy layout, and the content is easy to trust.
Kryvox Bonding digital site – Organized pages, smooth navigation, and details feel credible and well-presented.
Morixo Trustee business site – Straightforward layout, content is accessible, and the site feels credible.
Morixo Trustee main site – Organized layout, readable content, and browsing is effortless.
qavon page – Modern design, content is clear, and browsing is effortless
online storefront – Payment felt protected and the receipt email was immediate.
qavon network – Clear structure with modern design and concise information
shopping platform – The transaction felt safe and emails came through fast.
Learn about Nolaro Trustee – Professional appearance, sections are easy to scan, and users can navigate effortlessly.
Nolaro Trustee hub – Clear sections, easy-to-follow layout, and users can quickly find what they need.
Qelaro Bonding platform – Clear structure, professional appearance, and browsing is simple and smooth.
Qelaro Bonding network – Concise content, intuitive navigation, and the site feels polished.
Kryxo Next – Interface clear, navigation intuitive and checkout worked perfectly.
Kryxo Select Shop – Fast pages, interface neat and product details well organized.
RelationshipNavigator – Helpful and clear, business relationship strategies are easy to follow.
landing hub – Pages appear instantly and the structure is easy to understand
explore nixra – Lightweight pages and smooth navigation, very pleasant experience
StrategicRelationsCenter – Practical guidance, forming business connections feels intuitive and manageable.
QuickBond – Fast site, clean layout, and navigation feels natural.
YavonAccess – Pages load instantly, content clear, and navigation is effortless.
Zylra Online Shop – Pages fast, product info clear and overall experience reliable.
Zylra Zone – Product details clear, interface simple and checkout steps straightforward.
focusbuildsenergy spot – Minimal layout, logical flow, and the overall experience is smooth
Quvexa Trust Main Page – Clean design, structured content, and users can navigate easily.
focusbuildsenergy source – Well-structured design, clean pages, and navigating feels effortless
Cavaro Bonding digital site – The site is visually clean and information appears credible.
Visit Cavaro Bonding – The platform is engaging, with a tidy layout and reliable content.
LongTermVisionPro – Insightful content, spotting promising long-term options is quick and easy.
FuturePlanningHub – Insightful platform, long-term options are easy to find and analyze.
Zavix Central – Minimalist layout, content clear, and ordering process worked perfectly.
Zavix Online – Layout simple, information organized well, and completing purchases was easy.
main link – Opened instantly, navigation smooth and content accurate.
web portal – Fast response, pages rendered properly and everything made sense.
Ravion Bonded homepage – The platform is intuitive, with detailed guides and ongoing updates.
Ravion Bonded web page – Documentation is clear, updates are regular, and the platform feels trustworthy.
Visit Nixaro – Content well organized, navigation smooth and purchasing straightforward.
Visit Nixaro – Content well organized, navigation smooth and purchasing straightforward.
Kryvox Capital web page – Clear sections, intuitive layout, and the site exudes a professional, trustworthy vibe.
marketplace – Clear design helps me focus on products without getting lost.
Explore Kryvox Capital – Organized pages, straightforward information, and the interface seems reliable.
marketplace – Clear design helps me focus on products without getting lost.
Nolaro Trustee online platform – Smooth interface, concise sections, and navigation is simple to use.
Ravion Bond Resources – Simple structure, easy-to-read pages, and site feels trustworthy.
Nolaro Trustee digital site – Clear hierarchy, organized content, and browsing is straightforward.
Explore Naviro Bonding – Clean design, effortless navigation, and content is easy to understand.
Naviro Bonding digital site – Simple pages, structured content, and users can navigate naturally.
Qelaro Capital platform – Smooth browsing, organized content, and pages load quickly.
Qelaro Capital network – Clean headings, structured pages, and navigation is easy for users.
QuickClickUlvion – Pages open instantly, interface clean, and content well-organized.
Zexaro Direct – Pages organized, items easy to find and ordering without confusion.
Zexaro Online Hub – Fast loading, layout clear and overall shopping simple to complete.
UlvionDirect – Fast-loading pages, neat design, and all sections easy to navigate.
web access – Pages appear instantly, design is clean and easy on the eyes
Zavro Network – Layout intuitive, pages responsive and checkout steps easy to complete.
handy page – Fast response, organized content, navigation felt natural
Zavro Market – Pages respond fast, content organized and checkout steps straightforward.
ShopRavlo – Smooth navigation, clear visuals, and informative product pages.
RavloSpot – Clean design, images are precise, and product info is easy to access.
Cavaro Trust Group official page – Fast performance and logical layout make content easy to absorb.
Cavaro Trust Group main homepage – Responsive pages and clear details create a seamless browsing experience.
signal guides growth web – Clear hierarchy and minimal design help focus on the content
signal guides growth link – Easy to navigate, concise content, and clear layout throughout
official ravixo – Neat layout, fast-loading pages, and text that’s practical and clear
ravixo.click – Fast-loading pages with clear, concise, and useful information
Ravion Capital Landing – Simple interface, clear information, and overall site experience is smooth.
online site – Concept is appealing, content is clear, and the structure is consistent.
network page – Structured layout, information is easy to read, and the site concept stands out.
DiscoverInnovations – Fun and clear explanations, new concepts are easy to follow.
BrixelFlow – Pages open fast, interface clean, and content presented clearly.
Vixaro Next – Fast browsing, product pages clear and navigation intuitive overall.
InnovationEdgeOnline – Clear and engaging lessons, understanding innovations feels simple.
Vixaro Marketplace – Pages responsive, interface clean and checkout completed smoothly.
Cavix homepage – The navigation feels intuitive, and the goal of the site is well presented.
Visit Cavix – The layout is straightforward, and the site’s purpose is communicated clearly.
marketplace – The store had logical shipping choices, and arrival estimates were reliable.
Visit Korivo – Site opened without issues, layout clean and finding products was easy.
Korivo Zone – Site opened fast, content clear and purchasing steps easy to follow.
online storefront – Shipping choices made sense, and expected delivery times were trustworthy.
Pelixo Bond Group main page – Well-arranged sections, clear explanations, and browsing is intuitive.
Check out Kryvox Trust – Pages are responsive, browsing feels smooth, and details are immediately clear.
Pelixo Bond Group online – Intuitive navigation, readable layout, and the site feels reliable.
Kryvox Trust main homepage – Fast, intuitive browsing, well-structured content, and details are easy to find.
Visit Qelaro Trustline – Well-structured pages, fast loading, and browsing is intuitive.
Qelaro Trustline official site – Intuitive layout, concise content, and navigation works without effort.
Naviro Capital main homepage – Well-structured content, professional design, and fast-loading pages.
Naviro Capital online portal – Clear hierarchy, polished visuals, and browsing feels effortless.
TrivoxLink – Smooth click, site responded immediately and content appeared accurate.
TrivoxPortal – Smooth redirect, content appeared accurate and navigation was easy.
Ravion Trustline Portal – User-friendly interface, content loads quickly, and navigation works smoothly.
Velixonode Web – Clean design, links open properly and navigation easy to follow.
Velixonode Point – Pages load fast, content well organized and shopping experience straightforward.
Cavaro Union web portal – Clean presentation, consistent brand, and purpose is clearly outlined.
Cavaro Union web experience – Cohesive branding, neat layout, and the intent behind the platform is clear.
signalactivatesgrowth online – Minimal distractions and content is presented in a clear way
official signalactivatesgrowth – Clear sections and well-presented information make browsing simple
XelarionPortal – Layout tidy, pages fast, and finding items was straightforward.
PortalXelarion – Navigation simple, layout clear, and finding products is quick.
NextLevelGrowthGuide – Insightful content, strategies for growth are presented in simple steps.
StrategicGrowthHub – Well-organized guidance, growth concepts are easy to apply in practice.
Xelivo Direct – Pages load smoothly, navigation simple and purchasing steps easy to follow.
Xelivo Market – Browsing smooth, site feels reliable and ordering was straightforward.
web platform – Security measures are explained well, giving me peace of mind during browsing.
digital hub – Browsing felt safer thanks to clear details about security.
Rixaro Capital Hub – Logical structure, concise explanations, and navigation flows naturally.
product site – Smooth initial visit, no errors or weird behavior.
shopping site – Everything displayed correctly, giving a positive first impression.
online portal – Clear sections, responsive pages, navigation feels effortless
official site – Quick access, minimal clutter, content is easy to understand
Learn more at Naviro Trustee – Information is easy to locate, reinforcing a sense of reliability.
Naviro Trustee business site – The content is easy to follow and presented in a structured manner.
Check Pelixo Capital – Smooth navigation, easy-to-read content, and layout feels reliable.
QulixPoint – Pages load without delays, layout clean, and overall shopping experience pleasant.
Explore Pelixo Capital – Simple interface, concise explanations, and navigating the site feels effortless.
EasyQulix – Professional layout, navigation intuitive, and finding items is straightforward.
Qorivo Bonding Main Page – Fast interface, organized content, and the site is easy to follow.
Qorivo Bonding Web – Clean sections, easy navigation, and content is logically presented.
QuickXpress – Site responds quickly, interface clear, and finding what I needed was simple.
BondXpress – Pages load fast, design feels clean, and content is simple to navigate.
DigitalShopGuide – Well-organized layout, shopping online feels natural and easy.
bryxo hub – Straight to the point site where navigation behaves well
SmartCartHub – Smooth and efficient, shopping online feels natural.
Visit Neviror Trust – Clean design, reliable information, and navigating the site is effortless.
bryxo network – No-frills website with reliable movement between pages
Neviror Trust official page – Professional layout, content is transparent, and browsing feels smooth.
Kavion Bonding homepage – Well-presented information, strong organization, and straightforward messaging.
Kavion Bonding official site – Reliable layout, solid organization, and messages are easy to understand.
Rixaro Holdings Online – Simple headings, clear content, and browsing feels seamless.
directionunlocksgrowth network – Crisp design, easy-to-follow sections, and pages load quickly
Visit Pelixo – Pages load quickly, navigation intuitive and shopping experience pleasant.
Pelixo Store – Navigation effortless, pages fast and product details clearly presented.
directionunlocksgrowth link – Simple navigation, readable content, and the overall feel is professional
main portal – Clean design, easy-to-read information, very user-friendly.
quvra hub – Clean layout, content is simple and very easy to follow.
store page – Items are listed neatly, and filtering helped me focus on what I wanted.
shopping platform – Products were clearly categorized, filters helped me focus quickly.
trusted resource – Clear design, pages respond quickly, content is informative
quick link – Simple interface, smooth browsing, information is concise and readable
Pelixo Trust Group digital site – Clear hierarchy, easy-to-follow content, and navigation feels natural.
Pelixo Trust Group platform – Well-laid-out sections, concise content, and navigation is straightforward.
Mivon official page – Clear structure and open communication make a strong impression.
Rixaro Trust Online – Well-laid-out content, smooth interface, and browsing is effortless.
plixo online hub – Navigation simple, layout clean and checkout process seamless.
Mivon online platform – A straightforward approach helps build early confidence.
plixo e-store – Fast loading pages, intuitive design and easy ordering steps.
Visit Kavion Trustee – The design is sleek, trust signals are visible, and pages feel refined.
Kavion Trustee online platform – Clear presentation, trust elements stand out, and the design is smooth.
Qorivo Holdings Official Portal – Easy interface, organized text, and overall experience is user-friendly.
Qorivo Holdings Official – Easy-to-use site, clear headings, and the layout feels reliable.
Official Torivo Site – Clean concept, seems reliable and built with longevity in mind.
QoriLink – Clean layout, content well-organized, and navigating between sections feels effortless.
TorivoUnion Portal – Promising structure, seems safe enough for serious long-term use.
ClickEaseQori – Layout neat, pages fast, and site structure makes navigating simple.
UlviroBondGroup Overview – Came across it, looks legitimate and information is well-organized.
Neviro Link – Pages responsive, layout clean and shopping process works without issues.
Neviro Union online site – Clean sections, professional layout, and browsing is effortless.
UlviroBondGroup Resource – Found today, looks legit and details are organized clearly.
Neviro Access – Layout neat, information accurate and overall shopping experience pleasant.
Neviro Union web page – Easy-to-read sections, organized information, and navigation feels seamless.
TrustedBuyOnline – Secure and convenient, checkout process is smooth and efficient.
SmartPurchasePro – Easy-to-use platform, shopping online is hassle-free and smooth.
progressmovesintelligently access – Straightforward navigation, concise content, and smooth browsing experience
progressmovesintelligently access – Straightforward navigation, concise content, and smooth browsing experience
Torivo Bond Portal – Well-organized content, simple navigation, and the site feels reliable.
cavix link – Nice flow overall, the design stays simple while sharing good info
this web portal – Content is readable, site responds well, and overall design feels professional.
shopping platform – I appreciated the straightforward checkout with no distractions.
qorla hub – Pages load quickly, text is clear, and the layout looks polished.
official cavix – Browsing felt comfortable thanks to a clear layout and balanced content
product site – Easy and direct checkout, no popups slowed the process.
brixo shop online – Responsive pages, order process smooth and delivery info reliable.
shop brixo – Layout is clean, products easy to find and shipping details well presented.
Qelix online platform – Everything flows naturally, with details presented in a way that avoids confusion.
Xeviro Home – Pages load quickly, navigation smooth and products easy to find.
Xeviro Online Market – Fast loading, layout intuitive and product info easy to follow.
Qorivo Trustline Info – Well-arranged content, fast navigation, and interface feels user-friendly.
Qelix main homepage – The site is easy to browse, with information presented without confusion.
Qorivo Trustline Hub – Organized content, professional look, and pages are easy to explore.
TrivoxBonding Access – Discovered this platform, information seems clean and easy to understand.
TrivoxBonding Overview – Came across this resource, content appears accurate and professionally written.
FuturesExplorerPro – Structured guidance, exploring upcoming trends is straightforward and intuitive.
Torivo Capital Online – Well-laid-out pages, smooth browsing, and information is accessible.
FutureVisionOnline – Engaging and practical, understanding trends and forecasts feels easy.
ToriVoConnect – Design minimal, site loads quickly, and shopping experience effortless.
SafeToriVo – Smooth browsing, intuitive interface, and checkout process straightforward and reassuring.
Visit Nixaro Holdings – Clean layout, intuitive navigation, and the site feels dependable overall.
Nixaro Holdings official page – Polished design, structured information, and the experience is smooth.
actiondrivesdirection access – Straightforward navigation, content is easy to understand, and layout is clean
actiondrivesdirection corner – Readable text, clear headings, and pages are responsive overall
SmartLearningBase – Lessons are concise and clear, making knowledge easy to absorb.
LearningNavigator – Educational and well-organized, concepts are easy to follow.
web shop – It gives the impression of a real store with visible policies.
shop website – The layout and info suggest a legitimate operation.
main hub – Layout is tidy, reading material is clear, and moving from page to page is effortless.
home page – Simple and clean, info is organized, and navigating the site is easy.
kavion center shop – User-friendly design, policies obvious and checkout smooth.
kavion main site – Trust badges visible, product info clear and site overall reliable.
Morixo Link – Browsing straightforward, content clear and checkout steps easy to follow.
Morixo Center – Navigation smooth, content well structured and product info easy to read.
Qulavo Bonding Home – Smooth navigation, content is easy to understand and pages load quickly.
Qulavo Bonding Hub – Organized structure, professional appearance, and pages are easy to browse.
Xaliro Drive main site – The concept is innovative, and the site runs smoothly from page to page.
Xaliro Drive homepage – Everything works without delay, giving a smooth and professional feel.
TrivoxCapital Access – Smooth browsing experience, offerings are explained plainly.
TrivoxCapital Online – Nice layout overall, details are easy to find and feel credible.
klyvo hub – Well-organized layout, clear content, and smooth overall experience
zalvo page – Organized content with responsive pages and easy-to-follow layout
Nixaro Partners info hub – Simple layout, readable sections, and users can find key details quickly.
zalvo homepage – Clear layout, information is easy to locate, and navigation feels smooth
Nixaro Partners digital site – Clear design, accessible menus, and the site projects professionalism.
Ulxra Connect – Well-structured pages, layout intuitive, and browsing items felt natural.
Ulxra Home – Pages loaded fast, navigation intuitive and browsing through products was effortless.
signalcreatesflow zone – Easy to follow design, nothing feels overwhelming or confusing
signalcreatesflow guide – Clean interface with readable content, everything feels polished
Zaviro Online Market – Navigation intuitive, pages organized and purchasing straightforward.
Zaviro Live – Layout clean, browsing simple and product details easy to understand.
brand store – The site felt responsive and browsing products was seamless.
storefront – Smooth page responses made the entire shopping experience enjoyable.
DecisionPathway – Step-by-step advice, making decisions simple and confident.
BondXpress – Functional layout, pages responsive, and product information clear.
ulvario hub – Clicked without problems, page loaded quickly and everything was as expected.
SmartDecisionHub – Simple and practical tips, content makes navigating decisions easier.
ZexaroSpot – Clean interface, product pages clear, and navigation is effortless.
digital portal – No issues clicking, page responded fast and content was correct.
Plavex Capital main site – Professional layout, content is concise, and navigation is simple.
Check Plavex Capital – Smooth interface, concise sections, and finding details is effortless.
Qulavo Capital Online – Fast interface, well-organized content, and pages are easy to explore.
Qulavo Capital Main Page – Easy-to-read sections, professional layout, and information is easy to follow.
globalenterprisealliances – Informative platform, global alliance strategies are explained clearly and practically.
Visit Trivox Trustline – Transparency is noticeable, most investor doubts seem well covered.
globalenterprisealliances – Informative platform, global alliance strategies are explained clearly and practically.
Ulvix web experience – The site feels uncluttered, with information presented logically.
UlviroCapitalGroup Online – Simple site design, content is clear and easy to digest.
TrivoxTrustline Overview – Honest presentation, it explains things investors usually ask about.
Ulvix business site – Clear presentation and organized content help users navigate efficiently.
UlviroCapitalGroup Online – Simple site design, content is clear and easy to digest.
online hub – Pages rendered fast and the layout made sense
visit site – Straightforward design and fast response, pleasant to explore
Kavion Trust Group web experience – Content is accessible, navigation works perfectly, and first impressions are strong.
Kavion Trust Group online hub – Well-laid-out pages, clear messaging, and navigation feels effortless.
Nixaro Trustline official site – Professional design, readable sections, and the interface feels reliable.
Nixaro Trustline online – Clean design, readable menus, and the site projects professionalism.
Trivox Gateway – Pages load quickly, navigation intuitive and overall experience pleasant.
Trivox Gateway – Pages load quickly, navigation intuitive and overall experience pleasant.
ClickEaseKori – Pages load fast, site feels organized, and checkout process smooth.
KoriPortal – Design minimalistic, content readable, and purchasing process smooth.
check focusanchorsmovement – Minimal clutter, clear sections, and navigation feels seamless
shopping destination – The descriptions sounded natural and not forced.
shopping site – The wording felt honest instead of salesy.
focusanchorsmovement corner – Simple structure, clean pages, and navigation is smooth
VelixoLink – Pages open quickly, content structured logically, and site navigation is simple.
VelixoCenter – Well-structured interface, pages open quickly, and browsing feels effortless.
bonded link – Appears reliable, pages organized and content readable.
main portal – Clean design, branding solid and browsing simple.
Explore Plavex Holdings – Simple interface, structured content, and overall user experience feels natural.
Plavex Holdings business portal – Intuitive pages, easy-to-follow content, and navigation feels seamless.
zavik network – Clear, well-organized interface with helpful and accessible content
zavik source – Pages are tidy, information is concise, and content is easy to read
Official site overview – Solid first impression, the layout looks clean and the information is easy to digest.
SafePurchasePro – Smooth and user-friendly, online buying is straightforward and secure.
Visit this online platform – The design and wording give off a trustworthy, polished feel.
TrustedMarketHub – Reliable and easy to use, online shopping is hassle-free and safe.
Qulavo Capital Platform – Clean sections, readable details, and the site feels professional.
Qulavo Capital Web – Simple navigation, clear headings, and information is presented neatly.
UlvaroBondGroup Info – Came upon it today, messaging is clear and layout feels uncluttered.
UlvaroBondGroup Info – Came upon it today, messaging is clear and layout feels uncluttered.
Korivo Capital homepage – Visual appeal is strong, content is structured logically, and browsing is smooth.
Brixel Bond Group website – Clear messaging and polished visuals enhance overall confidence.
Korivo Capital main homepage – Well-organized content, professional design, and browsing is simple and logical.
UlviroTrust Main Site – Polished design, content is clear and calm, promoting confidence.
Brixel Bond Group official page – A well-structured site that sends strong signals of legitimacy.
UlviroTrust Network – Smooth design, trust messaging is clear and comforting.
pelvo portal – Clear pages, minimal clutter, and content flows naturally
start browsing – Clean design, simple navigation, content feels well organized
explore now – Fast pages, minimal clutter, information is clear and easy to read
pelvo info – Simple design, structured content, and browsing feels effortless
QurixHub – Very responsive, all pages displayed clearly and easy to navigate.
QurixShop – Pages loaded quickly, and the products were easy to browse.
Nolaro Capital online – Organized sections, clean design, and users can find information quickly.
Nolaro Capital digital site – Smooth browsing, readable text, and trust signals are easy to spot.
shop website – Bookmarked the page and may come back.
naviro shop – Bookmarked this site and may come back to place another order.
signalcreatesmomentum portal – Information is easy to find, and the interface feels polished
signalcreatesmomentum network – Pages are easy to navigate, and the layout feels thoughtful
EasyNixaro – Design minimalistic yet effective, browsing effortless, and information clearly presented.
xaliro portal – Everything is organized neatly, nothing flashy, content stands out.
click site – Clear layout, minimal visual clutter, easy to navigate content.
NixaroExpress – Interface simple, content accessible, and shopping process easy to follow.
Plavex Trust Group online – Clear hierarchy, concise explanations, and browsing feels effortless.
Explore Plavex Trust Group – Simple design, clear sections, and overall user experience feels natural.
Quvexa Capital Official Portal – Clear design, structured pages, and browsing is simple and intuitive.
Quvexa Capital Main Page – Clean headings, content is concise, and overall experience is straightforward.
Korivo Holdings business site – Clear content, well-organized layout, and users feel reassured throughout.
Korivo Holdings main homepage – Clear hierarchy, concise explanations, and the site feels dependable.
CoreLink – Site responded quickly and everything displayed correctly.
CoreNavigator – Clean design, pages load quickly, and browsing is effortless.
UlvaroBonding Info – Well-structured pages, fast performance and clear descriptions.
Visit Ulvaro Bonding – Smooth experience overall, pages open quickly and content is easy to read.
FutureGrowthGuide – Clear explanations, strategies are practical and simple to execute.
FutureSuccessPath – Step-by-step instructions, strategies are easy to understand and apply.
Browse the trust homepage – Clean visuals and logical menus help build confidence while reading.
VelixoCapital Hub – Came across it researching, design is polished and content clear.
explore now – Straightforward interface, pages loaded fast, very comfortable to use
See trust group overview – Everything looks consistent and approachable for careful analysis.
Brixel Capital info site – The site balances clear communication with strong brand identity.
official site – Pages loaded quickly and the interface was very straightforward
item store – Smooth experience from start to finish, friends will hear about it.
Nolaro Holdings online – Intuitive layout, readable text, and overall site experience is polished.
web shop – The process was simple and pleasant, worth telling others about.
Nolaro Holdings official site – Strong structure, easy to follow information, and browsing feels natural.
morix site – Smooth and organized experience with clear sections and readable content
TrustedAlliancesCenter – Professional insights, frameworks make building business partnerships straightforward.
official morix – User-friendly design with intuitive navigation and text that’s easy on the eyes
PartnershipGuidePro – Highly reliable, frameworks for partnerships are clear and easy to implement for companies.
digital site – Page responded quickly, layout light and info clear.
Plivox Bonding home – Easy navigation, content is clear and pages feel responsive.
landing hub – Pages appeared fast, design minimal and content understandable.
Plivox Bonding online – Organized content, smooth transitions, and site feels trustworthy.
Ulviro Linker – Layout neat, content well-presented, and browsing felt fast and easy.
Ulviro Network – Pages responsive, layout clear, and browsing experience enjoyable and intuitive.
Korivo Trustline online hub – Consistent branding, useful content, and navigation feels reliable.
official travik – Neat interface, logical flow, and overall browsing feels effortless
Learn more at Korivo Trustline – Strong identity, well-presented information, and navigation works effortlessly.
travik – Clean design, easy to navigate, and content is engaging overall
Official UlvaroCapital – Good starting impression, information is presented clearly and without fluff.
UlvaroCapital Info – Positive first look, information is easy to understand and well paced.
Nice Simple Layout – Discovered this by chance and liked how clear everything looks
VelixoHoldings Resource – Site feels smooth, content loads fast and details are clear.
Check This Page – Came across this unexpectedly, the design is easy to follow
VelixoHoldings Online – Site is easy to navigate, pages load fast and content appears transparent.
DealFinderPro – User-friendly site, shopping for discounts feels straightforward.
TopShoppingDeals – Simple and trustworthy, browsing deals is smooth and hassle-free.
Discover bonding info – Content layout feels logical and easy to digest.
Browse the bonding site – A quick visit shows clear formatting and readable content.
Plivox Capital online – Friendly interface, easy-to-read content, and navigation feels natural.
click hub – Fast link response, landing page easy to follow and understandable.
Plivox Capital hub – Professional design, clear information, and users can find what they need quickly.
direct click – Worked as intended, page loaded fast, information made sense.
NolaroHome – Site feels organized, pages load fast, and finding products was simple and effortless.
NolaroSpot – Smooth navigation, clear product info, and overall browsing without any confusion.
quorly spot – Quick and organized pages with content that’s easy to digest
quorly web – Fast site with nicely arranged content that is relevant to users
Ulvion Bond Group – Website gives a trustworthy impression, visuals are consistent and the tone feels professional.
UlvionBondGroup Network – Trustworthy first impression, consistent look and professional tone throughout.
main hub – Simple design, concise explanations, perfect for quick browsing
useful link – Clean interface, smooth experience, information is easy to digest
VelixoTrustGroup Network – Neat layout, explanations are straightforward and jargon-free.
xelio platform – Clean design, text is readable, and pages load without delay
VelixoTrustGroup Details – Smooth layout, clear content without confusing terminology.
xelio page – Simple structure, headings are clear, and browsing is comfortable
Plivox Holdings web – Concise design, smooth experience, and content is clear at first glance.
Plivox Holdings platform – Clean structure, well-presented content, and browsing is hassle-free.
SmartPremiumShopping – Clear layout, finding and buying products is simple and enjoyable.
SmartBuyHub – Smooth navigation, shopping online feels premium and effortless.
Capital investment page – First look suggests quality, will return to analyze the content.
xelariounion network – The platform seems appealing and invites further exploration.
globalbusinessunity – Informative insights, global business unity strategies are clear and useful here.
See capital platform – Looks well structured at a glance, planning to review the finer points later.
xelariounion network – The platform seems appealing and invites further exploration.
MorvaHub – Design neat, navigation simple, and content trustworthy throughout.
MorvaCenter – Clean interface, links work well, and shopping process feels natural.
check this holdings platform – Simple layout and intuitive navigation make finding information straightforward.
zaviro alliance link – Smooth navigation and informative content make the site approachable for beginners.
UlvionCapital Details – Easy-to-use site, content is logically organized and simple to understand.
review zorivo holdings – Simple navigation and well-organized content make finding information convenient.
this alliance website – Navigation is intuitive and first-time visitors will find it informative.
UlvionCapital Online – Clean layout, content is clearly presented and easy to follow.
landing hub – Pages open smoothly, design is clean, navigation is effortless
browse quvix – Clear pages, quick response, very user-friendly browsing experience
VexaroCapital Resource – Clear and polished site, concise details give a sense of reliability.
VexaroCapital Network – Professional-looking pages, information is brief yet confidence-inducing.
mivox destination – Tidy layout with concise information, everything is easy to navigate
visit mivox – Easy to navigate, layout is straightforward and content is clear
SmartMarketGuide – Clear lessons, market ideas are actionable and easy to grasp.
MarketIdeasExplorer – Clear and structured guidance, market strategies are easy to grasp and use.
explore zorivo union – Intuitive structure and clean design allow users to browse and understand content efficiently.
learn about zorivo union – Clean interface, straightforward navigation, and helpful content enhance the browsing experience.
buying made simple – Layout keeps everything accessible without confusion.
xelivo bonding network – Clear explanations and a clean interface overall.
learn about xelivo – The presentation is smooth and explanations are very clear.
quick shop center – Finding items is convenient thanks to the smart layout.
official alliance link – Easy-to-use navigation combined with professional design gives a great first impression.
main zaviro alliance page – Looks polished, navigation is simple, and the information is clear for first-time users.
qerly access – Neat pages, readable content, and overall smooth browsing experience
qerly web – Structured design, readable text, and pages load efficiently for quick browsing
Trustline web portal – A clean setup that loads fast and presents current-looking details.
UlvionHoldings Network – Appealing layout, navigation is intuitive and the overall style is modern.
Trustline platform link – A simple interface combined with smooth performance and fresh info.
UlvionHoldings Details – Sleek presentation, user-friendly interface and easy to understand.
useful link – Fast pages, organized sections, content is concise and helpful
start browsing – Simple structure, quick response times, very user-friendly overall
Corporate hub – Simple interface, quick browsing, and information is easy to grasp for first-time users.
Visit Mivarotrust – Simple layout, smooth navigation, and content is clear and easy to understand.
Xanero Network – Pages load quickly, navigation clear, and checkout steps were hassle-free.
this pact website – Simple design and helpful details create a positive visit.
cavaro pact resource – Easy navigation and clear text improve the overall experience.
Xanero Center – Fast pages, content clear, and navigating between sections felt natural.
Trust services online – Clear interface, fast browsing, and details feel credible.
Explore Korivo Trust – Smooth layout, organized sections, and information is practical and clear.
VexaroPartners Website – Smooth and intuitive, service information feels clear and trustworthy.
Blog – Well-organized articles that are enjoyable and easy to read.
VexaroPartners Main Site – Browsing is smooth, service explanations are realistic and easy to understand.
Community – User interaction is organized well, making engagement straightforward.
explore zylavo capital – Quick-loading website with clear information ensures smooth navigation.
explore zylavo capital – Quick-loading website with clear information ensures smooth navigation.
Partners – Partner information is laid out logically for quick reference.
News – Updates and announcements are organized clearly for quick readability.
Partners – Partner information is neatly arranged, providing clarity for visitors.
Portfolio – Neat layout, content is concise, and exploring projects is straightforward.
Tutorials – Guides are clear and concise, pages are easy to navigate, and information is simple to follow.
check this bonding platform – The browsing experience is smooth, and pages respond quickly.
zaviro bonding overview – Fast page response and smooth navigation make the platform easy to use.
ProRelationshipGuide – Helpful and practical, advice makes professional alliances easier to form.
TrustedAllianceOnline – Practical and reliable, supports establishing strong professional connections.
check this capital platform – So far the site looks credible and the focus is clear.
capital platform details – The site maintains a professional tone with relevant content.
learnbusinessskillsonline – Excellent learning resources, business skills are explained clearly and practically.
learnbusinessskillsonline – Excellent learning resources, business skills are explained clearly and practically.
Mivarotrust Co official page – Organized pages, clear navigation, and information is concise and useful.
Platform overview – Smooth layout, responsive pages, and helpful details are easily available.
educational insights hub – Learning materials are easy to navigate and understand quickly.
grow knowledge portal – Clear explanations and intuitive layout support smooth learning.
click here – Clear layout, concise content, very readable and accessible
browse ulvix – Clear and concise content, fast pages, very user-friendly browsing
check velon – Easy navigation, tidy layout, and information that’s straightforward
velon portal – Fast navigation, well-laid-out pages, and digestible information
Digital bond portal – Professional look, consistent navigation, and convincing explanations.
zylavo holdings overview – Clean design and structured pages make it easy to gather relevant details quickly.
Online bond info – Logical structure, pleasant design, and information appears accurate.
zylavo holdings hub – Easy-to-use interface and organized content enable fast research and navigation.
Updates – Latest announcements are presented clearly and attractively.
Official Kryvox site – Clean layout, speedy pages, and content is well organized.
Testimonials – Feedback is showcased neatly, adding trust and credibility.
Xeviro Store – Smooth navigation, site organized logically, and checkout process easy.
Platform overview – Sleek design, fast performance, and details are clearly displayed.
Official bond group site – Came across this during research, the writing feels organic and low pressure.
Xeviro Network – Clean design, smooth browsing, and checkout was easy to complete.
Bond group platform link – Discovered it in research, content reads more informative than sales-focused.
VexaroUnity Portal – Concept is engaging, content communicates its values plainly without hype.
VexaroUnity Platform – Concept is engaging, and the site communicates principles without exaggeration.
Community – Interactive sections are structured well, allowing users to engage effortlessly.
Resources – Links and files are organized neatly, making it simple to locate materials.
zaviro capital info – The website communicates key points clearly without overwhelming the visitor.
zurix info – Smooth scrolling, content is easy to digest, and pages respond quickly
capital project homepage – Well-structured layout ensures that information is accessible quickly.
Gallery – Images and visuals are displayed in a clean layout, enhancing the user experience.
official zurix – Easy to navigate, text is readable, and overall presentation is solid
Resources – Files and links are neatly structured for quick access and clarity.
Support – Pages are simple to navigate, content is reliable, and users can find guidance quickly.
Support – Pages are simple to navigate, content is reliable, and users can find guidance quickly.
Financial information portal – Neat pages, fast navigation, and content is concise and user-friendly.
Official hub – Smooth design, organized pages, and information is easy to digest.
visit xelivo trust group – Navigation is clear and browsing around doesn’t feel confusing.
xelivo trust group network – Pages connect logically, helping avoid confusion.
main zylavo trust group page – Easy navigation, clean interface, and organized layout make browsing convenient and reliable.
this trust website – User-friendly navigation and simple layout make it easy for new visitors to understand.
DealNavigatorPro – Practical and user-friendly, shopping for deals feels efficient.
DealSpotOnline – Practical platform, shopping for bargains is easy and reliable.
top resource – Well-structured design, pages load quickly, information is straightforward
browse xenvo – Smooth design, concise sections, browsing experience is effortless
collaborative growth hub – Information flows well and highlights partnership value clearly.
Investment portal – Logical layout, strong loading speed, and information is well explained.
enterprise unity network – Content feels professional and explains alliances in a straightforward manner.
Bond solutions – Smooth interface, fast-loading sections, and details are easy to grasp.
Support – Quick-access guides and helpful resources are displayed clearly for visitors.
Contact – Fast and easy-to-use interface with all essential information easy to find.
Official Kryvox platform – Smooth interface, easy-to-follow layout, and information is easy to find.
Platform overview – Easy-to-follow structure, navigation is fast, and details are straightforward.
zaviro group link – Professional branding and useful information combine for a trustworthy experience.
Official VexaroUnity – Unique concept, values are presented in a straightforward and honest way.
explore zaviro group – Well-presented content and professional appearance give confidence to visitors.
Testimonials – Customer feedback is displayed cleanly and easy to trust.
VexaroUnity Hub – Concept is solid, site communicates its mission clearly and responsibly.
Morixoline resources – Clean interface, fast browsing, and content is relevant and concise.
Contact – Intuitive menus and clear contact details make navigation simple.
morixoline.bond – Smooth navigation, pages are easy to follow and information is clear.
Contact – Navigation is simple, and contact details are easy to find.
Home – Pages load fast, the layout is clean, and content is easy to read.
Services – User-friendly design, concise content, and pages are simple to browse.
brixel bond resource – Organized sections and straightforward content make the site easy to explore.
learn about brixel bond – The site’s structure helps present information logically and clearly.
Portfolio – Clear structure, smooth browsing, and content is reliable and accessible.
Explore the holdings overview – The structure makes sense, allowing a quick understanding of the services.
Start with holdings site – The intuitive setup helps new users understand things quickly.
official vexla – Fast pages, helpful content, and a neat, user-friendly interface
vexla info – Pages load quickly, interface is smooth, and content is easy to digest
explore xeviro bonding – Speedy loading helps it feel reliable and smooth.
visit xeviro bonding – Quick loading times create a smooth and trustworthy first look.
main hub – Easy navigation, concise content, professional appearance throughout
resource page – Clean design, smooth interface, first impression is strong and professional
Portfolio – Visual content is organized neatly, making it easy for users to explore.
rixon – Smooth interface, easy to navigate, and content is straightforward
Services – Information is structured neatly, making it effortless to find what you need.
rixon hub – Well-laid-out pages, minimal distractions, and information is easy to find
Kavion official page – Overall appearance is stable, with content organized for users.
Company homepage – A solid design with organized pages and clear structure.
SafeDealsCenter – Organized and reliable, purchasing online is quick and stress-free.
Morixo overview site – Simple layout, organized menus, and researching services is quick and efficient.
Official hub – Easy-to-follow layout, responsive pages, and information is clear for users.
SmartCartHub – Fast and clear, buying products online is safe and convenient.
zaviro trustline overview – Layout is clear, and moving through sections is smooth and easy.
zaviro trustline overview – Layout is clear, and moving through sections is smooth and easy.
Code promo 1xbet telecharger 1xbet apk
brixel core network – Smooth navigation and reliable content make it easy to browse confidently.
learning with depth – Makes it easy to explore ideas that actually matter.
explore brixel core – Pages are easy to move through, load quickly, and the content appears solid.
idea learning portal – Content sparks interest and supports meaningful understanding.
Visit Kryvox Line – Pages are organized, browsing feels natural, and details are simple to access.
Services – Pages load quickly, and content is structured for fast comprehension.
Platform overview – Easy-to-follow structure, navigation is fast, and details are straightforward.
Careers – Job postings are structured simply and easy to navigate for applicants.
About Us – Well-structured layout and responsive menus make navigation effortless.
Resources – Files and links are presented logically, giving users fast access to key information.
FAQ – Clear menus, structured content, and answers are easy to locate quickly.
Downloads – Fast pages, organized sections, and files are easy to locate and access.
Visit the trust platform – Overall impression feels legitimate, and the content stays consistent.
xeviro capital link – Pages are arranged in a way that simplifies research.
Trust homepage link – Everything reads cleanly, giving the site a credible feel.
official capital link – An informative setup that makes reviewing details convenient.
Corporate hub – Neat design, quick-loading pages, and content is easy to understand.
Information portal – Smooth layout, intuitive menus, and details are presented clearly.
click here – Quick loading pages, intuitive layout, perfect for easy browsing
review brixel line – Well-presented content and smooth browsing make gathering information straightforward.
learn about brixel line – Well-organized pages and clear information allow for smooth research exploration.
trusted link – Minimalist design with reliable navigation, everything functions well
Blog – Cleanly presented posts allow readers to enjoy content without clutter.
Community – Interactive sections are easy to browse and encourage visitor participation.
zexaro bonding resource – Smooth page performance and organized information create credibility.
main zexaro bonding page – Well-presented information and responsive design make the site look trustworthy.
kavioncore.bond – Nice experience, everything loads quickly and information is concise and understandable.
kavioncore.bond – Nice experience, everything loads quickly and information is concise and understandable.
kavlo source – Easygoing browsing experience with contemporary styling
kavlo hub – Fresh interface that makes moving around the site easy
Events – Event information is presented clearly for visitors to follow with ease.
Resources – Files and links are arranged logically, making it easy to find what’s needed.
Tutorials – Step-by-step instructions are arranged logically, making learning simple and clear.
Partners – Partner details are displayed clearly, simplifying exploration for visitors.
Official bond portal – Clean design, clear sections, and information is useful for learning.
SafeDealsCenter – Organized and reliable, purchasing online is quick and stress-free.
insight clarity portal – Organized information makes understanding and applying insights effortless.
Financial platform – Clear structure, intuitive menus, and information is straightforward.
SafeDealsCenter – Organized and reliable, purchasing online is quick and stress-free.
clarity insights hub – Platform is intuitive, making information easy to locate and understand.
Downloads – Well-structured pages, quick loading, and files are easy to access.
FAQ – Intuitive menus, pages load fast, and answers are easy to find.
official velixo – Straightforward pages, tidy layout, and information is accessible quickly
learn about brixel trustco – Smooth navigation combined with organized content allows for pleasant exploration of services.
velixo – Simple and clear design, content is easy to follow and understand
check this trustco platform – Simple navigation and clean presentation make understanding the offerings effortless.
Naviro overview site – Neat design, responsive menus, and content is easy to navigate and understand.
Official Naviro Bond site – Well-structured pages, smooth navigation, and details are easy to read.
xeviro holdings network – The brand presentation feels stable and deliberate.
zexaro capital platform – Navigation is intuitive, and content is practical for understanding topics quickly.
explore zexaro capital – Clear layout and helpful information make it simple to gather research insights.
holdings platform details – The site maintains a dependable tone and visual identity.
Events – Event details are easy to find and presented in a professional layout.
top resource – Well-organized interface, quick page loads, information is straightforward
Partners – Collaboration details are well-organized and easy to navigate.
explore here – Neat design, easy navigation, content is accessible and clear
Browse capital site – The navigation feels natural, helping users absorb information without friction.
Company website – Easy-to-use menus, clean design, and straightforward explanations.
Capital web portal – Clear and structured layout simplifies exploring the platform.
Bond information hub – User-friendly structure with details presented in a clear way.
Gallery – Images and visual resources are displayed clearly, improving browsing for research purposes.
Community – Interactive content is structured neatly, making navigation and engagement easy and efficient.
professional investment site – The platform gives a trustworthy vibe for extended investing.
explore cavaroline – The design is simple, visuals are clear, and content is informative without excess detail.
official cavaroline page – The website looks polished, and concise content makes browsing quick and effective.
finance investment portal – Seems trustworthy and suitable for sustained investment plans.
trusted investment site – Reliable feel with a clean and organized interface.
financial hub – Overall feels professional, with quick navigation and clear information.
Official Naviro portal – Organized interface, simple menus, and details are quick to find.
Naviro overview site – Neat structure, intuitive navigation, and content is easy to browse.
Partners – Clean layout, intuitive menus, and information feels reliable and accurate.
Events – Structured layout, smooth browsing, and event details are easy to find.
maveroline.bond – Smooth navigation, pages load quickly, and details are presented clearly.
Digital bond portal – Clear structure, smooth page transitions, and details are straightforward.
TrustedCorporateHub – Well-laid-out platform, networking feels professional and effective.
focused future guide – Clear directions simplify thinking about long-term goals.
CorporateRelationsPro – Helpful and clear, building corporate connections is simple and reliable.
focused goals center – Clear guidance makes planning future actions intuitive.
bavix network – Simple navigation and readable sections made it pleasant
official zexaro trustline page – Easy-to-use menus and clear content make browsing straightforward.
zexaro trustline network – Easy-to-follow layout and clear content help users find what they need.
bavix resource – Well-presented site with readable text and logical sections
Partners – Partner details are well-structured and easy to find.
yaverobonding.bond – Nice experience overall, pages are organized and fairly user friendly.
Services – Pages load quickly and content is structured for effortless browsing.
yaverobonding.bond – Nice experience overall, pages are organized and fairly user friendly.
useful link – Simple design, fast loading, and pages are easy to navigate
explore now – Smooth performance, fast pages, and content is concise and easy to read
Online trust solutions – Structured layout, useful information, and a fluid browsing feel.
Trusted bond site – Well-crafted layout, clear details, and a fluid browsing flow.
Official hub – Well-organized design, fast-loading pages, and content is easy to follow.
Corporate hub – Intuitive menus, organized pages, and content is clear and reliable.
investment hub – Professional feel, responsive design, and content is clear.
investment knowledge portal – Organized content, clear headings, and fast navigation create confidence.
talix web – Minimal distractions, smooth browsing, and information is easy to locate
Downloads – Files and resources are well-organized, providing fast access for users.
Home – Clean layout, easy navigation, and content is clearly organized for visitors.
bond investment platform – Everything is structured well, giving a polished and professional feel.
bond information hub – Smooth browsing experience and clearly presented content make it professional.
Trust site access – Layout feels logical and user-friendly, helpful for getting started online.
Review trust website – Everything is easy to navigate, offering a solid introduction to basic topics.
Careers – Clean interface, intuitive menus, and details are easy for visitors to find.
bond market website – The interface feels organized, allowing easy access to details.
Updates – Organized layout, quick pages, and information is clear and reliable.
finance investment hub – The clean look and simple structure help everything load nicely.
financial hub – Navigation is simple, and content is displayed clearly.
Official Maverotrust site – Credible design, neat structure, and the site appears professionally maintained.
zorivocapital.bond – Looks solid, user friendly, provides useful details without any confusion online.
zorivocapital.bond – Looks solid, user friendly, provides useful details without any confusion online.
Maverotrust official page – Professional look, smooth layout, and overall feel is trustworthy.
FrameworkNavigatorPro – Structured and helpful, frameworks are explained clearly and effectively.
Gallery – Images load fast and are arranged clearly for visitor viewing.
Portfolio – Visuals are organized cleanly and load quickly for easy browsing.
Digital hub – Clean pages, fast navigation, and details are clear and helpful.
this capital website – Seems insightful and might be useful on a future visit.
yavero capital resource – Looks like a reliable reference worth another glance.
useful link – Intuitive layout, concise content, smooth browsing experience
quick link – Minimal design, easy navigation, information is concise
Company homepage – Organized content, reliable menus, and relevant information throughout.
Digital bond site – Logical organization, smooth menus, and easy-to-read information.
online investment site – Clear headings, logical layout, and information is easy to follow.
Partners – Clear layout and fast-loading pages make finding partner information effortless.
financial resources portal – Layout is tidy, sections are clear, and browsing feels natural.
Community – Interactive content is arranged logically, and pages load quickly for easy browsing.
secure finance portal – Smooth experience with information that is easy to digest.
finance platform – Clear layout and concise information make browsing enjoyable.
Events – Organized layout, smooth menus, and information is presented clearly.
Features – Clean design, intuitive menus, and content is concise and helpful.
investment website – Content is straightforward and doesn’t overwhelm while browsing.
Trust services online – User-friendly pages, smooth navigation, and content is simple to access.
Visit Maverotrust Co – Clear interface, smooth navigation, and finding key details is effortless.
finance knowledge page – Easy-to-read information that feels practical today.
TrustNetworkInsights – Organized and clear, global networking is accessible and practical.
InternationalTrustHub – Professional guidance, forming global connections is simple and efficient.
Portfolio – Visuals are presented clearly, making it easy to browse examples.
Blog – Articles load quickly and are displayed in a neat, readable format.
loryx source – Easy navigation, logical layout, and content flows naturally
loryx network – Pages are clear, text is readable, and overall the site keeps you interested
yavero holdings platform – Information is presented clearly, making it easy to comprehend offerings.
yavero holdings platform – Information is presented clearly, making it easy to comprehend offerings.
Korva Resource – Came across this casually, the presentation is fresh and readable
Korva Portal – Came across this and enjoyed how easy the layout is to follow
Investment site – Feels dependable, easy to navigate, and information is quickly accessible.
Digital bond site – The site appears credible, browsing is easy, and insights come fast.
Downloads – Files are well-organized and pages are easy to explore.
Features – Key details are well-structured, and navigating pages is quick and easy.
<investment knowledge portal – Fast-loading, easy-to-read content, and structured navigation.
<bond resources portal – Responsive pages, clear structure, and content is easy to scan.
bond services page – Well-organized sections and fast page loading improve usability.
bond investment site – Layout is simple, keeping information easy to access.
Contact – Professional layout, structured navigation, and content is easy to read and understand.
Home – Clean layout, intuitive menus, and content is easy to find for new visitors.
zaviroline.bond – Interface is tidy, navigation is simple, and content is presented clearly.
Official Zaviro hub – Clear navigation, readable information, and interface is simple yet polished.
bond investment hub – The site feels reliable with smooth loading and clear text.
Official xeviro hub – Everything feels structured and easy to understand.
Visit the core platform – Navigation is smooth, and the content is straightforward to understand.
Corporate site – Clean layout, quick page loads, and content is logically arranged.
Corporate hub – Minimalist pages, fast navigation, and content feels structured and reliable.
online trust service – So far it looks solid, with menus that respond smoothly.
rixarotrustco.bond – Feels dependable at first glance, and moving between sections is smooth.
Official project page – This initiative looks intriguing, and the website presents the details in a clear, confident way.
Testimonials – Feedback is presented cleanly, making it simple to read and trust.
Testimonials – Feedback is presented cleanly, making it simple to read and trust.
Project resource – The website communicates the vision clearly, leaving a good first impression.
PlanWithEase – Clear and practical guidance, learning strategy planning is simple.
SmartStrategyAcademy – Easy-to-follow resources, learning strategies feels organized and approachable.
Trust services online – Clear layout, logically arranged content, and researching key points is fast.
Official Korivo site – Smooth navigation, clearly structured content, and insights are easy to locate.
qavrix.click – Informative content, easy to read and navigate without feeling pressured
official site – Clear design, fast-loading pages, information is simple to understand
Tutorials – Guides are presented in a clear, logical format, making learning straightforward.
Resources – Organized content, intuitive menus, and smooth browsing make information accessible.
trusted bond site – Site layout is intuitive, allowing easy navigation through content.
secure finance site – Easy-to-use design helps quickly find needed information.
investment info page – Quick-loading content, clean sections, and well-organized design.
trusted site – Navigation is smooth, content is concise, and overall presentation is strong.
Official Zaviro hub – Fast-loading pages, user-friendly navigation, and information is straightforward.
Downloads – Smooth interface, well-organized layout, and information is presented clearly.
Primary platform link – Smooth navigation, helpful content, and pages are easy to browse.
Community – Clean design, easy-to-use menus, and content is well structured and readable.
bavlo access – Easy navigation, readable content, and generally positive first impression
bavlo info – Clean interface, pages are responsive, and content is easy to read
Mivaroline official page – Clean navigation, smooth interface, and helpful content is easy to follow.
Visit Mivaroline – Simple layout, smooth navigation, and information is well presented.
Line overview page – Information is structured logically, making it simple to explore the site.
Main project page – The layout is intuitive, making it simple to find the details you need.
torivobond.bond – Good first look, pages load quickly and nothing feels cluttered.
bond market website – The overall experience feels fast and streamlined.
official site – Smooth experience, minimal design, everything works flawlessly
official site – Smooth experience, minimal design, everything works flawlessly
GlobalBusinessExplorer – Practical and clear, supports learning about international business relationships efficiently.
BizConnectionsPro – Very structured, helps understand international business dynamics quickly.
online investment portal – Design and branding feel professional and dependable.
Official Zaviro hub – Clear design, organized content, and intuitive menus make browsing a breeze.
bond info hub – Branding and layout together make the site feel trustworthy.
Main project page – Clear structure, professional appearance, and effortless navigation for users.
investment hub – Clean design, readable content, and intuitive navigation throughout.
financial info site – Professional appearance, concise content, and easy navigation overall.
Trust reference page – A solid design that makes the site feel dependable and clear.
Primary trust site – A simple and clear presentation that helps build confidence.
investment guidance site – Clean interface and smooth browsing make information easy to access.
Direct site access – Fast and intuitive, with content presented neatly and logically throughout.
Official site link – Pages load fast, and information is structured for quick understanding.
professional service portal – Straightforward styling keeps focus on the services provided.
business service portal – The design stays simple, keeping attention on essential info.
online portal – Simple structure and fast loading, felt comfortable exploring
resource page – Pages load reliably, layout is neat, enjoyable overall
View project details – Trustworthy content, easy-to-follow layout, and details are clear and useful.
Direct project access – Smooth interface, content is trustworthy, and information is easy to follow.
bond investment hub – Pages are clean, and content feels credible and professional.
financial resource page – Navigation and presentation together feel credible and smooth.
secure finance hub – Content is concise, and browsing feels simple and intuitive.
bond knowledge – Sections are arranged logically, making it simple to find information.
Website access – A professional presentation that keeps navigation simple and clear.
Check the site – The website looks refined and functions smoothly while exploring.
View project details – Clear layout, easy navigation, and content is accessible and well-presented.
Official portal – Content is easy to understand, pages are organized, and interface feels uncluttered.
financial resource page – Responsive design ensures information is always clear and accessible.
financial hub – Browsing was effortless with clearly presented information.
trust management site – Feels credible with a professional, user-friendly layout.
Direct project access – Clean design and logical structure make exploring the pages effortless.
investment trust portal – The site appears reliable with a clean, professional layout.
Primary platform link – Intuitive layout and helpful content make the site feel professional and approachable.
Looking for a casino? 8mbets Slots, table games, and live casino all in one place. Quick login, convenient registration, modern providers, stable payouts, and comfortable player conditions.
Playing at the casino? jwin 7 Play online for real money. We offer a wide selection of slots, live dealers, fast payments, easy login, and exciting offers for new and returning players.
Do you love gambling? j win 7 Online is safe and convenient. We offer a wide selection of games, modern slots, a live casino, fast deposits and withdrawals, clear terms, and a stable website.
bond knowledge – Content is straightforward, sections are easy to find, and the site feels reliable.
finance hub – Clean interface, well-organized information, and navigation works well.
ClickXpress – Layout clean, navigation smooth, and all links worked correctly.
UlvorAccess – Interface professional, pages fast, and finding products very simple.
Downloads – Resources and files are structured logically and load quickly for convenience.
Home – Quick-loading pages with a professional layout make browsing smooth and information easy to grasp.
secure bond hub – Pages load fast, and navigation feels natural and consistent.
Official Zexaro Line – Layout is clean, navigation is intuitive, and information is simple to understand.
Explore project – Well-structured content, smooth navigation, and a clean design throughout.
Продажа IQOS ILUMA https://ekb-terea.org и стиков TEREA в СПб. Только оригинальные устройства и стики, широкий ассортимент, оперативная доставка, самовывоз и поддержка клиентов на всех этапах покупки.
Купить IQOS ILUMA https://spb-terea.store и стики TEREA в Санкт-Петербурге с гарантией оригинальности. В наличии все модели ILUMA, широкий выбор вкусов TEREA, быстрая доставка по СПб, удобная оплата и консультации специалистов.
financial resource page – Content is direct, and the site feels credible overall.
investment guidance site – Explanations are simple and the platform gives a dependable impression.
trustco info portal – Mobile browsing is fluid and everything is clearly arranged.
investment trustco homepage – Smooth scrolling on mobile, and everything is in order.
online finance resources – Content is structured, navigation is simple, and the site feels professional.
trusted site – Navigation feels natural, content loads quickly, and everything is easy to understand.
xelariocore.bond – The layout is minimal and the services are explained clearly without clutter.
Core information page – No distractions here, just a clear explanation of the services.
IQOS ILUMA https://terea-iluma24.org и стики TEREA — покупка в Москве без риска. Гарантия подлинности, большой выбор, выгодные условия, доставка по городу и помощь в подборе устройства и стиков.
News – Updates are laid out neatly, helping visitors find important information quickly.
Services – Content is concise and presented clearly, making navigation smooth.
Direct project access – Content is well presented, navigation is smooth, and pages load without delay.
Explore Zexaro Trust – Well-structured pages, readable content, and browsing feels effortless.
Learn more here – Well-laid-out content and simple navigation make the site user-friendly.
zylavoline insight – Quick site speed enhances the clarity of the main message.
QuvexSpot – Fast-loading pages, sections well-structured, and content seems accurate.
Direct site access – The platform feels approachable, with clear navigation and well-organized content.
zylavoline main page – Quick response time and simple layout make the message easy to understand.
EasyClickQuvex – Navigation smooth, pages load fast, and all links functional.
online investment hub – Structured layout makes information simple to follow.
secure finance portal – Easy-to-navigate design and organized sections feel professional.
Head to head records, historical results between teams before matches
сервис рекламных рассылок сервис по рассылкам email
задвижка 30с41нж ду100 ру16 задвижки стальные фланцевые 30с41нж
фильмы онлайн в качестве сериалы от apple tv+ онлайн
trusted investment site – Direct explanations make finding information quick and easy.
bond platform – User-friendly layout with explanations that are simple to read.
xanerobond.bond – Great website, navigation works well and content feels organized for investors.
move forward – Wording encourages active steps and deliberate progress today.
finance info – First impression is positive, navigation is intuitive, and reading is smooth.
action insights – Messaging motivates users to act decisively and meaningfully.
Tutorials – Step-by-step guides are organized clearly, helping users learn efficiently.
Testimonials – Customer feedback is presented cleanly, increasing trust and credibility.
Direct site access – Navigation is effortless, content is concise, and layout feels reliable.
Здравствуйте дорогие друзья! Очень актуальная тема — шум покрышек. Хочешь качественно — могу рекомендовать толковый сервис: профессиональная шумоизоляция . В большинстве случаев проблема комплексная: двери и крыша — всё это резонирует. Короче, постучи по двери — чувствуешь вибрацию? То есть металл не демпфирован. Своими руками: это работает — демпфер плюс шумопоглотитель, главное — качественная прикатка. Что в итоге: реально работает.
zexarotrustco.bond – Browsing here is smooth, content is clear, and navigation works effortlessly.
Здравствуйте дорогие друзья! Рассмотрим, что работало ранее — почему течёт плоская кровля. Не хочешь заморачиваться — обращайся к мастерам: https://montazh-membrannoj-krovli-spb.ru. В принципе рубероид и битум — это прошлый век. На данный момент оптимальный вариант — ПВХ мембрана. Как это работает? Мембрана сваривается без щелей — так вот вода просто не проникает. Если решил сам: грунтовка. Что в итоге: удаётся достигать классных результатов.
forwardtrajectory.bond – Sleek and functional, site encourages clear thinking and consistent progress.
forwardtrajectory.bond – Sleek and functional, site encourages clear thinking and consistent progress.
financial guidance platform – Simple design, easy-to-read content, and smooth navigation.
CoreBridge Guide – Professional presentation makes the platform feel credible and solid.
CoreBridge Link Center – Clean, structured layout communicates reliability and ease of use.
enduringcapitalfocus.bond – Friendly but professional, content communicates stability and expertise.
enduringcapitalbridge.bond – Professional structure, site inspires assurance and dependable insights.
project zorivoline – Suggests potential value as more details are revealed.
this bond project – Feels like a concept that’s still forming but shows promise.
bondedheritagehub.bond – Professional interface, content emphasizes tradition and is easy to read.
explorerzone.bond – Inviting layout, pages highlight discovery and make learning enjoyable.
Official line site – Found this page recently, and the information is presented in a helpful way.
bondedpast.bond – Easy-to-follow structure, site highlights historical values in an engaging way.
journeydiscovery.bond – Bright and engaging, navigation supports curiosity and encourages deeper learning.
Learn more here – I ran into this site and found the content practical and direct.
bondedpro.bond – Modern interface, messaging feels authoritative yet approachable.
trustedcore.bond – Modern look, messaging highlights reliability and smooth user experience.
Primary project page – The site is easy to navigate, with clear and reliable information throughout.
Explore Yavero core – Smooth page flow and clearly presented information make browsing pleasant.
ideas journey – Messaging highlights movement and practical execution of concepts.
stonecrestcenter.bond – Well-presented, users can browse easily and the site feels dependable.
stonecresthub.bond – Polished interface, site feels structured and trustworthy from start to finish.
ideas portal guide – Text inspires readers to take the next steps confidently.
start with business – Messaging encourages professional action with clarity and assurance.
business stop – Messaging is clean and instills confidence in professional decisions.
MorixoSpot – Pages fast, minimal layout, and finding products effortless.
ClickXpress – Pages load fast, interface tidy, and finding items effortless.
StarlightEmporium – Pleasant shopping experience with smooth transactions.
TranquilFinds – Shopping feels relaxed and the cart process is smooth.
bond resources – Design looks solid, pages respond quickly, and content feels clear and helpful.
official site – Layout is simple, navigation works smoothly, and content is easy to understand.
refined oak workshop – The visual style feels peaceful and well thought out from start to finish.
creativepathideas.bond – Clean presentation, creative concepts are accessible and well-structured.
handcrafted oak pieces – Everything comes across as thoughtfully arranged, giving the site a gentle and welcoming mood.
creativepathguide.bond – Well-organized design, messaging communicates ideas clearly and effectively.
investment resource portal – Everything feels professional, enhancing user confidence.
View project details – Layout is user-friendly, content is concise, and browsing is seamless.
finance portal – Offers a professional impression and confidence when navigating carefully.
Zorivo Core overview – Well-structured pages, clear content, and easy navigation throughout.
Tutorials – Step-by-step guides are organized clearly for simple learning.
Services – Organized content and simple navigation make research and browsing smooth.
Vector Link Hub – Strong visual identity and readable content make the site approachable.
Legacy Center – Layout is crisp, content is structured, making information easy to follow.
Bonded Unity Centerpoint – Polished design, messaging feels cohesive and easy to follow.
growth journey – Words make strategic development feel manageable and clear.
Bonded Unity Flow – Clean interface, messaging highlights togetherness with clear guidance.
strategic link – Text focuses on deliberate steps and structured advancement.
zorivotrustco information – Clean visuals paired with intuitive browsing make it easy to explore.
continuumbond.bond – Clean presentation, messaging clearly communicates security and continuity.
zorivotrustco information – Clean visuals paired with intuitive browsing make it easy to explore.
stabilitytrust.bond – Cohesive visuals, navigation is easy and reinforces dependable messaging.
bondworks.bond – Professional layout, content inspires user trust and clear understanding.
bondcircle.bond – Well-structured design, content emphasizes honesty and smooth navigation.
mindcanvas.bond – Intuitive and modern, content is visually appealing and motivates new ideas.
strongholdpartners.bond – Crisp presentation, navigation is simple and design conveys stability.
mindlab.bond – Intuitive design, navigation is smooth and ideas are presented in an engaging, inspiring way.
strongholdnetwork.bond – Structured layout, browsing is simple and content highlights stability.
Learn more here – Content is easy to scan, and pages feel polished and user-friendly.
dreamvisionjourney.bond – Clean and approachable, site presents vision concepts smoothly.
dreamvisionfocushub.bond – Bright design, site makes vision-oriented ideas easy to grasp.
Project homepage – Layout is intuitive, making the content easy to follow and digest.
GreenMeadowBazaar – Browsing feels light and the checkout works flawlessly.
FreshFieldsShop – Light, airy design makes shopping enjoyable.
Primary platform link – Smooth layout, content is concise, and browsing feels natural.
zorivohold.bond – Smooth experience, pages load quickly and content is easy to understand.
PlivoxSpot – Pages load fast, design neat, and completing orders effortless.
PlivoxGo – Interface responsive, pages load quickly, and purchasing was simple.
Home – Pages load quickly, layout is clean, and information is easy to understand.
Events – Event information is structured clearly, helping users follow schedules easily.
Main trust homepage – The layout is tidy, and switching between sections is seamless.
Main trust homepage – The layout is tidy, and switching between sections is seamless.
coherent hub – Messaging organizes ideas in a purposeful and understandable format.
idea alignment – Content highlights purposeful connections and smooth flow of concepts.
investment hub – Pages load smoothly and the interface feels user-friendly.
growth path – Text and layout emphasize steady progress and practical direction.
Midpoint Gateway – Layout is intuitive, and content reads smoothly throughout.
online savings spot – Everything feels well organized, creating a smooth and pleasant buying experience.
growth insight – Text inspires users to take intentional steps toward advancement.
Midpoint Main – Layout feels approachable, content is easy to scan and understand quickly.
Anchor Capital Path – Smooth interface, content is structured and easy to follow naturally.
growthsphere.bond – Clean design, site communicates growth principles effectively and clearly.
Anchor Capital Point – Clean layout, navigation flows effortlessly and promotes trust.
growthbond.bond – Clear layout, site emphasizes progress and concepts are easy to follow.
zylavobond resource – Simple design ensures content is immediately understandable.
collabpath.bond – Modern visuals, messaging reinforces shared vision and effective alignment.
claritymechanism.bond – Clear messaging, site emphasizes process and understanding in a practical way.
zylavobond network – Content is straightforward and easy to absorb in one visit.
collabpath.bond – Modern visuals, messaging reinforces shared vision and effective alignment.
claritymechanismprocess.bond – Structured design, messaging communicates ideas in an easy-to-follow way.
harborstoreco.shop – Smooth browsing experience, layout feels inviting and organized for customers.
indigoshopharbor.shop – Simple and approachable, categories are easy to find and site layout is user-friendly.
motionworks.bond – Clean and approachable, layout reinforces continuous effort and forward thinking.
growthdrive.bond – Smooth layout, content inspires progress and reinforces goal-oriented behavior.
BlueTideGoods – Bright design and a pleasant shopping flow from start to finish.
start with clarity – Words guide readers through choices with ease and confidence.
BlueTideGoods – Bright design and a pleasant shopping flow from start to finish.
clarity insights – Text provides clear direction and thoughtful guidance throughout.
Trust Co overview page – Well-structured pages, dependable content, and easy to browse.
Trust Co overview page – Well-structured pages, dependable content, and easy to browse.
Unity Trust Hub – Interface feels reliable, navigation is simple and content fosters a sense of connection.
Unity Trust Flow – Smooth navigation, content highlights unity and dependable structure.
sparkpath.bond – Bright and motivating, content encourages steady advancement and practical planning.
growthigniter.bond – Modern feel, encourages users to take steps toward measurable progress.
ZaviroAccess – Browsing smooth, product info visible, and checkout feels easy.
ZaviroPortal – Pages loaded fast, layout clear, and finding products was easy and straightforward.
куба пицца доставка пицца куба отзывы
Zahnprobleme? zahnbehandlung kosten ubersicht Diagnostik, Kariesbehandlung, Implantate, Zahnaufhellung und Prophylaxe. Wir bieten Ihnen einen angenehmen Termin, sichere Materialien, moderne Technologie und kummern uns um die Gesundheit Ihres Lachelns.
пицца куба рязань пицца рязань сайт
trustcore.bond – Intuitive design, information is presented in a reliable and straightforward way.
trusthub.bond – Professional feel, messaging emphasizes reliability and clear guidance.
silvertrust.bond – Clean layout, site highlights professionalism and clear, organized messaging.
silverline.bond – Strong design, pages communicate stability and confidence effectively.
Bonded Framework Access – Professional structure, framework concept is easy to grasp at a glance.
Bonded Framework Link – Smooth interface, framework ideas are easy to understand and digest.
growth journey – Messaging feels methodical and encourages steady improvement.
intentional growth – Text feels purposeful, inspiring steady development and focus.
zylavocore platform – Visuals and text are balanced, making the site feel professional and clear.
handmade pine store – Smooth navigation and well-written descriptions make browsing relaxed and enjoyable.
wildgrainemporiumco.shop – Clean layout, shopping experience is simple and enjoyable for users.
zylavocore resource – Branding is clean, and the organization keeps the pages digestible.
rustic home finds – The site feels inviting, and it’s easy to move around while understanding each item.
wildgrainonline.shop – Rustic charm, site feels approachable and purchasing process is smooth.
Direct platform link – The page layout feels straightforward and easy to navigate.
Direct site access – Easy-to-follow structure gives a professional feel right from the start.
motionengine.bond – Smooth layout, content is clear, well-structured, and guides practical use.
motioncenter.bond – Organized and simple, pages help users understand processes quickly and easily.
FoggyHollowGoods – Relaxed layout, making exploration of products simple.
clarity center – Minimalist layout ensures ideas are noticeable and easy to understand.
AutumnValeMarket – Rustic aesthetic with an easy-to-use checkout process.
clarity page – Content flows naturally and highlights the main concepts clearly.
momentumstream.bond – Clean interface, messaging inspires action and reinforces forward direction effectively.
momentumvector.bond – Strong concept, layout supports clarity and forward movement effectively overall.
Platform overview – Neat pages and well-organized information make browsing simple.
Check this platform – The site is easy to scan, content is legible, and the design feels reliable.
bond resources page – Content is clear and structured, making browsing straightforward.
Nexa Connect – Polished layout, information comes across clearly and concisely.
clarity stop – Wording is clean, guiding users through focused actions efficiently.
clarity stop – Wording is clean, guiding users through focused actions efficiently.
Nexa Bridge – Well-organized layout, content is digestible and the site feels fast.
centralalliant.bond – Well-organized interface, site communicates core ideals clearly and efficiently.
alliantloop.bond – Clean interface, central ideas are highlighted and the layout feels professional and coherent.
silveredge.bond – Sleek presentation, messaging feels approachable and inspires confidence effectively.
linehaven.bond – Clean visuals, messaging reinforces clarity and professionalism naturally.
capitalunityhub.bond – Layout is clear, messaging about teamwork feels natural and approachable.
petalmarket.shop – Friendly layout, browsing products is effortless and checkout flows naturally.
capitalunityflow.bond – Layout feels organized, teamwork concepts are communicated clearly.
ironpetalstore.shop – Smooth design, products are showcased clearly and user experience is straightforward.
zylavoline hub – Quick navigation and simple messaging make the site easy to use.
zylavoline info – Site feels responsive, and the content is presented without distractions.
QuickVixaro – Smooth interface, responsive pages, and ordering was simple.
EasyClickVixaro – Pages load fast, layout organized, and checkout completed without delays.
HiddenMistShop – Attractive layout with easy navigation and fast checkout steps.
FogspireFinds – Smooth navigation, products are well organized and easy to explore.
creativepulsecore.bond – Energetic interface, messaging is lively and encourages interactive exploration.
creativepulsebridge.bond – Modern layout, site communicates creative ideas with clarity and impact.
wild branch outlet – The site has an organic feel, making it simple to browse products and place an order.
trustvault.bond – Feels secure, site layout is professional and gives reliable impression immediately.
trustvault.bond – Feels secure, site layout is professional and gives reliable impression immediately.
nature inspired shop – A fresh, natural look helps items stand out, and the buying process feels easy.
framework guide – Messaging makes structured planning simple, clear, and actionable.
growth stop – Messaging is precise and helps users follow structured growth strategies.
Official site link – Well-structured content and consistent design make navigation simple.
Main project page – Reliable content paired with consistent visuals makes the site approachable.
Direct project access – Smooth flow between pages and content is presented logically and reliably.
Official site link – User-friendly interface, reliable details, and smooth page transitions.
Tandem Portal – Interface feels welcoming, information is structured logically and clearly.
Tandem Center – Layout feels harmonious, messages are clear and user-friendly.
focus navigator – Crisp layout and text guide users through ideas with purpose.
harborcenter.bond – Professional yet approachable, messaging emphasizes trust and partnership effectively.
alliancenaut.bond – Smooth design, site communicates collaboration and trustworthiness effortlessly.
anchorhub.bond – Modern interface, content highlights reliability and clarity in a practical way.
focuslanepoint.bond – Minimalist design, site encourages attention to detail and organized work steps.
focuslanepathway.bond – Smooth navigation, site supports productivity and helps maintain clarity in goals.
loamlinenmarket.shop – User-friendly design, browsing categories is simple and purchasing is quick.
linenloamemporium.shop – Minimal and clean, shopping experience is clear and effortless.
capitalbondcohesion.bond – Organized and inviting, collective focus comes across clearly.
capitalbondconnection.bond – Friendly interface, group-centered messaging is straightforward.
discover zylavotrustco – Consistent visuals and messaging establish confidence in the platform.
zylavotrustco platform – Professional presentation enhances credibility and user confidence.
channel your progress – Text emphasizes clarity in direction and tangible forward movement.
progress access – Wording inspires confidence in moving ahead thoughtfully and purposefully.
MistyHavenStore – Calm interface, products are easy to locate, and checkout is reliable.
FoggyCrestMarket – Calm design makes browsing simple and cart process hassle-free.
unitysphere.bond – Intuitive navigation, content reinforces cohesion and a sense of dependable partnership.
unitycore.bond – Clear layout, content supports collaboration and builds confidence in purpose.
ZorivoHub – Clean interface, fast pages, and information easy to locate.
ZorivoHub – Clean interface, fast pages, and information easy to locate.
online investment page – Organized layout with clear information and minimal distractions.
wild iris shop – A clean layout highlights each item nicely and keeps the shopping experience pleasant.
wild iris shop – A clean layout highlights each item nicely and keeps the shopping experience pleasant.
Ideas to Results – Encourages moving beyond concepts with clarity and confidence in execution.
digitalsparkbridge.bond – Sleek layout, site highlights innovation and clarity in a natural way.
Actionable Ideas Portal – Layout and content make taking practical steps straightforward and engaging.
digitalsparkzone.bond – Modern interface, content flows smoothly and sparks curiosity effortlessly.
solidanchor.bond – Strong visuals, content emphasizes a stable and trustworthy experience overall.
apexhub.bond – Well-organized layout, content feels approachable and easy to navigate.
firmline.bond – Organized design, pages provide a steady impression and clear, concise messaging.
apexpath.bond – Organized pages, layout supports easy reading and conveys confidence.
Ridgecrest Insights Hub – Messaging reassures and gives a sense of trustworthiness overall.
Ridgecrest Insights Hub – Messaging reassures and gives a sense of trustworthiness overall.
moonpetalcollective.shop – Creative vibe, products feel unique and website navigation is user-friendly overall.
petalcollectiveonline.shop – Playful vibe, products stand out and shopping experience is seamless.
Bonded Legacy Path – Organized design, legacy content is approachable and well structured.
Bonded Legacy Framework – Neat layout, legacy concepts are communicated in a clear and structured way.
planning framework insight – Suggests a methodical and purpose-driven mindset.
Main project page – Easy navigation and clear content make the site very user-friendly.
strategy framework hub – Comes across as intentional and aimed at long-term impact.
FernGlowMarket – Clean design, products are easy to find and checkout works naturally.
View project details – The site feels approachable, with content that’s simple yet informative.
OpalMistGoods – Elegant design, products clearly showcased, and ordering is simple.
clarity main – Messaging is crisp and encourages rapid comprehension and application.
clarity insights – Messaging is streamlined, encouraging quick yet thoughtful action.
capitalpath.bond – Structured layout, navigation is clear and inspires confidence in the presented information.
bondedfocus.bond – Simple interface, content is straightforward and communicates reliability clearly.
simple discovery site – Feels light and easy to move through without effort.
simple discovery site – Feels light and easy to move through without effort.
focusandgrowpath.bond – Structured content, ideas guide readers toward consistent growth and insight.
focusandgrowlight.bond – Clean and modern, content flows naturally and supports clear progress.
solidbase.bond – Smooth layout, pages feel grounded and content is approachable and reliable.
clicky bargains hub – Efficient layout, makes shopping effortless and enjoyable.
NetworkNexus – Brings colleagues together and fosters long-term growth.
anchorcore.bond – Friendly design, content conveys stability and professionalism with a clear flow.
CollabCentral – Simplifies teamwork and helps groups reach their goals more efficiently.
easy click shop – Organized design, helps users find products without hassle.
bondedpinnacle.bond – Well-structured layout, navigation is intuitive and inspires confidence.
Momentum Link – User-friendly design, site communicates progress and clarity effectively.
click route portal – User-friendly layout, everything is easy to locate quickly.
trustpinnacle.bond – Clear presentation, content reinforces authority and trustworthiness naturally.
clickflow portal – Clean and practical, browsing the site is fast and intuitive.
Signal Path – Strong focus on momentum, messages guide users toward actionable moves.
QuickTrivox – Fast-loading pages, organized design, and navigating the site felt easy.
focus first portal – Structured approach makes understanding seamless.
TrivoxLink – Pages open fast, interface intuitive, and everything functioned properly.
navigation guide portal – Content feels intuitive and easy to absorb.
traditional maple goods – The site is straightforward to browse, with well-written product info.
heritage style emporium – Browsing feels simple thanks to a clear structure and brief descriptions.
quillmarket.shop – Friendly interface, store navigation is straightforward and details are clear.
northquillstore.shop – Simple structure, shopping is easy and information is well presented.
unifiedtrustgateway.bond – Intuitive flow, content feels structured and the overall experience is trustworthy.
unifiedtrustalliance.bond – Simple structure, messaging emphasizes clarity and a trustworthy experience.
relationship platform online – Clear guidance, site makes forming business connections easy and intuitive.
biz connect platform – Smooth interface, learning about relationship strategies is easy and quick.
StonePetalTreasures – Clean, organized layout makes browsing and checkout simple.
StonePetalTreasures – Clean, organized layout makes browsing and checkout simple.
simple decision support – The message comes across as steady and encourages thoughtful action.
mindset shift support – Suggests a healthy way to rethink decisions calmly.
buyer-focused resource – The content feels targeted and helpful.
buyer resource center – Nicely structured and helpful for consumers.
StrategicGrowth – Guides companies in planning partnerships and growth strategies that last.
SustainGrowth – Shares expert advice on achieving reliable partnerships and long-term progress.
trustnexus.bond – Trustworthy look, content flows logically and messaging is easy to understand today.
trustcircle.bond – Smooth layout, content is easy to follow and feels professional.
Direct project access – The pages are logically ordered, with details presented in a professional way.
groundpoint.bond – Organized site, pages clearly communicate trust and commitment to visitors.
steadypath.bond – Clean and intuitive, content emphasizes reliability and professional tone across the site.
Check this platform – Information flows logically and the design feels trustworthy.
horizon finance guide – Professional tone and layout make information easy to digest.
investment clarity site – Feels credible, with easy-to-read information on bonds.
principlebase.bond – Cohesive design, content clearly supports trustworthiness and sound principles.
trustpath.bond – Organized layout, content emphasizes integrity and a professional approach.
solid bond hub – Reliable information, makes understanding bond options easy and straightforward.
bond insight page – Informative and practical, makes exploring bonds hassle-free.
Future Insights – Messaging feels authoritative and thoughtfully aligned with progress.
discover new paths – Text invites exploration and makes action feel accessible.
Bonded Main – Thoughtful content combined with professional visuals feels trustworthy.
take the first step – Encourages action in a friendly and approachable way.
northwindoutletonline.shop – Approachable layout, product details are clear and checkout is simple.
purpose journey hub – Content feels inspiring and very easy to follow.
nwoutlet.shop – Organized layout, products are easy to find and checkout flows smoothly.
forward purpose portal – Very motivating and structured for easy comprehension.
urbanwaveinsighthub.bond – Minimalist style, content is concise and navigation is simple.
urbanwavecentral.bond – Streamlined design, content is readable and the site feels engaging overall.
XylorHub – Simple layout, fast pages, and everything functions as expected.
ClickXylor – Pages responsive, interface minimal yet effective, and content easy to read.
PartnerLink – Provides clear guidance and reliable access to secure business connections.
BusinessSafe – Offers a clear and safe way to browse potential business relationships.
aurumlane official – Modern styling, navigation is clear and shopping feels relaxed.
clear direction resource – The tone comes across calm and thoughtfully motivating.
>efficient click page – Smooth layout, quick loading, perfect for mobile use.
direction with meaning – Suggests clarity without pressure or rush.
aurumlane lifestyle – Minimal and classy, the browsing experience feels smooth and inviting.
>speed click hub – The layout is simple and responsive on handheld devices.
everyday bargain click – Fast browsing, prices are reasonable and shopping is stress-free.
daily deals online – Pleasant layout, makes checking offers fast and simple.
pillarsupport.bond – Logical navigation, messaging promotes unity and clarity in every section.
unitylink.bond – Professional layout, content communicates teamwork and foundational principles naturally.
sbventures.bond – Clear and approachable, site communicates stability and professionalism naturally.
capitalbridge.bond – Confident layout, pages feel polished while remaining easy to read and follow.
corecircle.bond – User-friendly layout, site communicates integrity and ethical focus effectively.
bond explorer hub – Very intuitive, provides clear insights on available bonds.
principlepath.bond – Clean visuals, navigation supports clarity and ethical messaging effectively.
shoproute path – Easy browsing, navigating options is smooth and stress-free here.
shoproute deals – Minimalist layout, makes finding deals easy and stress-free.
strategic development center – Helpful content, makes identifying smart growth paths easy and fast.
Trusted Nexus Bridge – Smooth design, information is presented clearly and confidently.
Trusted Nexus Base – Layout feels balanced, site conveys credibility and approachability.
opalcrestcollection.shop – Modern layout, browsing is intuitive and information is easy to read.
opalcrestcollection.shop – Modern layout, browsing is intuitive and information is easy to read.
momentum strategy site – Helpful ideas to maintain steady forward motion.
quick access shopping – The interface is clean and items are simple to locate.
build your momentum portal – Offers structured advice to grow consistently online.
structured shopping page – Layout is tidy, helps you move through items fast.
progresscatalyst.bond – Motivating layout, site encourages momentum and actionable steps effectively.
progresscatalystfoundation.bond – Simple navigation, emphasizes practical steps and continuous improvement.
meaning-driven platform – Communicates clarity, focus, and a strong sense of purpose.
Super subs, impact substitutes and their goal contributions
innovation methods hub – Very practical, encourages learning and trying new strategies today.
XanixLink – Navigation smooth, pages responsive, and shopping process seamless.
midnight cove storefront – The dark theme feels modern, navigation is simple and buying is stress-free.
midnight cove market – Dark theme enhances focus, product pages are clear and checkout flows nicely.
TrustedCart – Ensures customers can shop safely and pay effortlessly.
EasyBuy – Provides a simple, reliable way to complete purchases online without hassle.
corestrength.bond – Intuitive pages, content reinforces confidence and unified focus for users.
unitedstrength.bond – Layout is structured, messaging conveys cohesion and solid principles naturally.
merit bond guide – Very accessible, makes exploring investment options simple.
bond planning portal – Easy to use, provides useful insights for daily financial decisions.
modern buy curve – Contemporary feel, platform helps shoppers find products efficiently.
curve deals hub – Easy-to-use interface, browsing items is straightforward and quick.
direct click page – Clean visuals and a message that lands quickly.
clear message page – Feels well structured and quick to digest.
daily deals hub – Simple layout makes finding everyday items quick and easy.
affordable finds site – Easy to navigate, prices are reasonable and items are well-categorized.
EasyBuy – Ensures a smooth shopping process from search to checkout.
BuyZone – Makes finding products fast and purchasing them seamless.
idea explorer – Engaging content, really sparks creativity for new projects today.
idea inspiration click – Fun layout, discovering new ideas is simple and motivating here.
ZorlaLink – Pages open quickly, layout neat, and shopping experience feels natural.
click challenge online – Lively platform, engaging content makes exploring exciting.
win click platform – Entertaining experience, encourages users to interact with features.
ZorlaAccess – Layout minimalistic, product info clear, and shopping process easy.
lynx finance page – Navigating options is straightforward and user-friendly.
bond explorer portal – Quick access to options, very smooth user experience.
helpful content source – Looks worth keeping, I’ll revisit when needed.
practical resource – This seems useful, saving it to review more carefully later.
discover momentum – Language encourages proactive action and forward planning.
start moving forward – The site emphasizes progression, momentum, and clear purpose.
BizAlliance – Helps users learn the ins and outs of forming effective corporate partnerships.
StrategicLink – Offers professional explanations about partnership advantages and strategies.
Explore Mavero Capital – Well-organized pages, concise content, and smooth navigation throughout.
Explore Mavero Capital – Well-organized pages, concise content, and smooth navigation throughout.
next-gen deals hub – Sleek interface makes browsing modern and effortless.
next-level buy site – Website feels advanced and keeps the shopping experience simple.
Explore new possibilities platform – Modern layout makes it simple to move through pages.
Pathway discovery platform – Navigation is seamless, and the modern design is inviting.
next step ideas – Easy navigation, helps users discover exciting and practical opportunities.
advance mindset site – Clear and positive direction for making choices.
next step ideas – Easy navigation, helps users discover exciting and practical opportunities.
thoughtful growth hub – Helps focus on better decisions with ease.
momentum builder hub – Useful platform, helps maintain steady progress and track growth easily.
strategic alliance center – Professional content, simplifies evaluating business partnership options.
build forward online – Clean layout, encourages structured progress and productive habits.
business collaboration hub – Helpful and professional, ideal for exploring partnership strategies.
financial insight hub – Easy-to-follow security info makes bonds understandable.
investment assurance site – Reassuring layout that highlights bond safety and details.
Growth opportunity platform – An interesting site that’s easy to get around.
Growth opportunity platform – An interesting site that’s easy to get around.
смотря фильмы онлайн пацаны сериал смотреть без цензуры
ClickXelivo – Smooth browsing, everything displayed correctly and content looked accurate.
Mavero Holdings online site – Clean structure, reliable design, and details are simple to read.
Mavero Holdings main homepage – Organized layout, professional appearance, and content is clear and easy to follow.
XelivoPortal – Pages opened instantly, navigation was smooth and the content seemed trustworthy.
CorporateLink – Provides trustworthy tools to create professional connections efficiently and quickly.
TrustNetwork – Enables fast, trustworthy connections among business professionals.
focus hub – Content emphasizes concentration, creating a sense of strength and direction.
сервис массовых рассылок сервис email рассылок какой выбрать
discover focus power – Clear and relatable text positions focus as a practical tool.
the best adult generator https://pornjourney.app/ai-girlfriend/ create erotic videos, images, and virtual characters. flexible settings, high quality, instant results, and easy operation right in your browser. the best features for porn generation.
incremental progress portal – Focuses on achievable steps to maintain momentum every day.
daily growth click – Simple strategies to make steady progress over time.
Shopping convenience hub – Layout is clean, and loading times are impressive.
momentum path guide – The layout is clear and walks you through each step effortlessly.
Modern marketplace – Browsing items is seamless, and product organization is logical.
clear path website – Layout flows nicely, very easy to follow along.
easy shop center – Smooth and efficient, shopping experience feels seamless overall.
click-to-buy center – Smooth experience, checkout is fast and user-friendly.
pillar finance hub – Clear and reliable, ideal for first-time investors.
bond insights hub – Clean structure and helpful information for beginners.
future thinking hub – Exciting insights, motivates users to explore ideas beyond the present.
future paths click – Inspiring and practical, encourages planning for exciting opportunities ahead.
Skip to details: https://tgram.link/apps/safexess-vpn-bot/
SmartShopper – Browse products effortlessly with an organized platform that makes comparison simple.
BuySmart – Easily find and compare products while enjoying a user-friendly shopping experience.
Mavero Trustline digital site – Professional structure, clear messaging, and visitors can understand the content quickly.
Mavero Trustline landing page – Neatly structured, content is clear, and important details are easy to locate.
clear path resource – The structure makes understanding growth much easier.
growth clarity guide – Helps connect the dots in a simple, logical way.
Reliable e-store – Categories make it easy to find products, creating a positive experience.
new finds portal – Browsing is fun and full of unexpected surprises.
Trusted digital store – Shopping is straightforward, and the organization of items is clear.
exploration click hub – Fun interface that makes discovering new things effortless.
fast knowledge click – Useful content, lessons are clear and actionable without delay.
fast skill builder – Educational content, practical and immediately useful today.
creative click guide – Loads of unique and interesting ideas to explore quickly.
idea generator hub – Sparks creativity with fun and practical concepts.
continuous improvement hub – Inspires action, offers tips for developing skills consistently.
Explore Mivaro Trust Group – Site layout is easy to follow, content is informative, and visitors feel well-guided.
daily learning center – Useful resources, helps users improve and stay motivated daily.
Mivaro Trust Group online hub – Navigation is smooth, explanations are clear, and users feel well-supported.
uplifted mindset site – The writing style feels supportive and forward-looking.
next-step inspiration – Enjoyable read with a tone that pushes toward progress.
Contemporary strategy network – Content grabs attention, and browsing is intuitive.
Innovation planning platform – Browsing is simple, and the design is visually appealing.
digital shopper hub – Stylish design, attracts tech-savvy users looking for convenience.
online shopping nextgen – Innovative design, helps shoppers find products effortlessly.
top choice shopping site – Looks well-organized and practical for everyday needs.
compare & choose site – A useful tool for evaluating common purchases.
discounts hub – Fun and easy, browsing deals feels quick and effortless.
smart savings site – Practical and user-friendly, makes daily shopping more efficient.
Mivaro Trust Group online site – Navigation is simple, content is informative, and overall the user experience is smooth.
Mivaro Trust Group business site – Structured layout, helpful content, and the site is simple to use.
business collaboration center – Helpful layout, learning about corporate teamwork is simple today.
corporate alliance solutions – Well designed, site guides users through teamwork strategies effortlessly.
Unity commerce site – International focus is obvious, and the content is easy to follow.
International enterprise hub – Gives a global feel and presents business details clearly.
modern deal hub – Very practical design, makes online shopping fast and enjoyable.
smart shopping portal – Intuitive design, helps locate items quickly and complete purchases effortlessly.
barcelona real madrid 1×2 que significa en apuestas
quick info hub – Simple and informative, perfect for quick learning.
info click page – Layout is clear, providing fast access to product details.
future path builder – Encouraging platform, helps visualize goals and plan next steps easily.
Любишь азарт? бонус код joycasino большой выбор слотов, live-дилеры и удобный интерфейс. Простой вход, доступ к бонусам, актуальные игры и комфортный игровой процесс без лишних сложностей
future planning hub – Easy to follow and encourages taking small, meaningful steps.
Morixo Capital official site – Clean design, clear messaging, and navigation feels intuitive for visitors.
Check out Morixo Capital – Clear layout, professional feel, and users can access content easily.
Жіночий портал https://soloha.in.ua про красу, здоров’я, стосунки та саморозвиток. Корисні поради, що надихають історії, мода, стиль життя, психологія та кар’єра – все для гармонії, впевненості та комфорту щодня.
trusted business hub – Clear and professional, makes networking for commercial success simple.
Сучасний жіночий портал https://zhinka.in.ua мода та догляд, здоров’я та фітнес, сім’я та стосунки, кар’єра та хобі. Актуальні статті, практичні поради та ідеї для натхнення та балансу у житті.
networking solutions click – Well-structured platform, offers guidance for commercial networking success.
User-friendly retail platform – Navigation is smooth and the experience feels tailored for shoppers.
Intuitive online store – The layout is clear and makes finding products easy.
Портал для жінок https://u-kumy.com про стиль, здоров’я та саморозвиток. Експертні поради, чесні огляди, лайфхаки для дому та роботи, ідеї для відпочинку та гармонійного життя.
daily progress page – Motivates you to keep moving forward consistently.
action & growth site – Encourages small, consistent actions that lead to results.
Morixo Holdings business site – Simple design, easy-to-read content, and overall credibility is high.
Morixo Holdings main site – Navigation is effortless, design is uncluttered, and trustworthiness is apparent.
smart shop route – Clean interface, browsing products is simple and straightforward today.
Growth strategy portal – Information is easy to follow and emphasizes collaboration effectively.
shoproute marketplace – Efficient design, comparing and selecting items is quick and simple.
Business synergy platform – Clear, well-organized content supporting the partnership concept.
UFC Baku fan site ufc-baku.com.az/ for fans of mixed martial arts. Tournament news, fighters, fight results, event announcements, analysis and everything related to the development of UFC in Baku and Azerbaijan.
Galatasaray Football Club galatasaray latest news, fixtures, results, squad and player statistics. Club history, achievements, transfers and relevant information for fans.
Barcelona fan site barcelona with the latest news, match results, squads and statistics. Club history, trophies, transfers and resources for loyal fans of Catalan football.
Professional engagement platform – The information is presented in a clear and friendly way.
Smart business network – Looks like a solid platform with a clean layout and easy-to-follow content.
Hello everyone!
I came across a 153 helpful tool that I think you should take a look at.
This tool is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find interesting.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
https://www.six9ja.com/all-you-need-to-know-about-psychology/
Additionally don’t overlook, folks, which a person always may inside the piece find responses to the most the very complicated queries. Our team made an effort — lay out all data in the extremely easy-to-grasp way.
Rafa Silva rafa-silva.com.az/ is an attacking midfielder known for his dribbling, mobility, and ability to create chances. Learn more about his biography, club career, achievements, playing style, and key stats.
Education advancement portal – The platform is intuitive, and content is well organized.
Advance your knowledge portal – Navigation is simple, and resources encourage steady learning.
超人和露易斯第一季高清完整版AI深度学习内容匹配,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Сайт города Одесса https://faine-misto.od.ua свежие новости, городские события, происшествия, культура, экономика и общественная жизнь. Актуальные обзоры, важная информация для жителей и гостей Одессы в удобном формате.
Сайт города Винница https://faine-misto.vinnica.ua свежие новости, городские события, происшествия, экономика, культура и общественная жизнь. Актуальные обзоры, важная информация для жителей и гостей города.
Новости Житомира https://faine-misto.zt.ua сегодня: события города, инфраструктура, транспорт, культура и социальная сфера. Обзоры, аналитика и оперативные обновления о жизни Житомира онлайн.
Small enterprise online shop – Platform is practical and supports growth without complexity.
clicktolearnandgrow.click – Found this today, content seems helpful and worth checking again.
Small enterprise online shop – Platform is practical and supports growth without complexity.
clicktolearnandgrow.click – Found this today, content seems helpful and worth checking again.
Портал города Хмельницкий https://faine-misto.km.ua с новостями, событиями и обзорами. Всё о жизни города: решения местных властей, происшествия, экономика, культура и развитие региона.
Новости Львова https://faine-misto.lviv.ua сегодня: городские события, инфраструктура, транспорт, культура и социальная повестка. Обзоры, аналитика и оперативные обновления о жизни города онлайн.
Днепр онлайн https://faine-misto.dp.ua городской портал с актуальными новостями и событиями. Главные темы дня, общественная жизнь, городские изменения и полезная информация для горожан.
If some one wishes to be updated with most up-to-date technologies after
that he must be pay a visit this web site and be up to date everyday.
Автомобильный портал https://avtogid.in.ua с актуальной информацией об автомобилях. Новинки рынка, обзоры, тест-драйвы, характеристики, цены и практические рекомендации для ежедневного использования авто.
Новости Киева https://infosite.kyiv.ua события города, происшествия, экономика и общество. Актуальные обзоры, аналитика и оперативные материалы о том, что происходит в столице Украины сегодня.
познавательный блог https://zefirka.net.ua с интересными статьями о приметах, значении имен, толковании снов, традициях, праздниках, советах на каждый день.
Professional collaboration site – Alliance strategies are well presented, and the layout is intuitive.
Professional alliance platform – Clear, consistent, and smooth user experience throughout the site.
move with clarity – Design and content create a sense of direction and confidence.
clarity hub – Strong branding paired with clear messaging encourages decisive action.
Corporate alliance site – Simple layout and effortless navigation make exploring easy.
Professional growth network – Browsing was straightforward, and the concept comes across clearly.
Портал для пенсионеров https://pensioneram.in.ua Украины с полезными советами и актуальной информацией. Социальные выплаты, пенсии, льготы, здоровье, экономика и разъяснения сложных вопросов простым языком.
Объясняем сложные https://notatky.net.ua темы просто и понятно. Коротко, наглядно и по делу. Материалы для тех, кто хочет быстро разобраться в вопросах без профессионального жаргона и сложных определений.
Блог для мужчин https://u-kuma.com с полезными статьями и советами. Финансы, работа, здоровье, отношения и личная эффективность. Контент для тех, кто хочет разбираться в важных вещах и принимать взвешенные решения.
Advance ahead resource – Everything loads smoothly and the layout feels easy to grasp.
Professional growth hub – Pages open fast and the overall experience feels well designed.
Полтава онлайн https://u-misti.poltava.ua городской портал с актуальными новостями и событиями. Главные темы дня, общественная жизнь, городские изменения и полезная информация для горожан.
Портал города https://u-misti.odesa.ua Одесса с новостями, событиями и обзорами. Всё о жизни города: решения властей, происшествия, экономика, спорт, культура и развитие региона.
Новости Житомира https://u-misti.zhitomir.ua сегодня: городские события, инфраструктура, транспорт, культура и социальная сфера. Оперативные обновления, обзоры и важная информация о жизни Житомира онлайн.
site web du casino melbet melbet telecharger
Новости Хмельницкого https://u-misti.khmelnytskyi.ua сегодня на одном портале. Главные события города, решения властей, происшествия, социальная повестка и городская хроника. Быстро, понятно и по делу.
Львов онлайн https://u-misti.lviv.ua последние новости и городская хроника. Важные события, заявления официальных лиц, общественные темы и изменения в жизни одного из крупнейших городов Украины.
Новости Киева https://u-misti.kyiv.ua сегодня — актуальные события столицы, происшествия, политика, экономика и общественная жизнь. Оперативные обновления, важные решения властей и ключевые темы дня для жителей и гостей города.
Direction-focused resource – The site explains its value clearly without extra noise.
Strategic path platform – Everything feels straightforward and the goal is communicated well.
Винница онлайн https://u-misti.vinnica.ua последние новости и городская хроника. Главные события, заявления официальных лиц, общественные темы и изменения в жизни города в удобном формате.
Актуальные новости https://u-misti.chernivtsi.ua Черновцов на сегодня. Экономика, происшествия, культура, инфраструктура и социальные вопросы. Надёжные источники, регулярные обновления и важная информация для жителей города.
Новости Днепра https://u-misti.dp.ua сегодня — актуальные события города, происшествия, экономика, политика и общественная жизнь. Оперативные обновления, важные решения властей и главные темы дня для жителей и гостей города.
telecharger 1win 1win apk
Городской портал https://u-misti.cherkasy.ua Черкасс — свежие новости, события, происшествия, экономика и общественная жизнь. Актуальные обзоры, городская хроника и полезная информация для жителей и гостей города.
10 trucos para ganar paginas de apuestas mexico (Heidi)
Innovative viewpoint hub – The design helps you grasp the idea quickly.
Visionary ideas platform – The setup makes it easy to understand from the start.
Поставляем грунт https://organicgrunt.ru торф и чернозем с доставкой по Москве и Московской области. Подходит для посадок, благоустройства и озеленения. Качественные смеси, оперативная логистика и удобные условия для частных и коммерческих клиентов.
Op zoek naar een casino? WinItt Casino biedt online gokkasten en live games. Het biedt snel inloggen, eenvoudige navigatie, moderne speloplossingen en stabiele prestaties op zowel computers als mobiele apparaten.
joycasino зеркало сегодня скачать приложение джой казино
midnightfieldmarket.shop – Nicely structured layout, finding products is simple and the overall experience feels dependable.
midnight field shop – Products are arranged clearly, navigation is effortless and the platform feels solid.
Career improvement platform – Everything is clearly structured and readable.
Career progress hub – Information is presented in a clean and accessible way.
цена кв м квартиры светский лес сочи жк застройщик цена
midnight quarry storefront – Confident presentation, quick load speeds and easy navigation for shoppers.
midnight quarry outlet – Clear brand message, site feels fast and buying products is straightforward.
Fresh ideas platform – Feels energizing and well suited for creative exploration.
Solution discovery platform – Makes it easy to explore and learn through interaction.
Производим пластиковые https://zavod-dimax.ru окна и выполняем профессиональную установку. Качественные материалы, точные размеры, быстрый монтаж и гарантийное обслуживание для комфорта и уюта в помещении.
Изделия из пластмасс https://ftk-plastik.ru собственного производства. Продажа оптом и в розницу, широкий ассортимент, надёжные материалы и стабильные сроки. Выполняем заказы любой сложности по техническому заданию клиента.
Жалюзи от производителя https://balkon-pavilion.ru изготовление, продажа и профессиональная установка. Большой выбор дизайнов, точные размеры, надёжная фурнитура и комфортный сервис для квартир и офисов.
Производство оборудования https://repaircom.ru с предварительной разработкой и адаптацией под требования клиента. Качественные материалы, точные расчёты, соблюдение сроков и техническая поддержка.
Торговая мебель https://woodmarket-for-business.ru от производителя для бизнеса. Витрины, стеллажи, островные конструкции и кассовые модули. Индивидуальный подход, надёжные материалы и практичные решения для продаж.
Szukasz kasyna? kasyno internetowe w Polsce: wybor najlepszych stron do gry. Licencjonowane platformy, popularne sloty i kasyna na zywo, wygodne metody platnosci, uczciwe warunki i aktualne oferty.
Grasz w kasynie? Kasyno internetowe w Polsce to najlepsze miejsca do gry w latach 2025–2026. Zaufane strony, sloty i gry na zywo, przejrzyste warunki, wygodne wplaty i wyplaty.
Ищешь блины для штанки? https://blin-na-shtangy.ru для эффективных силовых тренировок. Чугунные и резиновые диски, разные веса, долговечность и удобство использования. Решение для новичков и опытных спортсменов.
que significa pa en las mejores casas de apuestas españa
(Maxine) apuestas
apuestas real sociedad barcelona – Susie – argentina colombia
Производим торговую мебель https://woodmarket-for-business.ru для розничного бизнеса и сетевых магазинов. Функциональные конструкции, современный дизайн, точные размеры и полный цикл работ — от проекта до готового решения.
Оборудование для отопления https://thermostock.ru и водоснабжения: котлы, циркуляционные насосы, радиаторы, мембранные баки и комплектующие от ведущих производителей. Что вы получаете: сертифицированные товары, прозрачные цены, оперативную обработку заказа. Создайте комфортный микроклимат в доме — выбирайте профессионалов!
Нужен памятник? заказать памятник в уфе — гранитные и мраморные изделия. Индивидуальные проекты, точная обработка камня, оформление и монтаж. Надёжное качество и внимательное отношение к деталям.
Нужен памятник? заказать памятник в уфе — гранитные и мраморные изделия. Индивидуальные проекты, точная обработка камня, оформление и монтаж. Надёжное качество и внимательное отношение к деталям.
Нужно авто? компании по привозу авто из японии поиск, проверка, оформление и доставка авто из разных стран. Прозрачные условия, помощь на всех этапах и сопровождение сделки до получения автомобиля.
дизайн студии studio дизайн интерьера в Санкт-Петербурге
Нужен памятник? заказать памятник в уфе — гранитные и мраморные изделия. Индивидуальные проекты, точная обработка камня, оформление и монтаж. Надёжное качество и внимательное отношение к деталям.
Все подробности: https://dzen.ru/a/aVQI4G_G1yJN0kAH
Нужен проектор? интернет-магазин проекторов большой выбор моделей для дома, офиса и бизнеса. Проекторы для кино, презентаций и обучения, официальная гарантия, консультации специалистов, гарантия качества и удобные условия покупки.
Dfb Pokal Wetten Tipps quoten erklärung
Нужен проектор? projector24 большой выбор моделей для дома, офиса и бизнеса. Проекторы для кино, презентаций и обучения, официальная гарантия, консультации специалистов, гарантия качества и удобные условия покупки.
sportwetten anbieter deutschland
Also visit my homepage … wetten doppelte chance strategie
kombiwetten vorhersagen
My web page – basketball wm 2023 wetten – Joy –
deutschland ungarn wett tipp
Feel free to surf to my homepage wetten sport (https://Sathyatech.com)
Hello lads!
I came across a 153 useful site that I think you should browse.
This tool is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find interesting.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
https://traveltweaks.com/what-you-need-to-know-when-traveling-through-a-country-that-allows-online-sports-betting-35781/
Furthermore do not overlook, folks, that one always may inside this particular piece find answers to address your the absolute confusing questions. Our team tried — lay out all information via the most most accessible method.
win.casino hisobni to‘ldirish usullari foydalanuvchilar uchun qulay va tezkor variantlarni taklif qiladi.
Проблемы с авто? автоэлектрик фольксваген спб диагностика, ремонт электрооборудования, блоков управления, освещения и систем запуска. Опыт, современное оборудование и точное определение неисправностей.
Celebrity World Care https://celebrityworldcare.com интернет-магазин профессиональной медицинской и натуральной косметики для ухода за кожей при ихтиозе, дерматитах, псориазе и других дерматологических состояниях. Сертифицированные средства с мочевиной, без отдушек и парабенов. Доставка по России.
Frederick Conservation Hub – Well-presented and informative, site shows strong community involvement.
Creative Solutions Hub – Clear and engaging, content encourages innovative approaches to challenges.
WFCC Community Portal – Informative and inviting, community-driven environmental efforts stand out.
Discover Answers – Engaging and clear, content helps users solve problems efficiently.
Enterprise partnership insights – Informative approach, the ideas are laid out clearly.
Enterprise collaboration tools – Useful setup, the partnership strategies feel realistic.
fastdealcenter – Very reliable shopping site, found great items quickly.
shopsmartzone – Found excellent offers, checkout was fast and smooth.
bondinsighthub – Very clear advice, helped refine our approach to enterprise bonds.
clickenterprisebondhub – Very informative tips, helped improve the structure of our enterprise bonds.
enterpriseconnecthub – Useful networking site, easy to find and reach relevant companies.
trustedbusinesslink – Excellent networking resource, navigating the site is straightforward.
Meaningful Creations – Motivating and approachable, ideas feel practical and exciting.
modernmarketplace – Browsing and buying feels simple, site is user-friendly and smooth.
efficiencycentral – Very actionable advice, improved how I handle tasks each day.
Build Something New – Thoughtful and inspiring, content motivates creativity daily.
worksmarterhub – Clear approaches, helped streamline my daily routine effectively.
shoppingeasezone – Online shopping is simple, interface is clear and items are easy to locate.
strategynavigator – Practical tips, allowed for faster planning and smoother execution.
customerchoicehub – Shopping process is straightforward, helps find what I need quickly.
OBDNet tech site – Useful and clear, information helps with routine vehicle diagnostics.
planwise – Practical tips, helped structure tasks clearly and efficiently.
OBDNet tech site – Useful and clear, information helps with routine vehicle diagnostics.
securelink – Quick and effective, supported forming strong business networks.
connectandshare – Helps to find people with shared hobbies or goals online.
networkhub – Reliable and efficient, quickly expanded my professional circle.
efficient purchase guide – User-friendly interface made online purchases fast and stress-free.
alliancesgrowthplanning – Practical direction that made long-term partnership goals easier to define.
online shopping guide – Effortless browsing and secure checkout made buying easy.
partnershipvalueinsights – Alliance suggestions are grounded and useful for future planning.
strategic insights page – Thoughtful strategies that made workflow and goal-setting more effective.
quickcheckoutzone – Navigation is smooth, completing my order was fast and easy.
modern business tactics – Useful advice that helped prioritize tasks and refine strategies.
smartconsumerclick – Website works well, made purchases quickly without any issues.
alliancesolutionshub – Suggestions are very helpful, improved our business partnership strategy instantly.
alliancebuilders – Helpful suggestions for forming alliances, made networking much easier.
Learn at your pace – Good concept, it gives the impression of stress-free learning.
Friendly learning site – Nice setup, it seems designed to make learning less intimidating.
businessinsightclick – Insightful and practical, really helpful for developing new business plans.
businessinsightclick – Insightful and practical, really helpful for developing new business plans.
dailyideasclick – Actionable advice is clear, made daily work processes smoother.
ideaexplorerclick – Actionable tips are practical, really simplified daily operations.
digitalcartzone – Platform made shopping simple, products easy to find and checkout fast.
easycheckoutportal – User-friendly experience, made online buying fast and hassle-free.
Happiness Tips Daily – Practical and engaging, posts make incorporating happiness into routines easy.
quickdigitaldeals – Platform helps find products quickly, checkout was very smooth.
Happiness Guide – Practical and approachable, content makes everyday happiness achievable.
consumeradvicehub – Very reliable guidance, streamlined product selection efficiently.
quickbuydigital – Digital store navigation is simple, checkout was seamless today.
savvyshoppingtips – Practical advice, made buying decisions fast and easy.
joint venture guide – Helpful insights that improved coordination and partnership outcomes.
partner growth hub – Smart guidance that enhanced partnership planning and execution.
insightfulideas – Very implementable suggestions, enhanced my work strategy.
The Gardens Local Portal – Peaceful and neat, community details are simple to follow.
brightideascentral – Insightful suggestions, gave me new ways to solve problems.
business alliance platform – The recommendations helped strengthen long-term professional ties.
The Gardens Local Site – Relaxed and organized, residents can quickly find helpful neighborhood info.
alliance strategy center – Practical insights that helped organize enterprise collaborations.
business alliance insights – Useful guidance that supported joint initiatives and enterprise expansion.
business growth alliances – Clear strategies that helped achieve team goals and foster productive partnerships.
essentialsmarketplace – Shopping for daily items was simple and stress-free.
essentialsmarketplace – Shopping for daily items was simple and stress-free.
smartpowerhub – Practical strategies that helped reduce energy waste significantly.
dailyenergysaver – Simple steps that improve efficiency and lower energy bills.
strategicguidanceclick – Recommendations are well-explained, improved efficiency in our planning.
planningstrategyhub – Tips are actionable, really improved our project planning approach.
corporatelearningclick – Lessons are well-organized, helped me understand business concepts fast.
bizlearningclick – Guides are straightforward, really improved my understanding of business concepts.
learnforwardskills – Learning platform is intuitive and clear, really helped me gain future-focused capabilities quickly.
futurefocusedlearning – Materials are insightful, allowed me to advance my capabilities effectively.
bizlinkportal – Great platform for networking, made professional connections effortless and fast.
growthstrategyzone – Strategy insights are actionable, helped me focus on key next steps efficiently.
bizconnectionsportal – Platform is smooth and reliable, connected me with the right people.
buildyourplan – Strategy support is effective, assisted in creating a structured approach for upcoming moves.
partnership planning link – Useful guidance that made long-term collaboration more structured.
Tech Tips Daily – Clear and insightful, resources simplify understanding of technology and digital tools.
business relationship guide – Practical ideas that improved long-term connection management.
shoppinginsightszone – Very helpful tips, site makes buying products simple and smooth.
Digital Simplified – Clear and engaging, site explains tech subjects in an easy-to-understand way.
consumeradvicehub – Very reliable guidance, streamlined product selection efficiently.
efficient retail experience – Browsing products is smooth and the platform is easy to use.
retail tech guide – Smooth interface allows fast browsing and easy checkout.
strategicdirections – Clear steps outlined, helped guide decisions smoothly.
strategicalliancescenter – Very informative tips, simplified planning and coordination for partnerships.
clickforlearningbiz – Very practical lessons, really helped me master business knowledge quickly.
Grenoble laser hub – Clear design, all treatments are easy to understand and booking works well.
pathfinderhub – Clear and concise advice, made navigating options easy.
businesslearningportal – Educational content is clear, provided actionable business knowledge.
partnershipplanningcenter – Helpful infrastructure suggestions, great for organizing collaborations efficiently.
Beauty treatment portal – Clear and organized, making appointments is straightforward.
Business relationship builder – Professional and calm, the long-term mindset stands out.
Strategic business alliances – Reliable tone, the long-term focus feels intentional and clear.
bizrelationclick – Platform worked very well for creating connections, straightforward and fast.
relationshiplinkcenter – Very useful site for networking, interface is simple yet effective.
smartshoppingcenter – Convenient platform, made ordering products online straightforward.
quickbuyhub – Smooth checkout process, made online shopping simple and stress-free.
alliance strategy guide – Smart recommendations that enhanced coordination between corporate partners.
Модульные дома https://modulndom.ru под ключ: быстрый монтаж, продуманные планировки и высокое качество сборки. Подходят для круглогодичного проживания, отличаются энергоэффективностью, надежностью и возможностью расширения.
partnership insight page – Helpful guidance that strengthened relationships and alliance planning.
collabworkplatform – Excellent features that enhanced team communication and workflow.
retailnextgenhub – Options are modern and varied, really improved my online shopping experience.
clickforfuturisticshopping – Shopping platform is well-organized, made my buying process very smooth.
partnershipprotools – Excellent resources that really boosted team coordination.
Opportunity Explorer – Practical and inspiring, opportunities are clearly presented for quick browsing.
globalshopzone – Fast navigation, locating and buying products was effortless.
Explore Opportunities – Clear and motivating, content helps users discover options efficiently.
smartshopnetwork – Very user-friendly, I completed my purchases without any problems.
startupstructurenetwork – Guidance is clear, concise, and trustworthy for building solid foundations.
businessframeworkportal – Extremely practical guidance, easy to implement for new companies.
corporate security guide – Clear insights that enhanced partnership planning and safe business dealings.
alliances safety guide – Practical advice that supported secure and effective commercial agreements.
collabinfrastructure – Very actionable advice, enhanced collaboration workflows.
Padel news Oviedo – Quick updates, information is useful and easy to follow.
teamcollabcentral – Helpful infrastructure advice, improved how we manage joint projects.
bondhub – Very practical advice, helped me build professional relationships smoothly.
Padel Oviedo Info – Clear layout, updates are practical and easy to digest.
networkpath – Easy to navigate advice, improved professional connection strategies.
bizgrowthnavigator – Informative guidance, made it easier to explore growth opportunities today.
nextlevelbusinesspaths – Informative and actionable advice, really supported exploring new ventures.
Получение водительской медицинской справки https://med-spravki-msk.ru
corporatecontactszone – Site is very practical for networking, found quality business contacts quickly.
professionalbizconnect – Fast and trustworthy, platform made connecting with professionals easy.
professionaladvancementportal – Guidance is clear and actionable, supported skill improvement efficiently.
careeradvancementhub – Excellent professional growth resources, helped improve skills efficiently.
Strategic partnership space – Clean and professional, it feels aimed at decision-makers.
Business collaboration hub – Thoughtful setup, collaboration seems to be the core strength here.
creative insight source – Thought-provoking concepts that helped generate new project directions.
project inspiration hub – Energizing ideas that sparked original project development.
Специализированный коррекционно-речевой https://neyroangel.ru детский сад для детей с особенностями развития в Москве. Беремся за самые тяжелые случаи, от которых отказываются другие. Нейропсихолог, логопед, запуск речи. Государственная лицензия: Л035-01298-77/01604531 от 09.12.24
shopconnectglobal – Practical and simple, helped me find everything I needed fast.
Learn Share and Grow – Engaging community, posts encourage both learning and meaningful sharing.
onlineshophub – Streamlined interface, purchasing items online was quick and stress-free.
Knowledge Hub – Friendly and supportive, content helps users grow while sharing ideas.
innovativeretailmarket – Modern options available, checkout process is quick and easy.
retailinnovationhub – Sleek and modern site, made online shopping smooth and effortless.
businessfinancehub – Practical, easy-to-follow guides for planning commercial investments effectively.
longtermbondguide – Clear and practical advice for planning commercial investments effectively.
knowledge growth tips – Clear explanations that accelerated learning and comprehension.
educational insights link – Useful material that made acquiring knowledge fast and practical.
discoverexpertadvice – Insights here are practical, really helped refine my professional strategies.
workinsightshub – Expert suggestions are clear, boosted my understanding of workplace dynamics.
enterpriseconnecthub – Practical insights that help establish reliable business partnerships.
corporatesynergytools – Clear, professional guidance for maintaining strong alliances.
growthplanner – Actionable insights, made planning business growth smooth.
The Gardens Community Info – Peaceful layout, residents can easily read updates and announcements.
growthplanner – Actionable insights, made planning business growth smooth.
The Gardens Neighborhood Hub – Peaceful design, community announcements are easy to read.
enterprise alliance hub – The guidance feels dependable and helped improve professional connections.
enterprise collaboration guide – Solid guidance that improved alliance-building outcomes.
studyandadvance – Educational content is well structured, made learning fast and effective.
Рэмси Диагностика: https://remsi-med.ru Сеть высокотехнологичных диагностических центров (МРТ, КТ). Точные исследования на оборудовании экспертного класса и качественная расшифровка снимков.
studyandadvance – Educational content is well structured, made learning fast and effective.
vision discovery page – Smart ideas that clarified where upcoming efforts should go.
planning inspiration link – Fresh viewpoints that helped shape future business actions.
safepurchasehub – Very easy to use, checkout and ordering was seamless.
Детский Доктор: https://kidsmedic.ru Специализированный медицинский центр для детей. Квалифицированная помощь педиатров и узких специалистов для здоровья вашего ребенка с первых дней жизни.
marketingideashub – Ideas provided are creative, helped our team design campaigns quickly.
Continuous Learning Hub – Helpful and motivating, posts make personal growth approachable and actionable.
safeonlineshopping – Smooth experience, orders were processed quickly without issues.
marketideasinsights – Suggestions are helpful, significantly improved our marketing planning today.
Daily Learning Hub – Engaging and helpful, posts encourage users to improve consistently.
global partnership guide – Practical strategies that supported building connections across regions.
cross-border business guide – Recommendations that streamlined forming partnerships across countries.
businesscollabtools – Clear and practical partnership strategies for expanding our network.
strategicalliancesportal – Insightful partnership strategies, I plan to use them immediately.
Wellspring therapy site – Gentle and professional, information about therapies is easy to follow.
Therapeutic wellness site – Calm and professional, the explanations make each treatment easy to understand.
Полесская ЦРБ: https://polesskcrb.ru Официальный портал центральной районной больницы Калининградской области. Информация об услугах, расписание врачей и важные новости здравоохранения для жителей региона.
trusted online checkout – Shopping here was easy with a smooth and reliable payment flow.
safe ecommerce zone – I liked how secure everything felt and how fast the purchase completed.
marketplacepro – Easy-to-use platform, improved my online shopping experience.
Handcrafted by Travis – Lovely craftsmanship, every item appears genuine and carefully made.
retailstream – Sleek interface, online shopping feels fast and convenient.
Travis Anderson handmade shop – Thoughtful and authentic, every item looks well made.
relationshipbuildinghub – Guidance is practical, strengthened collaborations and professional ties quickly.
corporateconnectionszone – Bonding strategies are insightful, helped improve business relationships effectively.
connectwithtrust – Smooth experience for global networking, interface is intuitive and clean.
globalconnectpro – Networking experience feels professional, platform is highly intuitive.
green collaboration tips – Useful strategies that strengthened collaborative business planning.
sustainable teamwork guide – Practical advice that enhanced collaboration and partner alignment.
АрсМед: https://arsmedclinic.ru Многопрофильная клиника, предлагающая широкий выбор медицинских услуг от диагностики до лечения. Современный подход и комфортные условия для пациентов всех возрастов.
проектор для фильмов магазин проекторов
partnershiphub – Great connections and resources for growing your company.
bizpartnershipportal – A useful platform for business networking and growth strategies.
securebuycentral – Platform is trustworthy, made my online shopping very smooth.
reliablepurchasehub – Clean interface, very straightforward to shop online today.
Progress Hub – Thoughtful and uplifting, ideas are presented in a clear, actionable format.
quickfinder – Simple and effective, it made finding my items a breeze.
Inspire Forward – Uplifting and insightful, resources guide users toward meaningful changes.
snapbuyhub – Smooth and fast, got exactly what I needed.
secure e-commerce guide – Quick browsing and safe transactions made shopping enjoyable.
safe marketplace guide – Browsing and purchasing was worry-free and convenient.
bondinsightportal – Valuable guidance, very clear and practical for everyday business use.
corporateglobalguide – Insights are easy to follow and provide real value for business decisions.
teambondingnetwork – Corporate bonding simplified, very easy to use for professional networking.
corporatebondinghub – Corporate bonding platform is trustworthy, made professional connections seamless.
learnskillsfast – Very informative resources, made advancing professional skills simple and fast.
learningandgrowthplatform – Informative learning resources, helped me advance career skills efficiently.
shop smarter tips – Efficient checkout and intuitive navigation improved the shopping journey.
next-gen store hub – Smooth interface and convenient features made buying products faster.
trusthubmarket – Reliable buying platform, made ordering online simple and fast.
Travel Texture Notes – Lively and authentic, posts offer a personal glimpse into travel moments.
trustedsaleshub – Secure and easy-to-navigate, checkout was fast and convenient.
Travel Texture Notes – Lively and authentic, posts offer a personal glimpse into travel moments.
Bathroom tubs showcase – Professional and clear, product features are easy to review.
RenovSystem tubs online – Clean design, it’s easy to find and compare details.
marketconnectguide – Practical tips on building connections, really improved networking smoothly.
relationshipgrowthhub – Advice is actionable, helped create stronger professional connections.
Creative Sparks – Bright and approachable, the site inspires new creative projects.
Creative Boost Daily – Fun and user-friendly, site design encourages artistic exploration.
enterprise value alliance guide – Actionable ideas that promoted steady growth and long-term collaboration.
value-focused partnership guide – Actionable ideas that strengthened alliances and promoted steady growth.
frameworkinsights – Clear and actionable suggestions, really helped our projects run smoothly.
strategicbizframework – Effective framework recommendations, made our team collaboration more structured.
corpstreamline – Practical tools that improved team efficiency instantly.
securepurchasehub – Shopping here is reliable, very smooth checkout and trustworthy service.
teamstreamline – Found tools that improved collaboration and sped up daily operations.
secureconsumerhub – Buying online is very secure, process is straightforward and convenient.
growth planning hub – Clear insights that supported fast and informed business decisions.
business insight hub – Useful ideas that made strategic choices faster and more accurate.
strategic bond portal – Everything works reliably for overseeing strategic bond positions.
strategic bond hub – The platform feels dependable and makes managing investments straightforward online.
FiatFive collector portal – Cheerful and curated, posts about vintage cars are easy to explore.
dealpoint – Smooth and quick process, great discounts for online buyers.
Fiat 500 lovers site – Engaging layout, updates on classic models feel carefully crafted.
Любишь азарт? up x казино играть онлайн в популярные игры и режимы. Быстрый вход, удобная регистрация, стабильная работа платформы, понятный интерфейс и комфортные условия для игры в любое время на компьютере и мобильных устройствах.
Играешь в казино? апх простой вход, удобная регистрация и доступ ко всем возможностям платформы. Стабильная работа, адаптация под разные устройства и комфортный пользовательский опыт.
globalpartneralliances – Platform is helpful for business connections, alliance tips are easy to apply.
alliancesplanninghub – Easy to use site for partnerships, suggestions are actionable and professional.
digitalbuyhub – Quick and reliable, online shopping process was effortless.
quickshopdigital – Easy to browse, checkout completed without any issues.
Ideas Daily – Clear and practical, content inspires effective problem-solving strategies.
intellectualgrowthcenter – Very useful resources, helped broaden my understanding efficiently.
businessgrowthsolutions – Practical strategies that can be applied directly to enhance company performance.
unity management tips – Insights supported stronger alignment, communication, and teamwork.
learningexpansionportal – Learning material is detailed, made grasping concepts fast and effective.
trustedenterprisehub – Offers well-structured strategies that help improve company operations.
unity collaboration guide – Recommendations supported better coordination and goal alignment.
Fast and clean website – Good usability, everything loads smoothly.
Minimalist website – Clean look, the fast loading makes browsing easy.
future growth insights – Actionable planning concepts that enhanced strategic confidence.
strategic foresight hub – Useful planning thoughts that helped outline extended strategies.
Любишь азарт? ап икс сайт играть онлайн легко и удобно. Быстрый доступ к аккаунту, понятная навигация, корректная работа на любых устройствах и комфортный формат для пользователей.
directionadvisor – Made understanding my career possibilities simple and straightforward.
trusted deal hub – The marketplace feels reliable and finding good offers was quick and simple.
directionfinderhub – Insightful tips that clarified my career options quickly.
reliable offer site – Purchasing deals here was easy and stress free.
ecopayz buchmacher
my blog: die besten online wettanbieter, http://www.vautron.cz,
shopsmartcenter – Deals were excellent, checkout was simple and hassle-free.
Cricket schedule platform – Straightforward interface, match times are current and reliable.
dealpoint – Smooth and quick process, great discounts for online buyers.
Cricket schedule tracker – Very helpful, fixtures are listed clearly and maintained regularly.
projectteamportal – Very intuitive and professional, helps manage teamwork seamlessly.
professionalconnectportal – Makes working with teams smooth and effective, very easy to use.
alliancesguidancecenter – Useful framework tips, made partnership execution easier and organized.
alliancesguidancecenter – Useful framework tips, made partnership execution easier and organized.
valuepartnershipnetwork – Useful partnership guidance, made enterprise decision-making easier.
enterprisecollabnetwork – Explanations on alliances are solid, made strategy planning more straightforward.
teamwise – Improved workflow, made teamwork smoother and more productive.
workstreamhub – Easy to use, improved project collaboration and team communication significantly.
квартиры от застройщика купить квартиру жк светский лес
химчистка и реставрация обуви химчистка обуви цена
Interactive digital portal – Stylish design, the layout encourages further exploration.
H5 platform experience – Clean and modern, the site sparks interest to explore more.
alliance planning toolkit – Well-structured guidance for developing professional alliances.
alliance planning toolkit – Well-structured guidance for developing professional alliances.
shoppinghub – Great deals, very simple and hassle-free checkout.
Play online puzzles https://pashasevkav.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=22&t=16096 anytime and train your logic and attention skills. Classic and themed puzzles, various sizes, simple gameplay, and comfortable play on computers and mobile devices.
dealnavigator – Smooth shopping experience, found exactly what I needed fast.
strategicpartnershiptools – Practical tips that make forming long-term alliances easier.
enterprisevaluehub – Tips and advice that help sustain strong business partnerships.
proinfrastructureguide – Practical advice here, really improved our business framework today.
digitalretail – Seamless experience, navigation and checkout were very simple.
shopcentral – Very convenient platform, browsing and checkout are smooth and easy.
infrastructurestrategycenter – Advice is solid, very easy to use for business planning purposes.
Portfolio gallery page – Strong design, the personal work is displayed clearly.
Professional portfolio page – Neat and polished, the content is presented effectively.
digitaltrade – Modern setup, helped me complete transactions smoothly.
digitaltradehub – Streamlined experience, simplified commerce and checkout processes.
smartpurchasehub – Intuitive platform with a simple and efficient purchasing flow.
quickpurchaseportal – Easy-to-use interface that sped up my purchase.
corporatesynergyhub – Platform is practical, made team projects easier to manage and organize.
teamconnecthub – Collaboration is seamless, helped our teams work together more effectively.
alliancehub – Very helpful guidance, made forming international partnerships straightforward.
partnershiphub – Clear guidance, improved our approach to global collaborations.
fastorderportal – Easy checkout and consistently quick shipping.
onlineshopportal – Shopping is fast, smooth, and delivery is always reliable.
bizrelationclick – Made building connections simple and fast, platform is smooth to navigate.
corporateconnectclick – Intuitive platform, made connecting with industry peers smooth and efficient.
knowledgeportal – Informative resources, made complex topics simple to understand.
intellecthub – Clear content, very useful for building knowledge fast.
learningcentral – Great platform, helped me advance my professional knowledge.
skillshub – Very practical content, improved my abilities effectively.
Hello this is somewhat of off topic but I was wanting to know if blogs
use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML.
I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding skills
so I wanted to get guidance from someone with experience.
Any help would be greatly appreciated!
hotdealhub – Couldn’t resist grabbing a few items, deals were impressive.
shopandsaveonline – Found everything I wanted, prices made me smile.
teamlinker – Practical and actionable advice, made teamwork smoother.
collabinsights – Useful advice, helped the team achieve better results together.
digitalmarketportal – Smooth navigation and secure payment options make buying easy.
digitalbuyclick – Streamlined platform, buying digital products is convenient and safe.
strategicinsights – Very helpful, made planning next steps straightforward and effective.
smartstrategyhub – Easy to use, provided insights that shaped key business moves.
canadian online bingo games, best online live casino united states and black jack australia, or new casino uk
Here is my website: play blackjack on phone (Stefan)
premiumbuyhub – Excellent digital products, checkout process is very straightforward.
digitalhubshop – Simple and fast purchasing process, products meet high standards.
Hello everyone, it’s my first go to see at this website, and article is truly fruitful in support of me, keep up posting these articles.
united kingdom online modern charm casino – Derrick
– minimum deposit dollar 10, bingo online play usa and real money pokies
online united states, or free online pokies win real money united states
super bowl wetten deutschland
Look at my site; neue sportwetten seiten
fallsview casino us exchange rate amusements united kingdom, best online casino sites new
zealand and new usa free spins no deposit, or
$10 deposit casinos united kingdom
Electric vehicles in the US include popular models from Tesla, Ford, Hyundai, and Chevrolet. Buyers often choose EVs based on range, charging access, and brand reputation, Skoda Enyaq 2025
недорогой мужской костюм мужские костюмы спб
Деньги в долг в Казахстане можно получить без сложных процедур. Онлайн кредитование экономит время и силы. Заявка заполняется в удобное время. Решение приходит в короткие сроки. Кредит наличными может быть выдан без залога – взять кредит наличными
Электромонтажные работы https://electric-top.ru в Москве и области. Круглосуточный выезд электриков. Гарантия на работу. Аварийный электрик.
Кент казино предлагает удобный формат онлайн игры без лишних сложностей. Регистрация занимает минимальное время. После входа пользователь получает доступ к каталогу игр. Все основные разделы расположены логично. Это упрощает использование сервиса: кент казино
коррозия у авто? Авто Тех Центр «Защита» эффективная защита от влаги, соли и реагентов. Комплексная обработка кузова и днища, качественные составы и надёжный результат для новых и подержанных авто.
7k casino ориентировано на удобство игроков. Основные разделы логично структурированы. Переходы между страницами быстрые. Игры работают корректно. Это улучшает общее впечатление: 7к казино вход
пылесос дайсон беспроводной спб пылесос дайсон беспроводной спб .
пылесос дайсон пылесос дайсон .
как заказать алкоголь через интернет с доставкой как заказать алкоголь через интернет с доставкой .
пылесосы dyson спб pylesos-dn-8.ru .
дайсон пылесос дайсон пылесос .
пылесос дайсон v15 купить в спб dn-pylesos-kupit-4.ru .
дайсон пылесос спб pylesos-dn-10.ru .
пылесос dyson спб dn-pylesos-2.ru .
dyson спб официальный pylesos-dn-6.ru .
пылесосы дайсон санкт петербург dn-pylesos-3.ru .
dyson санкт петербург купить pylesos-dn-7.ru .
Коррозия на авто? антикоррозийная обработка днища автомобиля мы используем передовые шведские материалы Mercasol и Noxudol для качественной защиты днища и скрытых полостей кузова. На все работы предоставляется гарантия сроком 8 лет, а цены остаются доступными благодаря прямым поставкам материалов от производителя.
пылесос дайсон беспроводной спб пылесос дайсон беспроводной спб .
пылесос дайсон беспроводной купить в спб вертикальный пылесос дайсон беспроводной купить в спб вертикальный .
доставка алкоголя ночью в москве доставка алкоголя ночью в москве .
сервис дайсон в спб сервис дайсон в спб .
дайсон центр в спб dn-pylesos-kupit-4.ru .
пылесос дайсон v15 купить в спб dn-pylesos-2.ru .
дайсон спб официальный магазин pylesos-dn-8.ru .
dyson v15 купить спб dn-pylesos-4.ru .
сайт дайсон спб dn-pylesos-3.ru .
ремонт пылесоса дайсон в спб pylesos-dn-6.ru .
dyson пылесос спб pylesos-dn-7.ru .
Планируете мероприятие? корпоративы с ии под ключ уникальные интерактивные форматы с нейросетями для бизнеса. Мы разрабатываем корпоративные мероприятия под ключ — будь то тимбилдинги, обучающие мастер?классы или иные активности с ИИ, — с учётом ваших целей. Работаем в Москве, Санкт?Петербурге и регионах. AI?Event специализируется на организации корпоративных мероприятий с применением технологий искусственного интеллекта.
dyson пылесос беспроводной купить спб pylesos-dn-9.ru .
Украшения для пирсинга https://piercing-opt.ru купить оптом украшения для пирсинга. Напрямую от производителя, выгодные цены, доставка. Отличное качество.
вертикальный пылесос дайсон купить спб dn-pylesos-kupit-5.ru .
пылесос dyson спб pylesos-dn-10.ru .
dyson магазин в спб dn-pylesos-kupit-4.ru .
дайсон пылесос дайсон пылесос .
пылесос дайсон v15 купить в спб dn-pylesos-4.ru .
сервис дайсон в спб dn-pylesos-3.ru .
дайсон купить спб дайсон купить спб .
ремонт дайсон в спб pylesos-dn-6.ru .
купить пылесос dyson спб pylesos-dn-9.ru .
пылесос дайсон купить dn-pylesos-kupit-5.ru .
вертикальный пылесос дайсон купить спб вертикальный пылесос дайсон купить спб .
dyson пылесос купить dn-pylesos-kupit-4.ru .
дайсон пылесос дайсон пылесос .
dyson пылесос беспроводной купить спб dn-pylesos-4.ru .
dyson пылесос dyson пылесос .
алкоголь доставка 24 часа москва алкоголь доставка 24 часа москва .
Ищешь сокращатель сылок? https://l1l.kz надежный сокращатель ссылок в Казахстане, рекомендуем заглянуть на сайт, где весь функционал доступен бесплатно и без регистрации
Противопожарные двери https://bastion52.ru купить для защиты помещений от огня и дыма. Большой выбор моделей, классы огнестойкости EI30, EI60, EI90, качественная фурнитура и соответствие действующим стандартам.
санкт петербург магазин дайсон pylesos-dn-9.ru .
купить пылесос дайсон в санкт pylesos-dn-7.ru .
Нужны цветы? хризантемы купить букет закажите цветы с доставкой на дом или в офис. Большой выбор букетов, свежие цветы, стильное оформление и точная доставка. Подойдёт для праздников, сюрпризов и важных событий.
пылесос dyson спб pylesos-dn-6.ru .
дайсон где купить в спб dn-pylesos-kupit-5.ru .
O’zbekiston uchun https://uzresearch.uz iqtisodiyot, moliya, ijtimoiy jarayonlar, bozorlar va mintaqaviy rivojlanish kabi asosiy sohalarda tadqiqotlar olib boradigan analitik platforma. Strukturaviy ma’lumotlar va professional tahlil.
пылесос дайсон v15 купить в спб пылесос дайсон v15 купить в спб .
dyson санкт петербург купить dn-pylesos-3.ru .
dyson пылесос dn-pylesos-kupit-4.ru .
пылесосы dyson спб dn-pylesos-4.ru .
купить пылесос дайсон спб pylesos-dn-8.ru .
Savdo va biznes https://infinitytrade.uz uchun xalqaro platforma. Bozor tahlili, xalqaro savdo, eksport va import, logistika, moliya va biznes yangiliklari. Tadbirkorlar va kompaniyalar uchun foydali materiallar, sharhlar va ma’lumotlar.
Ijtimoiy rivojlanish https://ijtimoiy.uz va jamoat hayoti uchun portal. Yangiliklar, tahlillar, tashabbuslar, loyihalar va ekspert fikrlari. Ijtimoiy jarayonlar, fuqarolik ishtiroki, ta’lim va jamiyatni rivojlantirish bo’yicha materiallar.
заказать алкоголь с доставкой круглосуточно заказать алкоголь с доставкой круглосуточно .
I absolutely love your blog and find a lot of your post’s to
be just what I’m looking for. Do you offer guest writers to write content available for you?
I wouldn’t mind writing a post or elaborating on a
few of the subjects can you split any 10 in blackjack write about here.
Again, awesome web site!
Qurilish materiallari https://emtb.uz turar-joy va sanoat qurilishi uchun beton va temir-beton. Poydevorlar, pollar va inshootlar uchun ishonchli yechimlar, standartlarga muvofiqlik, izchil sifat va loyihaga xos yetkazib berish.
Foydali maslahatlar https://grillades.uz va g’oyalar bilan panjara va barbekyu haqida loyiha. Retseptlar, panjara qilish texnikasi va jihozlar va aksessuarlarni tanlash. Mukammal ta’m va muvaffaqiyatli ochiq havoda uchrashuvlar uchun hamma narsa.
new zealand casino no deposit bonus, uptown pokies no deposit bonus 2021 united states and free united statesn poker money, or casino united states stock
my web site … the effects of Gambling
https://mhp.ooo/
dyson оригинал спб pylesos-dn-7.ru .
Ijtimoiy jarayonlar https://qqatx.uz va jamiyat taraqqiyoti bo’yicha onlayn axborot platformasi. Tegishli materiallar, tahliliy sharhlar, tadqiqotlar va murakkab mavzularning tushuntirishlari aniq va tuzilgan formatda.
Любишь азарт? игровые автоматы комета казино современные слоты, live-форматы, понятные правила и удобный доступ с ПК и смартфонов. Играйте онлайн в удобное время.
дайсон санкт петербург официальный pylesos-dn-6.ru .
Контрактная служба включает социальное обеспечение. Предусмотрены различные меры поддержки. Их условия определяются нормативами. Перейти на страницу с подробной информацией – сколько платят контрактникам в россии
casino in toronto ontario australia, cash online poker canada and best casino
sites in canada, or usa online casino no europcar
deposit not returned; Jayson, bonus codes 2021
Играешь в казино? ап х Слоты, рулетка, покер и live-дилеры, простой интерфейс, стабильная работа сайта и возможность играть онлайн без сложных настроек.
Лучшее казино upx играйте в слоты и live-казино без лишних сложностей. Простой вход, удобный интерфейс, стабильная платформа и широкий выбор игр для отдыха и развлечения.
Когда на первом месте стоят деньги и надежность, логично выбирать формат, в котором выплаты не зависят от случайностей и всегда приходят вовремя. Контрактная служба обеспечивает именно такую стабильность с прозрачными условиями и поддержкой. Используй возможность начать новый этап прямо сейчас: рекрут на сво
дайсон пылесос купить спб pylesos-dn-kupit-7.ru .
дайсон пылесос спб dn-pylesos-kupit-6.ru .
пылесос dyson pylesos-dn-kupit-6.ru .
Nations League livescore updates, UEFA competition with promotion and relegation
купить дайсон в санкт петербурге dn-pylesos-2.ru .